Limb Deformities – बच्चों में पैर / हाथ की टेढ़ी–मेढ़ी हड्डियाँ
Limb Deformities – Angular, Rotational & Length Problems in Children
कुछ deformity normal ग्रोथ का हिस्सा, कुछ को सही समय पर correction की ज़रूरत – अंतर जानना बहुत जरूरी
Some deformities are physiological, others need timely correction – knowing the difference is crucial
Limb Deformity क्या है? – Normal vs Problem
What Are Limb Deformities? – Normal Variants vs True Deformity
Limb deformity का मतलब है हाथ या पैर की हड्डियों का अत्यधिक टेढ़ा होना, घूमना या लंबाई में अंतर जो सामान्य सीमा से बाहर हो और चाल, संतुलन या appearance पर असर डालने लगे।
सामान्य vs असामान्य
• छोटे बच्चों में कुछ हद तक bow legs या knock knees physiological हो सकते हैं और उम्र के साथ अपने आप सुधारते हैं।
• जब deformity बहुत ज़्यादा हो, असमान हो, उम्र के हिसाब से गलत दिशा में जाए या pain/functional problem दे – तब इसे pathological deformity माना जाता है।
• यही अंतर पहचानने के लिए Pediatric Orthopedic evaluation जरूरी है।
कब deformity को गंभीर मानें?
• केवल एक पैर ज़्यादा टेढ़ा होना या दोनों में बहुत फर्क।
• बच्चा लंगड़ाकर चले, जल्दी थक जाए या बार–बार गिरता हो।
• deformity उम्र के साथ घटने के बजाय बढ़ती जाए।
• घुटने/ankle में दर्द, walking में difficulty या cosmetic/social concern ज़्यादा हो।
• family history में rickets, Blount disease, skeletal dysplasia या previous fracture deformity हो।
त्वरित तथ्य
Limb deformities refer to abnormal angulation, rotation or length difference of the arms or legs beyond normal age-related limits, affecting gait, balance or cosmetic appearance.
Physiological vs Pathological
• Mild bowing or knock knees at certain ages can be physiological and self-correcting.
• Deformity is considered pathological when severe, progressive, asymmetric or associated with pain and functional limitation.
• Pediatric orthopedic evaluation is crucial to distinguish between the two.
When to worry?
• Marked deformity on one side only or significant asymmetry.
• Limping, frequent tripping or difficulty keeping up with peers.
• Deformity worsening instead of improving with age.
• Pain around knee/ankle or strong cosmetic/social concerns.
• Family history of rickets, Blount disease, skeletal dysplasia or prior malunited fractures.
Quick facts
Limb Deformities – आम प्रकार
Common Types of Limb Deformities in Children
Angular Deformities – bow legs / knock knees आदि
1. Bow Legs (Genu Varum)
• घुटनों के बीच gap, पैर O–shape जैसे दिखें।
• 2 साल से पहले mild bowing अक्सर physiological होता है।
• severe, asymmetrical या बढ़ती deformity में rickets, Blount disease या अन्य pathology rule out करना ज़रूरी।
• time, vitamin D/calc correction, bracing या corrective osteotomy – कारण और severity पर निर्भर।
2. Knock Knees (Genu Valgum)
• घुटने आपस में टकराते हैं, ankles में gap – X–shape।
• 3–7 साल की उम्र में mild–moderate knock knees normal range में हो सकते हैं।
• excessive deformity, pain या age mismatch में guided growth या osteotomy जैसी correction option।
3. Post-traumatic / Growth Plate Related Angular Deformity
• fracture के बाद गलत जुड़ने (malunion) या growth plate damage से धीरे–धीरे टेढ़ापन बढ़ना।
• accurate X-ray, mechanical axis analysis और timing–based corrective surgery से alignment सुधारी जा सकती है।
Rotational और Length Deformities
4. Rotational Deformities (In-toeing / Out-toeing)
• foot, tibia या femur की rotation बदलने से चाल में अंदर–बाहर घूमना।
• कई cases physiological, लेकिन severe या asymmetric deformity में derotation osteotomy की जरूरत पड़ सकती है।
• gait analysis और clinical rotation profile बहुत महत्वपूर्ण।
5. Limb Length Discrepancy (LLD)
• एक पैर दूसरे से छोटा–बड़ा दिखना, limp या pelvic tilt होना।
• कारण – जन्मजात, infection, fracture, growth plate injury आदि।
• छोटा अंतर shoe raise से, बड़ा अंतर limb lengthening या growth modulation (epiphysiodesis) से correction।
6. Congenital / Syndromic Deformities
• skeletal dysplasia, fibular hemimelia, congenital tibial bowing आदि।
• multi-stage planning, limb reconstruction, lengthening या कभी-कभी amputation–prosthesis का individualized निर्णय।
Deformity Analysis क्यों जरूरी?
