ऑस्टियोमाइलाइटिस (हड्डी का संक्रमण)
Osteomyelitis Treatment
विशेषज्ञ हड्डी संक्रमण उपचार - एंटीबायोटिक्स, सर्जरी, पुनर्निर्माण | इंदौर
Comprehensive Bone Infection Management - Medical & Surgical | Indore
ऑस्टियोमाइलाइटिस क्या है?
What is Osteomyelitis?
Osteomyelitis एक bone infection (हड्डी का संक्रमण) है जो bacteria, fungi, या tuberculosis के कारण होता है। यह बहुत serious condition है - early treatment बेहद जरूरी! अगर ignore किया तो bone damage, chronic infection, amputation तक हो सकता है।
🚨 Emergency Signs - तुरंत डॉक्टर को दिखाएं!
बुखार + bone pain। Red, warm, swollen area over bone। चलने में या हिलने में दर्द। Recent trauma या surgery के बाद ये signs। Wound से pus। बच्चों में refuse to bear weight! Joint के पास infection।
📊 Important Statistics:
में होते हैं
सबसे common
अवधि
Success
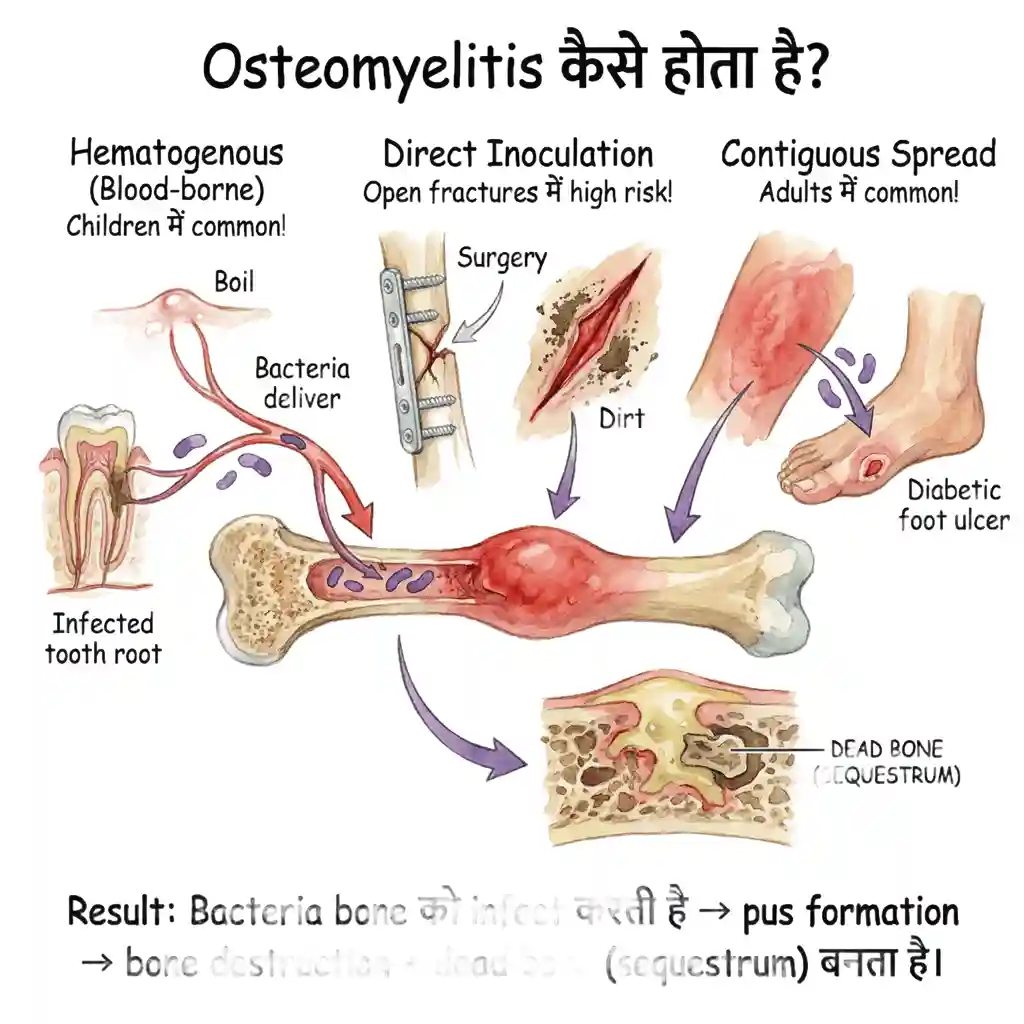
🧠 Osteomyelitis कैसे होता है?
तीन main routes हैं:
- Hematogenous (Blood-borne): Bacteria bloodstream में enter करती है (boil, infected tooth, UTI से) → bone में पहुँच जाती है। Children में सबसे common!
- Direct Inoculation: Trauma, fracture, surgery के दौरान bacteria directly bone में enter करती है। Open fractures में high risk!
- Contiguous Spread: Nearby infection (cellulitis, diabetic foot ulcer) से spread होती है bone में। Adults में common!
🔑 Result: Bacteria bone को infect करती है → pus formation → bone destruction + dead bone (sequestrum) बनता है।
🎯 Risk Factors - किन्हें ज्यादा खतरा?
Children (सबसे ज्यादा)
Especially under 5 years! Rich blood supply to growing bones। Immune system developing। Trauma common। Boys > Girls!
Diabetes & Immunocompromised
Diabetics - foot infections! Poor immunity। Slow healing। Peripheral vascular disease। HIV, cancer patients भी high risk!
Recent Trauma/Surgery
Open fractures - 30% risk! Joint replacement। Bone surgery। IV drug users। Any bone penetration!
