In-toeing / Out-toeing – बच्चा पैर अंदर या बाहर घुमाकर चलता है
In-toeing / Out-toeing – When Your Child Walks Inward or Outward
ज़्यादातर मामलों में सामान्य, कुछ में जांच ज़रूरी – आसान भाषा में पूरी जानकारी
Often normal and self-correcting, sometimes needs evaluation – clear guidance for parents
In-toeing / Out-toeing क्या है? – सामान्य बनाम समस्या
What is In-toeing / Out-toeing? – Normal vs Problem
In-toeing में बच्चा चलते समय पैर अंदर की ओर घुमाकर चलता है (pigeon toe चलना), जबकि Out-toeing में पैर बाहर की ओर घूमे रहते हैं। कई बार यह सिर्फ ग्रोथ का हिस्सा होता है और समय के साथ ठीक हो जाता है, पर कुछ स्थितियों में यह हड्डी के rotation की समस्या या अन्य कारण से हो सकता है।
सामान्य तथ्य
• In-toeing छोटे बच्चों में बहुत common – खासकर जब वे चलना शुरू करते हैं।
• ज़्यादातर बच्चों में उम्र बढ़ने पर बिना किसी इलाज के धीरे-धीरे सुधार होता है।
• Out-toeing सामान्य से थोड़ा कम common है, लेकिन कुछ मामलों में विशिष्ट समस्या का संकेत हो सकता है।
• असली ज़रूरत – यह पहचानना कि कौन सा case सिर्फ observation से ठीक होगा और किसे उपचार चाहिए।
कब चिंता करें?
• केवल एक पैर में ज़्यादा in-toeing या out-toeing हो।
• बच्चा चलते समय बार-बार ठोकर खाए / गिरता हो।
• उम्र के साथ सुधार के बजाय ज़्यादा बढ़ता जाए।
• बच्चा दर्द, थकान या चलने से मना करने लगे।
• family में hip, neuromuscular या deformity की strong history हो।
स्टैट्स (संक्षिप्त)
In-toeing means the child walks with feet turned inward, and out-toeing means the feet point outward during walking. Many of these patterns are physiological and improve with age, but some represent structural or neuromuscular problems that need attention.
Key Points
• In-toeing is one of the most common reasons parents seek gait opinion.
• Most children improve spontaneously with growth without active treatment.
• Out-toeing is less common and sometimes linked to specific issues.
• The main task is to distinguish benign variants from pathologic causes.
When should you worry?