• केवल X-ray देखकर नहीं, mechanical–anatomical axis, CORA (center of rotation of angulation) और growth potential समझकर ही सही correction की योजना बनती है।
• एक ही surgery में over– या under–correction से future में फिर से समस्या हो सकती है।
Angular Deformities – Varus / Valgus
1. Bow Legs (Genu Varum)
• Legs curved outward, knees apart, ankles closer.
• Mild bowing under 2 years often physiological.
• Severe, unilateral or progressive deformity requires evaluation for rickets, Blount disease etc.
• Management ranges from observation and medical treatment to bracing or corrective osteotomy.
2. Knock Knees (Genu Valgum)
• Knees touch, ankles apart – X-shaped legs.
• Physiological between 3–7 years within limits.
• Excess deformity or persistence may need guided growth or osteotomy.
3. Post-traumatic / Growth Plate Angular Deformity
• Develops after malunited fractures or physeal damage.
• Requires detailed axis analysis and planned corrective osteotomy at the CORA.
Rotational & Length Deformities
4. Rotational Deformities
• Excess in-toeing or out-toeing due to femoral/tibial or foot rotation.
• Many are benign, but severe symptomatic deformities may need derotation osteotomy.
• Gait analysis and rotational profile are key.
5. Limb Length Discrepancy (LLD)
• One limb shorter or longer causing limp or pelvic tilt.
• Causes include congenital, infection, trauma, physeal arrest.
• Treatment varies from shoe raises to growth modulation or lengthening procedures.
6. Congenital / Syndromic Deformities
• Seen in conditions like fibular hemimelia, congenital bowing, skeletal dysplasia.
• Often need staged reconstruction, lengthening or limb reconstruction strategies.
Why detailed deformity analysis?
• Correct planning requires mechanical/anatomical axis evaluation, CORA identification and growth potential assessment.
• Over- or under-correction can create new problems later.
Limb Deformity – जांच और इलाज की योजना
Evaluation & Treatment Planning for Limb Deformities
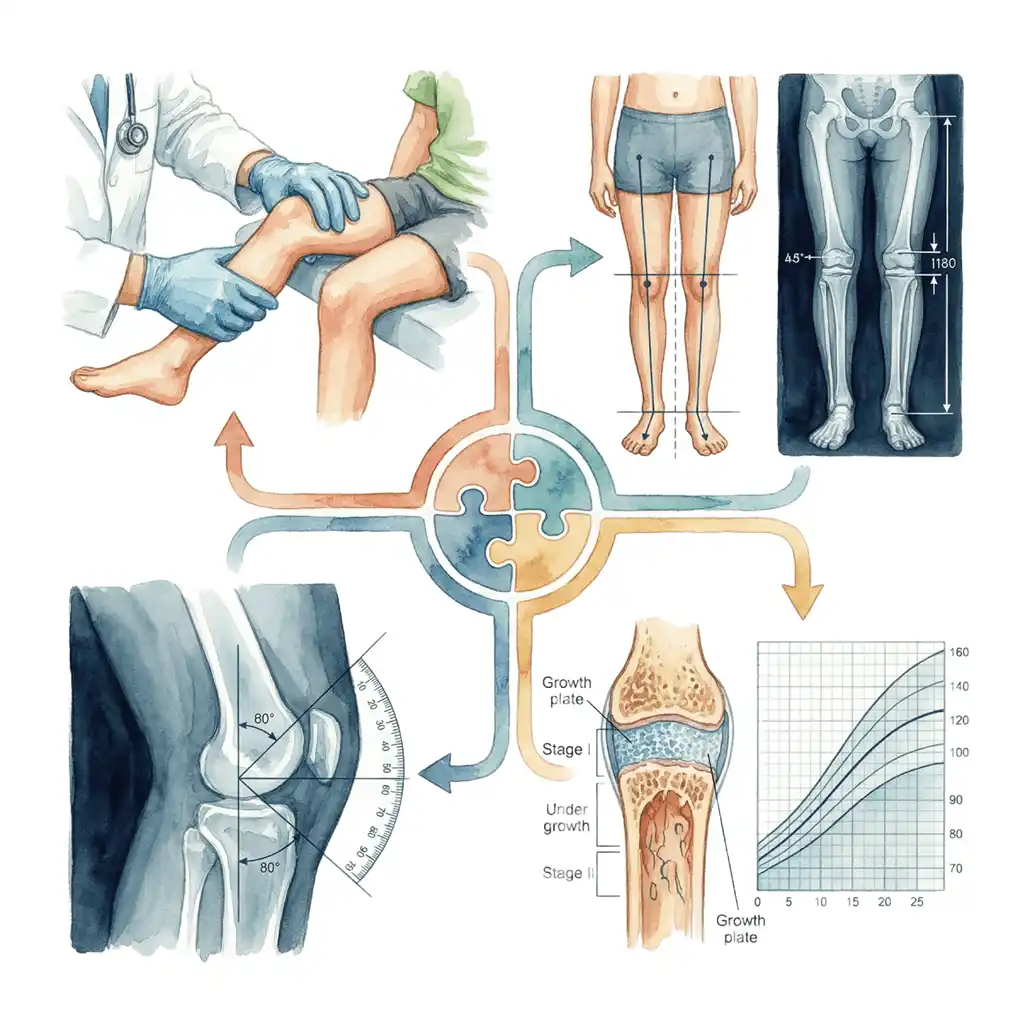
सिर्फ X-ray नहीं – पूरा deformity workup
सही treatment के लिए clinical examination, standing alignment, X-ray measurements और growth potential – सबको जोड़कर individualised योजना बनाना जरूरी है।
Evaluation में क्या–क्या शामिल?