⚠️ Common Misconceptions:
- Myth: Antibiotics 2-3 दिन काफी हैं। Fact: Minimum 4-6 weeks IV + oral antibiotics!
- Myth: सूजन खत्म = infection खत्म। Fact: Deep infection remains - full course complete करें!
- Myth: केवल antibiotics से cure हो जाएगा। Fact: Many cases need surgery + antibiotics!
- Myth: बुजुर्गों को ही होता है। Fact: Children सबसे ज्यादा affected!
Osteomyelitis is bone infection caused by bacteria, fungi, or TB. Very serious! Early treatment crucial - can lead to bone damage, chronic infection, amputation if ignored.
🚨 Emergency Signs!
Fever + bone pain. Red, warm swelling. Post-trauma/surgery. Pus drainage. Child refuses to walk!
📊 Statistics:
🎯 Risk Factors:
Children, Diabetes, Immunocompromised, Recent trauma/surgery, IV drug use, Poor circulation
ऑस्टियोमाइलाइटिस के प्रकार
Types of Osteomyelitis
🎯 Duration के हिसाब से 2 Types!
Acute (नया infection) | Chronic (पुराना infection)
📋 Types Based on Duration:
1. Acute Osteomyelitis
नया infection - <2 weeks! Sudden onset। High fever (101-104°F)। Severe bone pain। Red, warm swelling। Most common in children! Rapid progression। Good response if treated early! Usually single organism। X-ray initially normal - MRI shows early changes।
2. Chronic Osteomyelitis
>4-6 weeks duration! Persistent or recurrent infection। Low-grade fever या no fever। Drainage tracts (sinus)। Dead bone (sequestrum) formation। Much harder to treat! Often needs surgery। Multiple organisms possible। X-ray shows bone destruction।
📋 Types Based on Route of Infection:
3. Hematogenous Osteomyelitis
Blood से spread! Most common in children। Usually single site affected। Metaphysis (growing end) ज्यादा affected! S. aureus most common। From skin infections, UTI, pneumonia। Long bones affected - femur, tibia।
4. Post-Traumatic Osteomyelitis
Trauma या surgery के बाद! Open fractures - 30% risk। Direct bacterial inoculation। Mixed organisms common! Fixation hardware may get infected। Needs aggressive treatment। Often requires hardware removal।
5. Contiguous Osteomyelitis
Nearby tissue से spread! Common in diabetic foot। Pressure ulcers। Dental infections to jaw bone। Polymicrobial often! Adults > children। Vascular compromise common। Difficult to heal।
6. Vertebral Osteomyelitis
Spine infection - serious! Usually hematogenous। Back pain + fever। Neurological compromise risk! Staph या TB common। MRI essential। May need surgical decompression। Long antibiotic course।
✅ Common Causative Organisms:
- Staphylococcus aureus (80%): सबसे common! All age groups। Most acute cases।
- Streptococcus: Children। Post-viral infections।
- Salmonella: Sickle cell disease patients।
- Pseudomonas: IV drug users। Puncture wounds (foot)।
- Mycobacterium tuberculosis: Vertebral osteomyelitis (Pott's disease)। Slow progressive।
- Mixed organisms: Diabetic foot। Open fractures।
🎯 Cierny-Mader Classification (Severity):
Anatomic Types:
- Stage 1: Medullary (inside bone cavity)
- Stage 2: Superficial (cortical surface)
- Stage 3: Localized (cortical + medullary, stable bone)
- Stage 4: Diffuse (through-and-through, unstable bone) - सबसे serious!
Host Factors: A (healthy), B (compromised), C (treatment worse than disease)
🎯 Main Types!
Acute vs Chronic | Hematogenous vs Post-traumatic vs Contiguous
📋 Types:
Acute Osteomyelitis
<2 weeks. Sudden onset. High fever. Good prognosis if treated early!
Chronic Osteomyelitis
>6 weeks. Persistent/recurrent. Sequestrum. Surgery often needed!
🔬 Common Organisms:
S. aureus (80%), Streptococcus, Salmonella (sickle cell), Pseudomonas (IV drugs), TB (spine)
निदान कैसे होता है?
How is it Diagnosed?