• Marked deformity on one side only.
• Frequent tripping, falling or difficulty keeping up with peers.
• Deformity worsens instead of improving with age.
• Complaints of pain, fatigue or functional limitation.
• Strong family history of hip problems or neuromuscular disorders.
Quick Facts
In-toeing / Out-toeing – प्रकार और कारण
Types & Causes of In-toeing / Out-toeing
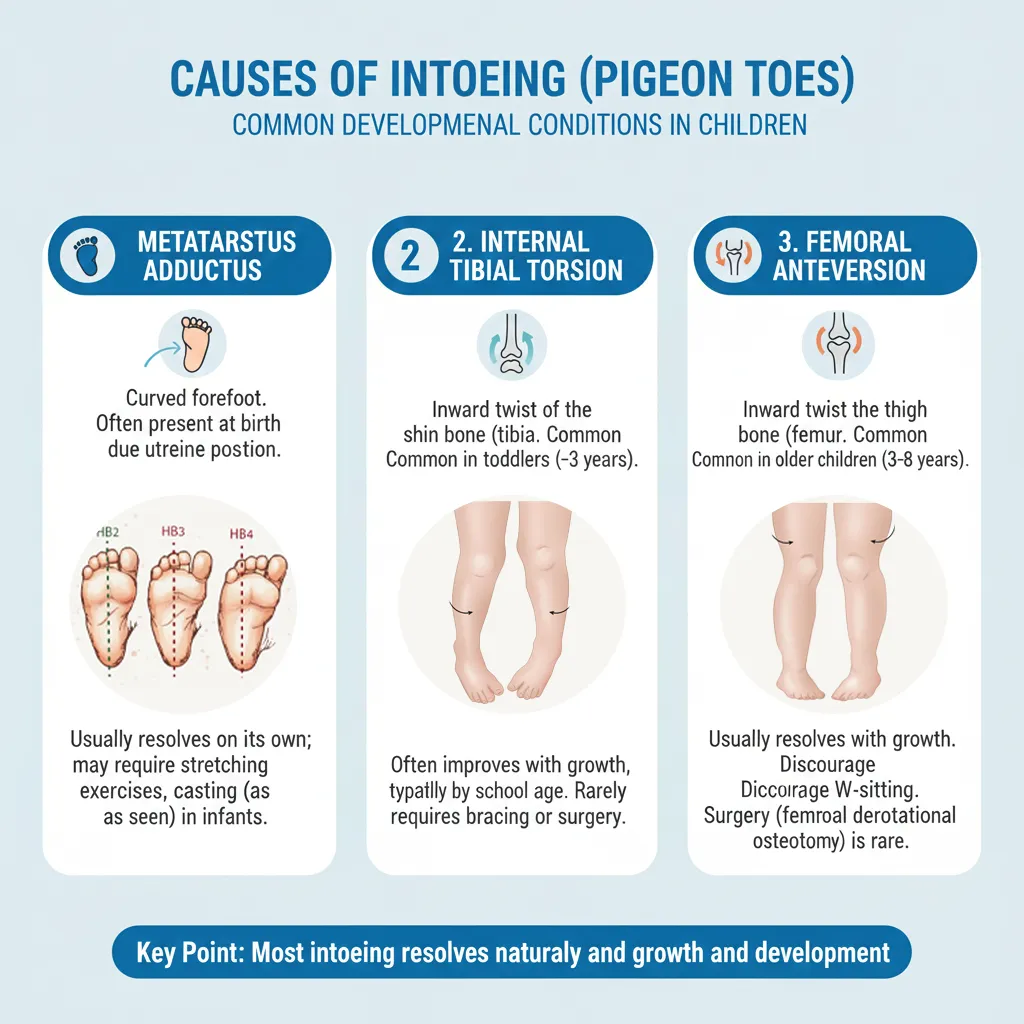
In-toeing के मुख्य कारण
1. Metatarsus Adductus (पैर के आगे वाला हिस्सा अंदर)
• पैर का आगे का हिस्सा (forefoot) अंदर की ओर मुड़ा हुआ।
• नवजात और छोटे शिशु में common।
• अधिकांश हल्के cases में stretching और समय से सुधार।
• बहुत stiff deformity में casting/brace की जरूरत हो सकती है।
2. Internal Tibial Torsion (टिबिया अंदर घुमी)
• टिबिया (नीचे की हड्डी) शरीर की मध्य रेखा की तरफ घुमी हुई।
• toddler age में सबसे common कारण।
• ज़्यादातर में 8 साल तक अपने आप या बहुत कम हस्तक्षेप से सुधार।
• मदर की गोद में certain posture, पेट के बल सोना इससे जुड़ा हो सकता है।
3. Increased Femoral Anteversion (हिप से जांघ अंदर घुमी)
• बच्चा अक्सर W-sitting करता है, पैर बहुत अंदर घुमाकर बैठता है।
• चलने पर पूरे पैर/घुटने अंदर दिखते हैं।
• आमतौर पर 10–12 साल तक धीरे-धीरे सुधार।
• अत्यधिक symptomatic और बहुत severe cases में surgery rare विकल्प।

Out-toeing के आम कारण
1. External Tibial Torsion
• टिबिया बाहर की ओर घुमा।
• बड़े बच्चों में ज़्यादा दिख सकता है।
• कुछ में केवल cosmetic, कुछ में pain/functional issues हो सकते हैं।
2. Femoral Retroversion / Hip Issues
• जांघ की हड्डी का rotation ऐसा कि पैर बाहर की ओर दिखे।
• कुछ neuromuscular समस्याओं या slipped capital femoral epiphysis आदि में भी out-toeing दिख सकता है – इसलिए specialist evaluation जरूरी।
महत्वपूर्ण
• सही diagnosis के लिए foot, tibia, femur और hip सबकी rotation को अलग-अलग जांचना पड़ता है।
• कोई single exercise या जूता हर कारण के लिए काम नहीं करता।
Main Causes of In-toeing
1. Metatarsus Adductus
• Forefoot curved inward, “C-shaped” foot.