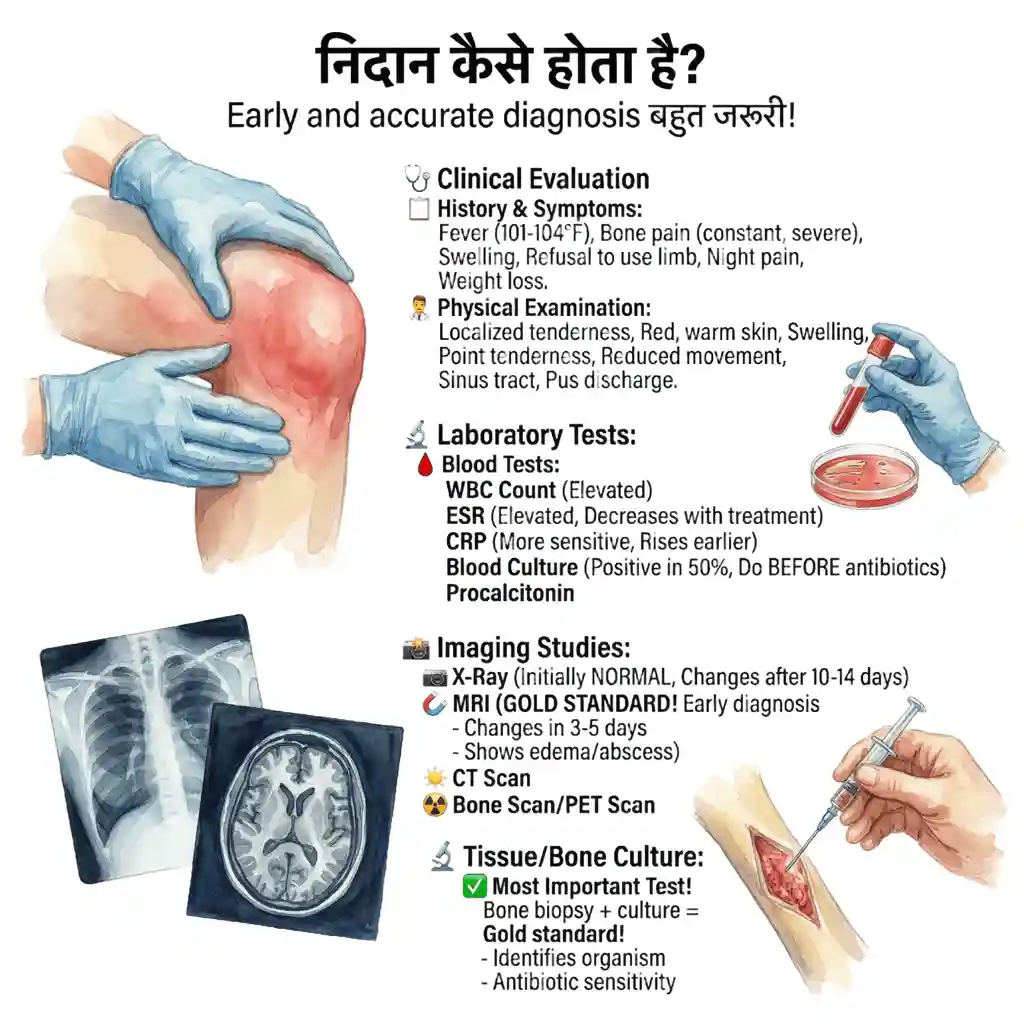
Early और accurate diagnosis बहुत जरूरी! Clinical examination + blood tests + imaging + culture। Diagnosis में delay = complications!
🩺 Clinical Evaluation:
History & Symptoms
Fever - often high (101-104°F)! Bone pain - constant, severe। Swelling over affected area। Recent trauma, surgery, infection? Refusal to use limb। Night pain। General malaise। Weight loss (chronic)। Duration of symptoms।
Physical Examination
Localized tenderness! Red, warm skin। Swelling। Point tenderness over bone! Reduced movement। Sinus tract (chronic)। Pus discharge। Lymphadenopathy। Systemic examination।
🔬 Laboratory Tests:
🩸 Blood Tests - Essential!
- WBC Count: Elevated (leukocytosis)। But normal भी हो सकता है chronic में!
- ESR (Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate): Almost always elevated। Useful for monitoring response! Decreases with treatment।
- CRP (C-Reactive Protein): More sensitive than ESR। Rises earlier, falls faster! Better for tracking treatment।
- Blood Culture: Positive in 50% acute cases। Do BEFORE starting antibiotics! May identify organism।
- Procalcitonin: Helps differentiate bacterial infection। Newer test।
📸 Imaging Studies:
X-Ray (First Test)
Initially NORMAL in acute! Changes appear after 10-14 days। Shows: Bone destruction। Periosteal reaction। Sequestrum (chronic)। Sclerosis। Cheap, available - start here!
MRI (GOLD STANDARD!)
Best test for early diagnosis! Changes visible in 3-5 days। Shows: Bone marrow edema। Abscess। Soft tissue involvement। Extent of infection। Essential for surgical planning! No radiation।
CT Scan
Better than X-ray for bone detail! Good for sequestrum। Surgical planning। Sinus tract evaluation। 3D reconstruction possible। Useful in spine। Faster than MRI।
Bone Scan/PET Scan
Whole body screening! Detects early infection। Multiple sites। Not specific - false positives! Expensive। Special situations only। Combined with CT (SPECT-CT)।
🔬 Tissue/Bone Culture:
✅ Most Important Test!
Bone biopsy + culture = Gold standard!
- Direct bone sampling: Surgery या needle biopsy। Most accurate।
- Identifies organism! Gram stain + culture। Takes 2-5 days।
- Antibiotic sensitivity: Which antibiotics will work। Essential for targeted therapy!
- TB testing: AFB stain + culture। GeneXpert। Takes weeks।
- Histopathology: Confirms infection। Rules out tumor। Chronic changes।
⚠️ Important: Take culture BEFORE starting antibiotics whenever possible!
🎯 Diagnostic Criteria
Definite: Bone culture positive + clinical + imaging। Probable: 2 of 3: Clinical signs, Labs (ESR/CRP↑), Imaging positive। Early imaging (MRI) + high suspicion = start treatment!
🔍 Diagnosis:
Clinical + Blood tests (WBC, ESR, CRP, Culture) + Imaging (X-ray→MRI best) + Bone biopsy/culture
🩸 Key Tests:
ESR/CRP elevated. Blood culture (before antibiotics!). MRI = Gold standard (early detection). Bone culture = confirms organism + sensitivity!
📸 Imaging:
MRI - Best!
Early detection (3-5 days). Shows extent. Surgical planning!
चिकित्सा उपचार (दवाई से इलाज)
Medical Treatment
Antibiotics = Cornerstone of treatment! But long duration essential - minimum 4-6 weeks। Never stop early!
💉 Antibiotic Therapy:
🎯 Treatment Protocol
Phase 1 - IV Antibiotics (2-4 weeks):
- Initial empiric therapy: Broad spectrum। Start immediately। Cover S. aureus!