• Common in infants.
• Many flexible feet improve with stretching and growth.
• Rigid deformity may need casting or splints.
2. Internal Tibial Torsion
• Tibia rotated inward.
• Very common in toddlers learning to walk.
• Often resolves spontaneously by around 8 years.
• Certain sleeping/ sitting positions may be associated.
3. Increased Femoral Anteversion
• Thigh bone rotated inward at hip.
• Children prefer W-sitting, knees and feet point inward while walking.
• Usually improves by 10–12 years as bones remodel.
• Surgery is rarely needed and reserved for severe, symptomatic cases.
Common Causes of Out-toeing
1. External Tibial Torsion
• Outward rotation of tibia.
• May become more apparent with age.
• Mild cases may just be cosmetic; severe ones can cause pain or patellofemoral issues.
2. Femoral Retroversion / Hip Pathology
• Decreased femoral anteversion or hip problems can present with out-toeing.
• Important to rule out conditions like slipped capital femoral epiphysis in older children with pain.
Important
• Accurate assessment requires separate evaluation of foot, tibia, femur and hip rotation.
• There is no single shoe or exercise that corrects every cause of in/out-toeing.
जांच और इलाज – In-toeing / Out-toeing
Evaluation & Treatment – In-toeing / Out-toeing
अधिकांश बच्चों में केवल निगरानी, कुछ में targeted इलाज
सिर्फ X-ray या reports से नहीं, पूरा clinical gait assessment बहुत महत्वपूर्ण है – यही तय करता है कि केस में सिर्फ follow-up, exercises, braces या सर्जरी की जरूरत है या नहीं।
जांच कैसे होती है?
1. Clinical Gait Analysis
• बच्चे की चाल को सामने, साइड और पीछे से देखना।
• थकने पर gait बदलता है या नहीं, note करना।
• जगह कम होने पर या तेजी से दौड़ते समय स्थिति कैसी है – यह भी useful जानकारी देता है।
2. Rotation Profile Examination
• prone/supine position में hip, femur, tibia और foot की rotation अलग-अलग मापना।
• thigh-foot angle, hip internal–external rotation, foot shape इत्यादि देखे जाते हैं।
• इससे पता चलता है कि deformity कहाँ से आ रही है।
3. X-ray / Imaging (जब ज़रूरी)
• हर बच्चे को X-ray की जरूरत नहीं।
• दर्द, असमान deformity, trauma या hip pathology के संदेह में imaging helpful।
• torsional CT केवल selected complex cases में।
मुख्य उपचार विकल्प
1. Observation & Reassurance
• physiological in-toeing / out-toeing में सबसे important parents को समझाना कि यह normal range का हिस्सा है।
• periodic follow-up से धीरे-धीरे सुधार को डॉक्यूमेंट करना।
2. Exercises & Posture Advice
• W-sitting से बचने की सलाह, tailor sitting प्रोत्साहित करना।
• certain stretching/strengthening programs, balance activities।
• यह structural deformity को drastic नहीं बदलते, पर gait control और confidence improve करते हैं।
3. Braces / Splints (Selected)
• flexible metatarsus adductus या कुछ foot–related issues में night splints या corrective shoes consider हो सकते हैं।
• routine in-toeing में हर बच्चे को special जूते या भारी braces की जरूरत नहीं होती।
4. Derotation Osteotomy (Rare)
• बहुत severe, cosmetic/functional रूप से disturbing और उम्र अधिक होने पर।
• femur या tibia की हड्डी को घुमाकर सही position में फिक्स करना।
• carefully selected cases, detailed counselling और planning के बाद ही।
डॉ. गौरव जैन की भूमिका
- पूरी gait और rotation profile की detailed clinical assessment
- Physiological बनाम pathological case की स्पष्ट पहचान
- Exercises, posture modification और follow-up का स्पष्ट roadmap
- ज़रूरत होने पर derotation osteotomy जैसी advanced सर्जरी की planning
Most children need guidance, not heavy treatment
Detailed clinical examination is more important than just X-rays to decide whether your child needs observation, exercises, bracing or rarely surgery.
How is evaluation done?
1. Clinical Gait Analysis
• Watching child walk from front, side and back.
• Assessing endurance, balance and tripping.
• Noting changes with speed, fatigue or different surfaces.
2. Rotation Profile
• Measuring hip, femur, tibia and foot rotation separately.
• Thigh–foot angle, hip internal/external rotation, foot shape.
• Helps localize the source of in/out-toeing.
3. Imaging When Needed
• Not every child needs X-rays.
• Used when there is pain, asymmetry, trauma or suspicion of hip pathology.
• CT torsion scans reserved for complex decision-making.
Main Treatment Options
1. Observation & Reassurance
• For physiological patterns, explaining natural history to parents is crucial.
• Regular follow-up to document improvement with growth.
2. Exercises & Posture Training
• Avoiding W-sitting, encouraging cross-legged or tailor sitting.
• Balance, coordination and strengthening exercises as needed.
• Improve control and confidence rather than drastically changing bone structure.
3. Bracing / Splints (Selected)
• Used in specific foot deformities like metatarsus adductus.
• Not routinely recommended for all in-toeing children.
• Choice of brace should be individualized, not generic.
4. Derotation Osteotomy (Rare)
• Reserved for older children with severe cosmetic/functional issues.
• Corrects bone rotation at femur or tibia with internal fixation.
• Requires careful selection, counselling and rehabilitation.
Role of Dr. Gaurav Jain
- Comprehensive gait and rotational profile assessment
- Clear differentiation between benign and pathological causes
- Structured plan for observation, posture advice and exercises
- Advanced planning for derotation osteotomy when truly indicated
माता-पिता के लिए सुझाव और भविष्य
Parent Tips & Long-term Outlook
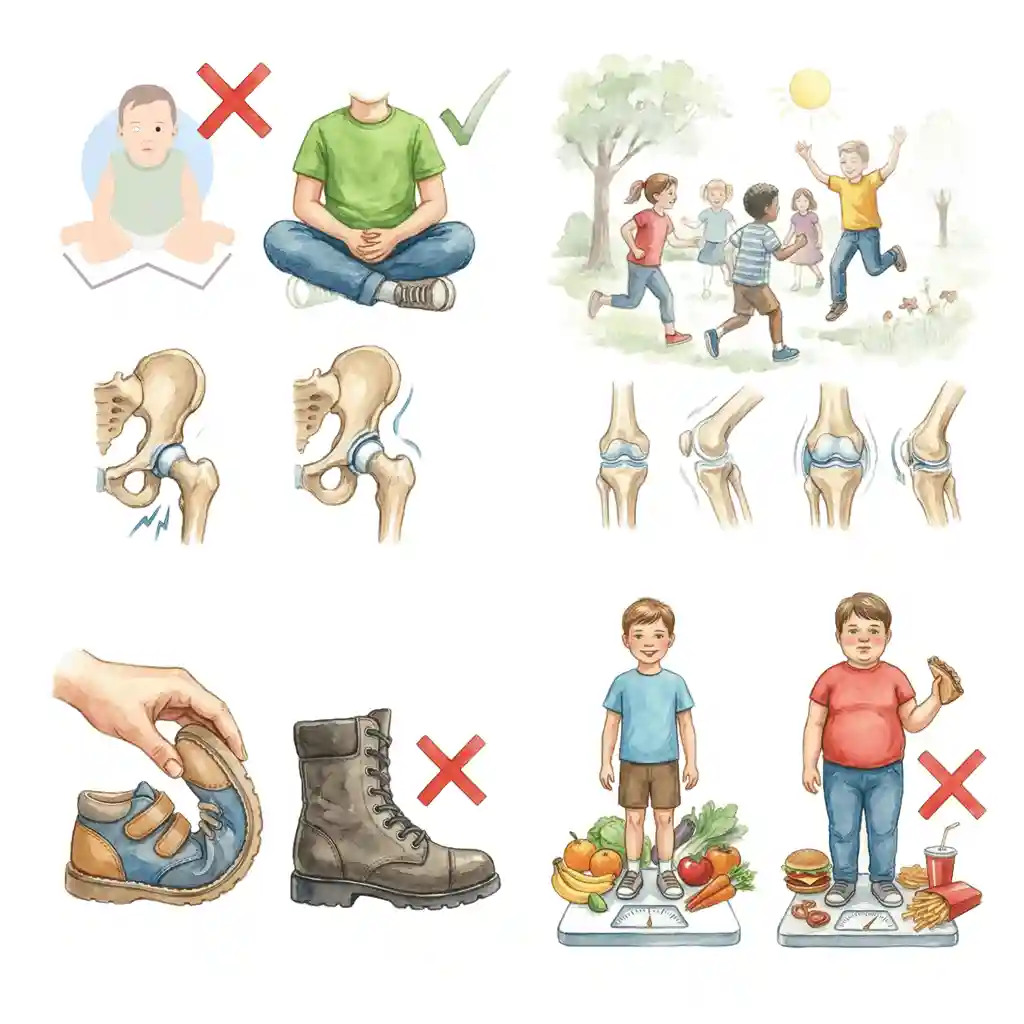

घर पर ध्यान रखने वाली बातें
1. बैठने की आदतें
• W-sitting (घुटने आगे, पैर पीछे बाहर) लंबी अवधि तक avoid करें।
• cross-legged / tailor sitting encourage करें – यह hip के लिए ज़्यादा सुरक्षित माना जाता है।
2. एक्टिविटी और खेल
• open playground में running, jumping, balance games से coordination और muscle control बेहतर होता है।
• लगातार screen time और sedentary lifestyle deformity की perception को worse कर सकते हैं।
3. वजन और जूते
• बहुत भारी जूते, गलत size के shoes से चाल awkward दिख सकती है – सही fitting वाले हल्के shoes चुनें।