- IV route essential! Better bone penetration। High concentration।
- Duration: Usually 2-4 weeks IV। Until clinical improvement।
- Hospital admission: Often needed। Daily monitoring।
Phase 2 - Oral Antibiotics (2-4 weeks or more):
- Switch criteria: Fever resolved। CRP/ESR decreasing। Clinically improving।
- High-dose oral: Good bioavailability। Continue until markers normalize।
- Total duration: Acute: 4-6 weeks। Chronic: 6-12 weeks या longer!
- Compliance crucial! Missing doses = treatment failure।
💊 Common Antibiotic Choices:
First-Line (Empiric)
Cefazolin या Vancomycin (IV)! Covers most S. aureus। Safe। For MRSA: Vancomycin essential। Linezolid alternative। Monitor levels।
Oral Options
Ciprofloxacin + Rifampicin! Good bone penetration। Clindamycin: Excellent for MSSA। Linezolid (expensive)। Co-trimoxazole।
Organism-Specific
MRSA: Vancomycin। Pseudomonas: Ceftazidime + Aminoglycoside। TB: DOTS (6-12 months)। Fungal: Antifungals।
📊 Monitoring Treatment Response:
✅ How to Know Treatment Working?
- Clinical: Fever resolves (3-5 days)। Pain decreases। Swelling reduces। Improved mobility।
- Labs: CRP normalizes (2-3 weeks)। ESR slower to normalize (4-6 weeks)। WBC normalizes।
- Imaging: Repeat MRI if not improving। X-ray healing signs (months)।
- Weekly monitoring: ESR + CRP। Clinical assessment। Adjust antibiotics if needed!
⚠️ Supportive Treatment:
Rest & Immobilization
Affected limb rest! Splint या cast। Crutches। No weight bearing initially। Reduces pain। Prevents spread। 2-4 weeks।
Pain Management
NSAIDs (Ibuprofen, Paracetamol)। Pain reduces as infection controlled। Avoid opioids long-term। Ice packs helpful।
Nutrition & General Care
High protein diet! Vitamin C। Hydration। Control diabetes! Stop smoking। Treat anemia। Boost immunity।
⚠️ Treatment Failures - Why?
- Inadequate antibiotic duration! Most common। Never stop early!
- Wrong antibiotic: No culture done। Resistant organism।
- Dead bone (sequestrum): Antibiotics can't penetrate। Needs surgery!
- Abscess formation: Needs drainage।
- Hardware infection: Implant needs removal।
- Poor compliance: Patient skips doses।
- Immunocompromised host: Diabetes, HIV। Needs aggressive treatment।
🎯 Success Criteria
Clinical: Pain-free. No fever. Full mobility। Labs: ESR/CRP normal। Imaging: No progression. Patient can resume normal activities!
💊 Treatment:
Antibiotics 4-6 weeks minimum! IV (2-4 weeks) → Oral (2-4+ weeks). Never stop early!
💉 Protocol:
Start: IV antibiotics (broad spectrum). After culture: targeted therapy. Monitor: ESR/CRP weekly. Continue until normalized!
📊 Common Drugs:
MSSA: Cefazolin. MRSA: Vancomycin. Oral: Ciprofloxacin+Rifampicin, Clindamycin. TB: DOTS 6-12 months
⚠️ Failures:
Short duration, Wrong antibiotic, Sequestrum (needs surgery), Poor compliance!
शल्य चिकित्सा प्रबंधन (सर्जरी कब और कैसे?)
Surgical Management
Surgery कई cases में जरूरी! Especially chronic osteomyelitis में। Goal: Remove infected/dead tissue। Drain abscess। Restore blood supply। Surgery + Antibiotics = Best results!
🏥 Surgery की जरूरत कब है? (WHEN?)
8 Main Indications for Surgery!
🎯 WHY Surgery? - Indications (कब करनी है?):
1. Sequestrum (Dead Bone)
Most common reason! Dead bone = antibiotic नहीं पहुँच सकता। Acts as nidus for ongoing infection। Must remove। Chronic osteomyelitis में almost always present! X-ray या CT पर visible।
2. Abscess Formation
Pus collection! Needs drainage! Antibiotics alone won't work। Subperiosteal या soft tissue। Ultrasound या MRI guided। May recur if not completely drained। Emergency if large।
3. Failed Medical Treatment
4-6 weeks antibiotics = no improvement! Persistent fever। ESR/CRP not falling। Progressive bone destruction। New abscess। Worsening clinically। Don't delay surgery!
4. Chronic/Recurrent Infection
Infection keeps coming back! Sinus tract present। Biofilm on bone/hardware। Multiple previous courses। Only surgery breaks cycle। Remove ALL infected tissue।
5. Hardware-Associated
Infected implants/plates! Biofilm can't be cleared। Usually needs removal। After fracture union - remove। Before union - exchange। Challenging cases।
6. Pathological Fracture
Bone weakness → fracture! Unstable। Needs stabilization + debridement। May need bone graft। External fixator often best। Protected weight bearing।
7. Neurological Compromise
Vertebral osteomyelitis! Spinal cord compression। Abscess। Weakness। EMERGENCY surgery! Decompression essential। Fusion may be needed।
8. Diagnostic Biopsy
Diagnosis unclear? Tumor vs infection? Culture needed। Tissue diagnosis। Surgical biopsy most accurate। Before antibiotics ideally।
🔪 HOW? - Surgical Procedures (कैसे की जाती है?):
✅ Step-by-Step Surgery Process:
Pre-operative Planning:
- Complete imaging: MRI + CT। Extent mapping।
- Blood work: Type & cross। Coagulation।
- Pre-op antibiotics: 30-60 min before। Therapeutic levels।
- Consent: Explain risks। Multiple stages possible।
- Anesthesia: Usually general। Regional sometimes।
Procedure 1: Debridement
Core procedure!