• उचित weight maintain रखना joints पर अनावश्यक stress कम करता है।
भविष्य – क्या उम्मीद रखें?
• अधिकांश physiological in-toeing / out-toeing बच्चे के बड़े होने पर खुद काफी सुधार कर लेते हैं।
• सही diagnosis और समय पर intervention होने पर भविष्य में normal या near-normal चाल और activity possible है।
• बहुत late, severe या untreated pathological cases में pain या cosmetic चिंता रह सकती है, लेकिन correction से quality of life में सुधार होता है।
कब तुरंत डॉक्टर से मिलें?
• अचानक नया limp, दर्द या चलने से मना करना शुरू हो जाए।
• केवल एक पैर में deformity हो और तेजी से बढ़े।
• रात में pain, बुखार या weight loss जैसी अन्य worrying symptoms हों।
ऐसे में जल्द से जल्द Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon को दिखाएँ।
Practical Tips for Parents
1. Sitting Habits
• Discourage prolonged W-sitting.
• Encourage cross-legged sitting and varied postures to reduce stress on hips and knees.
2. Play & Activity
• Outdoor play with running, jumping, balance activities improves coordination.
• Avoid excessive gadget use and sedentary time.
3. Footwear & Weight
• Use comfortable, well-fitting shoes; avoid heavy, stiff footwear.
• Healthy weight reduces stress on growing joints.
Long-term Outlook
• Most children with physiological in/out-toeing have excellent long-term outcomes without intervention.
• With correct diagnosis and timely treatment, even pathological cases can achieve good function and cosmetic appearance.
• Untreated severe torsional deformities may lead to pain or cosmetic concerns later, but corrective surgery can improve quality of life.
When to seek urgent review?
• New-onset limp, significant pain or refusal to walk.
• Rapidly worsening deformity on one side.
• Associated systemic symptoms like fever, weight loss or night pain.
In such circumstances, consult a Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon promptly.
In-toeing / Out-toeing – अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न
क्या In-toeing हमेशा खराब है? / Is in-toeing always bad?
नहीं। अधिकांश बच्चों में in-toeing normal variation है जो हड्डियों के धीरे-धीरे घूमने (remodelling) से समय के साथ सुधार जाता है। समस्या तब मानी जाती है जब यह बहुत ज़्यादा हो, असमान हो, pain या बार-बार गिरने का कारण बने या बड़े होने पर भी बना रहे।
In-toeing और pigeon toe में क्या अंतर है? / Is pigeon toe same as in-toeing?
Pigeon toe आम बोलचाल का शब्द है जो उसी स्थिति को दर्शाता है जहाँ बच्चा पैर अंदर की ओर मोड़कर चलता है – यानी medical भाषा में in-toeing। कारण अलग-अलग हो सकते हैं (foot, tibia, femur)।
Out-toeing ज़्यादा serious है क्या? / Is out-toeing more serious than in-toeing?
हर बार नहीं, लेकिन out-toeing कुछ मामलों में hip या tibial torsion जैसी deeper समस्याओं या neuromuscular conditions से जुड़ा हो सकता है। इसलिए out-toeing में clinical evaluation और hip की जांच विशेष रूप से महत्वपूर्ण है।
यह problem किस उम्र तक अपने आप ठीक हो सकती है? / Till what age can it improve on its own?
Metatarsus adductus आमतौर पर 1–2 साल में, internal tibial torsion अक्सर 8 साल के आसपास और femoral anteversion लगभग 10–12 साल तक काफी सुधार दिखा सकते हैं। हर बच्चा अलग होता है, इसलिए periodic assessment ज़रूरी है।
क्या special shoes या चप्पल जरूरी हैं? / Do special shoes help in in-toeing?
विज्ञान के आधार पर सामान्य physiological in-toeing में routinely heavy shoes, reverse shoes या metal bars की जरूरत नहीं होती और इनका लाभ सीमित है। हल्के, आरामदायक और सही size के shoes अधिक लाभदायक हैं। विशिष्ट foot deformity में ही special orthotics की सलाह दी जाती है।
क्या physiotherapy से हड्डी घूम जाती है? / Can physiotherapy rotate the bones back to normal?
Exercises और physiotherapy मसल control, balance और gait को सुधार सकती हैं, लेकिन वे में major bony torsion को जादुई तरीके से reverse नहीं करतीं। हड्डियों का natural remodelling उम्र के साथ होता है; therapy मुख्य रूप से symptom control और confidence के लिए उपयोगी है।
Derotation osteotomy कब ज़रूरी होती है? / When is derotation osteotomy needed?
केवल उन बच्चों में जहाँ deformity बहुत severe हो, उम्र ज़्यादा हो, cosmetic/social रूप से बहुत disturbing हो या pain और functional limitation पैदा कर रही हो। यह major surgery है, इसलिए decision हमेशा detailed evaluation, imaging और counselling के बाद लिया जाता है।
क्या plaster लगाने से चाल ठीक हो जाती है? / Will plaster casts straighten in-toeing?
Plaster या cast का उपयोग मुख्यतः rigid foot deformities जैसे कुछ metatarsus adductus cases में होता है। tibia या femur के rotational issues में routine plaster से correction नहीं होता; इसके लिए या तो natural remodelling या rare cases में osteotomy की जरूरत होती है।
क्या हर in-toeing / out-toeing के लिए X-ray करवाना जरूरी है? / Is X-ray always required?
नहीं। केवल clinical evaluation से ही अधिकांश physiological cases में diagnosis हो जाता है। दर्द, असमान deformity, trauma या hip pathology के संदेह में X-ray / अन्य imaging की जरूरत पड़ सकती है। अनावश्यक radiation से बचना भी उतना ही महत्वपूर्ण है।
क्या बच्चा आगे चलकर normal दौड़-भाग कर पाएगा? / Will my child run and play normally?
अधिकांश physiological in-toeing / out-toeing वाले बच्चे बड़े होकर पूरी तरह सामान्य या लगभग सामान्य दौड़-भाग, sports और daily activities कर पाते हैं। सही समय पर evaluation और timely intervention से long-term outcome उत्कृष्ट रहता है।
क्या future में arthritis या joint damage का risk बढ़ता है? / Does in-toeing cause arthritis later?
सामान्य सीमा के भीतर रहने वाले torsional variations आमतौर पर long-term arthritis का कारण नहीं होते। लेकिन severe, untreated deformities, खासकर out-toeing या asymmetrical cases में, भविष्य में joint overload और दर्द का risk बढ़ सकता है – इसलिए सही समय पर correction helpful है।
कितने समय पर follow-up करना चाहिए? / How frequently should we follow up?