- Wide exposure: Adequate access। Previous scars avoided।
- Remove ALL infected tissue: Necrotic bone। Pus। Granulation। "Debride until bleeding!"
- Sequestrum removal: Dead bone pieces। Often multiple।
- Saucerization: Create cavity। Open involucrum।
- Curette thoroughly: Medullary canal। No infected tissue left।
- Multiple cultures: Different sites। Deep samples।
Procedure 2: Local Antibiotic Therapy
High concentration locally!
- Antibiotic-loaded PMMA beads: Gentamicin usually। Released over 2-4 weeks।
- Antibiotic cement spacers: If joint involved। Maintains space।
- Calcium sulfate beads: Biodegradable। With antibiotics।
- Direct instillation: Antibiotic solution। Wash cavity।
- Benefits: Very high local concentration। Minimal systemic side effects।
Procedure 3: Drainage Systems
Evacuate fluid/pus!
- Suction drains: 2-3 days। Remove when output minimal।
- Continuous irrigation: Through catheters। Antibiotic solution। 3-7 days।
- Open packing: Wet-to-dry dressings। Daily changes। Allows granulation।
- Negative pressure (VAC): Wounds. Promotes healing। Expensive।
Procedure 4: Bone Grafting
Fill bone defects!
- AFTER infection control! Usually 2nd stage। 6-12 weeks later।
- Autograft (own bone): Iliac crest। Gold standard। Best healing।
- Cancellous graft: Fills cavity। Vascularizes well।
- Vascularized fibula: Large defects। Microsurgery। Complex।
- Synthetic substitutes: Calcium phosphate। Demineralized bone। Adjunct।
Procedure 5: Hardware Management
Infected implants?
- Stable union: Remove hardware। Thorough debridement।
- Unstable/no union: Exchange to external fixator। Remove internal fixation। Stabilize।
- Biofilm removal: Ultrasonic। Curette। Pulse lavage।
- New hardware: Only if absolutely needed। After thorough cleaning।
- External fixator advantages: Adjustable। Minimal soft tissue। Weight bearing possible।
Procedure 6: Soft Tissue Coverage
Cover bone defects!
- Primary closure: If adequate soft tissue। No tension। Drains।
- Muscle flap: Brings blood supply। Gastrocnemius for tibia। Latissimus for humerus।
- Free flap: Large defects। Microsurgery। Specialized centers।
- Skin graft: Over granulation। Split thickness।
- Goal: Well-vascularized coverage। No dead space।
Procedure 7: Amputation
Last resort!
- Indications: Failed multiple surgeries। Sepsis। Non-functional limb। Better prosthesis।
- Life-saving: Overwhelming infection। Septic shock।
- Rare in children: Try to salvage। Growth considerations।
- Level: Through healthy tissue। Above infection।
- Rehabilitation: Prosthesis। Physical therapy। Psychological support।
Advanced: Ilizarov/Bone Transport
For large bone gaps!
- Ilizarov external fixator: Circular frame। Wires।
- Bone transport: Grow bone to fill gap! Corticotomy. Daily distraction। Months.
- Advantages: No donor site। Infection control। Simultaneous correction।
- Disadvantages: Long duration। Pin care। Compliance needed।
- Success rate: 80-90% in experienced hands।
⏰ Post-Operative Care:
🏥 After Surgery - Critical Period!
- IV antibiotics continue: 2-6 weeks post-op। Longer if extensive।
- Wound care: Daily dressing। Watch for complications।
- Drain management: Remove when output <30ml/day। Usually 2-3 days।
- Pain control: Adequate analgesia। Nerve blocks helpful।
- Immobilization: Splint/cast। External fixator। 4-12 weeks।
- No weight bearing: Initially। Protected weight bearing gradually।
- Physical therapy: ROM exercises। Muscle strengthening। Gradual।
- Monitoring: Serial ESR/CRP। Weekly initially। X-rays monthly।
- Bead removal: If placed, remove at 4-6 weeks (2nd surgery)।
- Watch complications: Wound issues। Recurrence। Non-union।
⚡ Complications of Surgery:
Recurrence (10-30%)
Infection comes back! Inadequate debridement। Resistant organism। Biofilm. Host factors। May need revision। Longer antibiotics।
Non-Union/Malunion
Bone doesn't heal properly! Large defect। Infection। Bone graft may fail। May need bone transport। Prolonged treatment।
Wound Complications
Dehiscence (wound opens)। Hematoma। Skin necrosis। Needs revision। VAC dressing। Flap coverage। Meticulous technique prevents।
General Surgical Risks
Bleeding। Nerve/vessel injury। Anesthesia complications। Stiffness। Limb length discrepancy। Chronic pain। Function loss। Rare but possible।
📊 Success Rates & Prognosis:
(single stage)
Procedures
Healing Time
Outcomes
🎯 Keys to Surgical Success!
Thorough debridement (remove ALL infected tissue). Adequate drainage. Long-term antibiotics (4-6 weeks post-op). Staged approach if needed. Expert surgeon. Patient compliance. Early intervention! Multidisciplinary team.
⚠️ Red Flags After Surgery - तुरंत डॉक्टर को दिखाएं!
- Fever return! Infection recurrence।
- Wound dehiscence: Opens up। Pus discharge।
- Increasing pain: After initial improvement।
- Red, swollen wound: Not improving।
- ESR/CRP rising: After falling। Check immediately।
🏥 Surgical Management:
Surgery Essential When:
Dead bone (sequestrum), Abscess, Failed antibiotics, Chronic infection, Hardware infection, Pathological fracture, Spinal cord compression!
🔪 HOW - Procedures:
1. Debridement
Remove ALL infected/dead tissue! Thorough cleaning. Multiple cultures. "Debride until bleeding!"