Physiological cases में आमतौर पर 6–12 महीने के अंतराल पर review पर्याप्त है ताकि improvement को monitor किया जा सके। यदि दर्द, तेजी से बढ़ती deformity या कोई नई समस्या हो तो follow-up अंतराल कम किया जा सकता है।
क्या हमें बच्चे को दौड़ने या खेलने से रोकना चाहिए? / Should we restrict running or sports?
अधिकांश physiological cases में general play, दौड़ना और खेल-कूद को रोकने की आवश्यकता नहीं होती, बल्कि यह coordination और strength के लिए अच्छा होता है। केवल pain, repeated falls या specific instructions होने पर activity modification की जरूरत होती है।
क्या W-sitting पूरी तरह बैन करना चाहिए? / Is W-sitting always harmful?
कभी-कभार W-sitting हर बच्चे में हो सकता है, पर अगर बच्चा लगातार केवल इसी posture में बैठना पसंद करे, तो इसे धीरे-धीरे avoid कराना बेहतर है। यह hip और knee पर अतिरिक्त stress डाल सकता है, खासकर जब पहले से torsional issue हो।
क्या यह problem hereditary हो सकती है? / Is in-toeing hereditary?
कुछ परिवारों में torsional pattern (जैसे femoral anteversion) अधिक common दिख सकता है, पर अधिकांश cases में यह simple developmental variation होता है। Detailed family history लेने से risk की बेहतर समझ बनती है, पर हर in-toeing hereditary नहीं होता।
क्या difference दोनों पैरों में होना खतरनाक है? / Is it dangerous if one leg turns more than the other?
हल्का अंतर सामान्य हो सकता है, लेकिन स्पष्ट asymmetry – खासकर साथ में limp, pain या previous injury history – pathological cause का संकेत हो सकता है। ऐसे में evaluation delay नहीं करना चाहिए।
क्या घर पर online exercises से काम चल जाएगा? / Are online exercises enough, without seeing a doctor?
General fitness exercises useful हो सकते हैं, पर बिना सही diagnosis के केवल online videos पर निर्भर रहना सही नहीं है। पहले specialist से consult करके पता करना जरूरी है कि case physiological है या नहीं, फिर exercises को personalize किया जा सकता है।
किस specialist को दिखाएँ? / Which specialist should we consult?
In-toeing, out-toeing, bow legs, knock knees या gait संबंधी किसी भी चिंता के लिए Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon सबसे उचित विशेषज्ञ हैं। इंदौर में डॉ. गौरव जैन ऐसे बच्चों के comprehensive gait evaluation और correction की सुविधा प्रदान करते हैं।
क्या बाद में cosmetic रूप से पैर normal दिखेंगे? / Will the legs look normal cosmetically in future?
काफी बच्चों में, खासकर physiological torsion वाले केस में, बड़े होने पर चाल और पैर लगभग पूरी तरह normal दिखते हैं। residual हल्का in-toeing/out-toeing कई बार दूसरों को noticeable भी नहीं होता। severe या pathological deformity में cosmetic correction के लिए targeted treatment helpful रहता है।
माता-पिता की सबसे महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका क्या है? / What is the most important role of parents?
समय पर evaluation कराना, follow-up miss न करना, डॉक्टर की सलाह के अनुसार posture और activities में बदलाव लाना, और बच्चे की चाल पर calmly नज़र रखना – यही सबसे महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका है। डर या guilt की जगह जानकारी और सहयोगपूर्ण दृष्टिकोण बच्चे के लिए सबसे सुरक्षित होता है।
In-toeing / Out-toeing के लिए डॉ. गौरव जैन से परामर्श – इंदौर
Consult Dr. Gaurav Jain in Indore for In-toeing / Out-toeing Evaluation
बच्चों की चाल (gait) की विस्तृत जांच, rotation profile, उचित follow-up और ज़रूरत होने पर उन्नत correction – एक ही जगह समर्पित बाल हड्डी रोग सेवा। Comprehensive gait assessment, rotation profile evaluation, structured follow-up and advanced correction when needed – specialized pediatric orthopedic care in Indore.
कॉल करें Call Now