2. Local Antibiotics
PMMA beads with antibiotics. High local concentration. 2-4 weeks. Remove later (2nd surgery).
3. Bone Grafting
After infection controlled (2nd stage). Fill defects. Autograft best. Vascularized fibula for large gaps.
4. Hardware Management
Remove if stable union. Exchange to external fixator if unstable. Biofilm can't be cleared!
📊 Success Rates:
✅ Keys to Success:
Thorough debridement + Long antibiotics (4-6 weeks post-op) + Staged approach + Early surgery + Patient compliance!
रोकथाम और रोग का निदान
Prevention & Prognosis
🛡️ Prevention Strategies:
Post-Surgical Prevention
Prophylactic antibiotics! 30-60 min pre-op। Sterile technique। Minimize operative time। Careful tissue handling। Adequate debridement। Drain placement।
Trauma Care
Open fracture = emergency! Immediate antibiotics। Thorough irrigation। Early debridement (<6-8 hrs)। Cover wound। Tetanus prophylaxis। No primary closure if contaminated।
Chronic Condition Management
Control diabetes! HbA1c <7%। Foot care। Treat infections early। Boost immunity। Stop smoking। Nutrition। Regular check-ups।
In Children
Treat infections promptly! Skin infections। UTI। Don't ignore fever + limping। Early doctor visit। Vaccination। Good hygiene।
📊 Prognosis - How Good is Recovery?
✅ Excellent Prognosis If:
- Early diagnosis और treatment! Best outcomes।
- Acute infection: 90-95% cure rate।
- Complete antibiotic course: 4-6 weeks minimum।
- Good host: Healthy, non-diabetic। Good immunity।
- Single organism: S. aureus। Sensitive to antibiotics।
- Children: Better healing। Growth plates।
⚠️ Poor Prognosis Factors:
- Delayed treatment! >2 weeks।
- Chronic osteomyelitis: Recurrence 10-30%।
- Multiple organisms: Polymicrobial। Resistant।
- Poor host: Diabetes। HIV। Malnutrition।
- Large bone defect: After debridement।
- Hardware infection: Biofilm। Difficult।
- Inadequate surgery: Incomplete debridement।
- Non-compliance: Skipping antibiotics।
🎯 Long-term Outcomes:
(Acute, Early)
(Chronic)
(Chronic)
Rate
💡 What to Expect Long-term?
- Most patients: Complete recovery। Normal function।
- Some limitation: Stiffness। Mild pain। Managed।
- Growth disturbance: Rare in children। If growth plate damaged।
- Chronic pain: Small percentage। Pain management।
- Recurrence risk: Lifetime। But very low if treated properly।
- Regular follow-up: First year important। Then annual।
🛡️ Prevention:
Prophylactic antibiotics in surgery. Early treatment of infections. Diabetes control. Open fracture care (<6-8 hrs). Treat skin infections. Good hygiene!
📊 Prognosis:
✅ Good If:
Early treatment, Acute infection, Complete antibiotics, Healthy host, Single organism, Children!
⚠️ Poor If:
Delayed, Chronic, Diabetic, Immunocompromised, Large defect, Non-compliance!
🩺 अभी संपर्क करें!
ऑस्टियोमाइलाइटिस में जल्दी उपचार = सफलता! हमारी विशेषज्ञ टीम के साथ परामर्श लें।
अभी अपॉइंटमेंट बुक करेंअक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न
Frequently Asked Questions
ऑस्टियोमाइलाइटिस कितने दिन में ठीक हो जाता है?
How long does osteomyelitis take to heal?
Acute osteomyelitis: 4-6 weeks antibiotics + 2-3 months complete healing। Chronic osteomyelitis: 6-12 weeks antibiotics। With surgery - 3-12 months total healing।
Key factors: Early treatment = faster। Surgery needed? Longer। Your health status। Compliance with treatment।
⚠️ Important: Never stop antibiotics early! Complete course essential। Even if feeling better।
Acute: 4-6 weeks antibiotics + 2-3 months healing। Chronic: 6-12 weeks antibiotics। With surgery: 3-12 months।
Factors: Early treatment, Surgery, Your health, Compliance।
सर्जरी जरूरी है क्या?
Is surgery always necessary?
Nahi! Many acute cases antibiotics se hi theek ho jaate hain। Surgery needed if:
- Dead bone (sequestrum) present
- Abscess formation
- Failed medical treatment (4-6 weeks)
- Chronic infection
- Hardware infected
- Bone fracture (pathological)
Approximately 30-40% chronic cases need surgery। Decision based on MRI, response to antibiotics।
No! Many acute cases heal with antibiotics alone। Surgery if: Sequestrum, Abscess, Failed treatment, Chronic, Hardware infection।
~30-40% chronic cases need surgery।
ऑस्टियोमाइलाइटिस संक्रामक है क्या?
Is osteomyelitis contagious?
Nahi! Osteomyelitis NOT contagious! Ek person se dusre ko spread nahi hota।
Reason: Infection bone के अंदर है। Direct contact से spread nahi ho sakta। However, causative bacteria (like S. aureus) can spread through direct contact with infected wounds या drainage।
✅ Safety: Normal interaction safe। Family members को risk nahi। But wound care during dressing - use gloves!
No! Osteomyelitis is NOT contagious! Can't spread person-to-person। Infection is deep in bone।
Safety: Normal interaction safe। Use gloves for wound care।
एंटीबायोटिक्स किस प्रकार की दी जाती हैं?
What antibiotics are used?
Initial (Empiric):
- IV Cefazolin या Vancomycin (MRSA suspected)
- 2-4 weeks IV
After Culture:
- Organism-specific antibiotics
- MSSA: Cloxacillin, Cefazolin
- MRSA: Vancomycin, Linezolid
- Pseudomonas: Ceftazidime
Oral (later): Ciprofloxacin + Rifampicin, Clindamycin, Linezolid
Duration: Total 4-6 weeks (acute), 6-12+ weeks (chronic)
Initial: IV Cefazolin or Vancomycin। Later: Culture-specific। Oral: Ciprofloxacin+Rifampicin।
Duration: 4-6 weeks (acute), 6-12+ weeks (chronic)
बच्चों में ज्यादा आम क्यों है?
Why is it more common in children?
3 main reasons:
- Rich blood supply: Growing bones में zyada blood vessels। Bacteria easily reach। Metaphysis (growth plate area) most affected।
- Developing immunity: Immune system mature nahi hota। Infections easily होते हैं।
- More trauma: Active play। Falls। Injuries common। Entry point for bacteria।
Peak age: Under 5 years। Boys > Girls (more active)।
Good news: Children heal better! Early treatment = excellent prognosis।
Reasons: Rich blood supply in growing bones। Developing immunity। More trauma।
Peak: Under 5 years। Good news: Children heal better!
सीक्वेस्ट्रम क्या है और क्यों हटाना पड़ता है?
What is sequestrum and why remove it?
Sequestrum = Dead bone piece!
Formation: Infection → blood supply cut off → bone dies। Necrotic bone separates। Surrounded by pus। Protected by new bone (involucrum)।
Problem:
- Antibiotics can't penetrate! No blood supply।
- Acts as "nidus" - bacteria hide here। Keep multiplying।
- Chronic infection persist। Never heals with antibiotics alone।
- Biofilm forms on dead bone। Bacteria protected।
⚡ Solution: Surgical removal essential! Debridement। Remove all necrotic tissue। Then antibiotics work।
Sequestrum = Dead bone! Forms when infection cuts blood supply।
Problem: Antibiotics can't reach। Bacteria hide। Chronic infection। Must remove surgically!
कब तक अस्पताल में रहना पड़ता है?
How long is hospital stay?
Varies greatly:
- Acute, no surgery: 1-2 weeks। IV antibiotics। Then home with oral।
- With surgery: 2-4 weeks। Post-op care। Drain removal। Wound healing।
- Complicated cases: 4-6 weeks। Multiple procedures। ICU care sometimes।
Outpatient IV options: Some cases। Home IV antibiotics। PICC line। Weekly visits। Saves hospital stay।
Factors affecting stay: Surgery needed? Complications? Response to antibiotics। Your general health।
No surgery: 1-2 weeks। With surgery: 2-4 weeks। Complicated: 4-6 weeks।
Outpatient IV possible in some cases (PICC line)।
क्या घर पर इलाज हो सकता है?
Can treatment be done at home?
Partially yes!
Initial phase (Hospital):
- Diagnosis और culture
- Start IV antibiotics
- Surgery if needed
- Stabilization
Later phase (Home):
- PICC line: Special IV line। Take home। Self या nurse IV antibiotics।
- Oral antibiotics: After IV phase।
- Weekly visits: Doctor check-up। Blood tests। Monitor progress।
- Physical therapy: At home or clinic।
⚠️ Requirements: Good home support। Compliant patient। Regular follow-up। No complications।
Partial home treatment possible! Initial hospital stay। Then PICC line for home IV। Weekly visits। Oral antibiotics later।
Need: Good support, Compliance, Regular follow-up।
व्यायाम और फिजियोथेरेपी कब शुरू करें?
When to start exercise/physiotherapy?
Phased approach:
Phase 1 (Week 1-2): Rest! Immobilization। Ice। Elevation। No active movement।
Phase 2 (Week 2-4):
- Passive ROM: Physical therapist moves joint। No patient effort।
- Pain reduces। Infection controlled।
- Maintain joint mobility।
Phase 3 (Week 4-8):
- Active ROM: Patient moves joint। Gentle।
- Isometric exercises। Muscle strengthening begins।
- Protected weight bearing (if lower limb)।
Phase 4 (2-3 months+):
- Progressive loading। Full weight bearing।
- Strengthening exercises। Functional training।
- Return to normal activities। Gradual।
⚠️ Never rush! Follow doctor's timeline। Pain = stop। X-rays guide progression।
Week 1-2: Rest। Week 2-4: Passive ROM। Week 4-8: Active ROM। 2-3 months+: Progressive loading।
Never rush! Follow doctor's advice।
डायबिटिक रोगियों में ज्यादा जोखिम क्यों?
Why higher risk in diabetics?
Multiple reasons:
- Poor immunity: High sugar → weak white blood cells। Can't fight infection effectively।
- Vascular disease: Poor blood circulation। Especially feet। Wounds don't heal। Antibiotics can't reach।
- Neuropathy: No pain sensation। Minor injuries ignored। Progress to infection।
- Foot ulcers: Very common। Direct entry for bacteria। Contiguous spread to bone।
- Slow healing: Everything takes longer। Infection progresses। Chronic wounds।
Prevention crucial: Control blood sugar! HbA1c <7%। Daily foot inspection। Proper footwear। Treat injuries immediately।
⚡ If infection: More aggressive treatment। Longer antibiotics। Surgery more likely। Multi-disciplinary approach।
Reasons: Poor immunity, Vascular disease, Neuropathy, Foot ulcers, Slow healing।
Prevention: Control sugar, Foot care, Treat injuries immediately!
बोन ग्राफ्ट कब और क्यों जरूरी होती है?
When and why is bone graft needed?
Indication: Large bone defect after debridement। Extensive dead bone removal। Gap >2-3 cm।
Timing:
- NOT immediately! First control infection।
- 2nd stage surgery: 6-12 weeks later। ESR/CRP normalized। No active infection। Healthy granulation tissue।
Why needed?
- Bridge the gap: Too large to heal on its own।
- Promote healing: Provides scaffold। Bone-forming cells।
- Restore strength: Structural support। Prevent fracture।
Types:
- Autograft (best): Your own bone। Iliac crest। 100% success।
- Vascularized fibula: Large gaps। Microsurgery। Complex।
- Bone substitutes: Synthetic। Adjunct।
When: Large defect (>2-3cm)। Timing: 2nd stage, 6-12 weeks after infection control।
Why: Bridge gap, Promote healing, Restore strength। Type: Autograft best!।
पुनरावृत्ति का जोखिम कितना है?
What's the risk of recurrence?
Overall risk:
- Acute, well-treated: <5% recurrence। Excellent prognosis।
- Chronic osteomyelitis: 10-30% recurrence। Even after surgery।
- Diabetic foot: 20-40% recurrence। High risk।
Risk factors for recurrence:
- Incomplete debridement। Residual infected tissue।
- Short antibiotic course। Stopped early!
- Poor compliance। Missed doses।
- Immunocompromised। Diabetes। HIV।
- Hardware retention। Biofilm।
- Recurrence usually within first year।
Prevention: Complete treatment। Follow-up। Control underlying conditions। Early detection if recurs।
⚡ If recurs: More aggressive approach। Longer antibiotics। Revision surgery। Specialized care।
Risk: Acute <5%, Chronic 10-30%, Diabetic 20-40%।
Factors: Incomplete treatment, Poor compliance, Immunocompromised, Hardware।
Prevention: Complete treatment, Follow-up, Control conditions!
इलाज का कुल खर्चा कितना आता है?
What's the total treatment cost?
Varies significantly:
Medical treatment only: ₹50,000 - ₹2,00,000
- Hospital stay (1-2 weeks): ₹30,000 - ₹1,00,000
- IV antibiotics: ₹10,000 - ₹50,000
- Investigations (MRI, cultures): ₹10,000 - ₹30,000
- Oral antibiotics: ₹5,000 - ₹20,000
With surgery: ₹1,50,000 - ₹5,00,000+
- Surgery charges: ₹50,000 - ₹2,00,000
- Hospital stay (2-4 weeks): ₹60,000 - ₹2,00,000
- Antibiotics (longer): ₹20,000 - ₹1,00,000
- 2nd stage surgery if needed: Additional ₹50,000 - ₹1,50,000
Factors affecting cost: Hospital type। City। Complications। Surgery type। Duration।
💡 Insurance usually covers! Check policy। Government hospitals cheaper।
Medical only: ₹50K - ₹2L। With surgery: ₹1.5L - ₹5L+।
Depends on: Hospital, City, Complications, Surgery type, Duration।
Insurance usually covers!
क्या ऑस्टियोमाइलाइटिस कैंसर बन सकता है?
Can osteomyelitis turn into cancer?
NO! Osteomyelitis NEVER turns into cancer।
However:
- Rare complication: Very long-standing chronic osteomyelitis (decades) → squamous cell carcinoma in sinus tract। Extremely rare! <1%।
- Confusion: Sometimes bone tumors misdiagnosed as osteomyelitis। Or vice versa। That's why biopsy important।
Key difference:
- Osteomyelitis: Infection। Fever। Pus। Responds to antibiotics। Culture positive।
- Bone tumor: No fever usually। Progressive। No response to antibiotics। Biopsy shows malignancy।
⚠️ If doubt: Biopsy essential! MRI findings। Tumor markers। Don't worry unnecessarily - cancer very rare!।
NO! Osteomyelitis does NOT turn into cancer। Rare: Very chronic cases (>decades) - sinus tract carcinoma (<1%)।
Confusion: Tumors misdiagnosed as infection। Biopsy differentiates। Don't worry - cancer extremely rare!
खेल और सामान्य गतिविधियां कब फिर शुरू कर सकते हैं?
When can I resume sports/normal activities?
Timeline:
Week 1-4: Complete rest। Immobilization। No weight bearing।
Week 4-8: Gentle movement। Walking (if lower limb)। Light activities। No sports!
Week 8-12: Progressive loading। Daily activities। Work possible (non-physical)।
Month 3-6:
- Light sports: Swimming। Cycling (low resistance)।
- Range of motion full। Strength 70-80%।
- X-ray shows healing।
Month 6-12:
- Return to full sports: Gradual progression।
- Contact sports last। After complete healing।
- Doctor clearance essential!।
⚠️ Warning signs - STOP immediately: Pain। Swelling। Fever। Drainage। Limping।
💡 Every case different! Follow YOUR doctor's advice। Don't compare with others। X-rays guide decision।
Week 1-4: Rest। Week 4-8: Gentle movement। Week 8-12: Daily activities। Month 3-6: Light sports। Month 6-12: Full sports gradually।
STOP if: Pain, Swelling, Fever। Follow YOUR doctor's timeline!
To Know more about Osteomyelitis, Book your Appointment Today!
Consult Dr. Gaurav Jain – Orthopedic & Spine Specialist in Indore
Book Appointment⚠️ Medical Disclaimer: यह information general educational purpose के लिए है। हर patient का case अलग होता है। Treatment plan आपकी specific condition पर depend करता है। Self-medication dangerous है! Proper medical evaluation और personalized treatment के लिए qualified orthopedic surgeon से consult करें। Dr. Gaurav Jain (Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon, Indore) के साथ detailed consultation book करें।
⚠️ Medical Disclaimer: This information is for general educational purposes. Every patient is different. Consult a qualified orthopedic surgeon for proper evaluation and personalized treatment. Self-medication can be dangerous! Book detailed consultation with Dr. Gaurav Jain (Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon, Indore).