1. Clinical Assessment & Gait Analysis
• child की चाल, standing posture, pelvic tilt, trunk inclination देखना।
• joint range of motion, ligament laxity, pain points और muscle power की जांच।
• limb length measurement – tape measure, block test आदि।
2. X-ray & Deformity Mapping
• standing long–limb X-ray से mechanical axis और joint orientation angles मापना।
• CORA, proximal/distal segment contribution और growth plate स्थिति का आकलन।
• कुछ cases में CT scan / scanogram / EOS imaging helpful हो सकते हैं।
3. Metabolic / Systemic Evaluation
• rickets, renal disease, metabolic bone disease या syndromic causes का suspicion हो तो relevant blood tests और अन्य जांच।
• underlying cause treat किए बिना केवल surgery करना पर्याप्त नहीं होता।
मुख्य Treatment Options
1. Observation & Medical Management
• physiological bowing/knock knees में केवल follow-up और vitamin D–calcium optimization।
• mild deformity में नियमित monitoring और parents को natural history समझाना।
2. Guided Growth (Temporary Epiphysiodesis)
• बढ़ते बच्चों में growth plate के एक side पर small plate/ screw लगाकर deformity को धीरे–धीरे straighten करना।
• minimally invasive, सही timing और angle calculation पर आधारित।
• deformity सुधरने पर implant removal – ताकि आगे की normal growth हो सके।
3. Corrective Osteotomy
• जब उम्र अधिक हो, growth कम बची हो या deformity बहुत severe / complex हो।
• हड्डी को CORA level पर काटकर सही angle में align कर plate, nail या external fixator से fix करना।
• single–plane या multi–plane deformity correction के लिए planning software या templates उपयोगी।
4. Limb Lengthening / Epiphysiodesis for LLD
• छोटे LLD में growth modulation (shorter limb को grow होने देना, longer की growth को नियंत्रित करना)।
• बड़े LLD में external fixator या internal lengthening nail के जरिए gradual lengthening।
• लंबे समय तक close follow-up और physiotherapy की जरूरत।
डॉ. गौरव जैन की भूमिका
- Clinical आणि radiological deformity analysis और growth prediction
- Physiological vs pathological deformity की स्पष्ट पहचान
- Guided growth, corrective osteotomy और limb lengthening जैसी advanced प्रक्रियाओं की planning और execution
- Long-term follow-up के साथ child और parents को realistic expectations समझाना
Comprehensive deformity workup – not just an X-ray
Effective correction needs clinical assessment, alignment analysis, imaging-based measurements and growth prediction, all integrated into a child-specific plan.
Evaluation Components
1. Clinical & Gait Assessment
• Observation of standing alignment, gait, pelvic tilt and compensatory mechanisms.
• Joint ROM, ligament laxity, pain and muscle strength.
• Clinical limb length measurement and block tests.
2. Radiological Deformity Analysis
• Standing long-limb radiographs to calculate mechanical axis and joint orientation angles.
• Identification of CORA and contribution of each bone segment.
• CT/scanogram/EOS imaging in selected complex cases.
3. Metabolic / Systemic Workup
• For suspected rickets, renal or metabolic bone disease, or syndromic causes.
• Treating the underlying cause is essential along with mechanical correction.
Main Treatment Options
1. Observation & Medical Therapy
• For physiological deformities, observation with vitamin D and nutritional optimisation.
• Regular monitoring and parental counselling on natural history.
2. Guided Growth
• Temporary hemiepiphysiodesis using small plates/screws to gradually correct deformity while child grows.
• Minimally invasive, relies on accurate timing and angle calculations.
• Implant removal once desired correction is achieved.
3. Corrective Osteotomy
• For older children, severe or complex deformities with limited growth remaining.
• Osteotomy at CORA with fixation using plates, nails or external fixators.
• Single- or multi-plane corrections based on detailed planning.
4. Limb Lengthening / Epiphysiodesis
• Growth modulation for predicted moderate LLD.
• Lengthening with external fixators or internal lengthening nails for larger discrepancies.
• Requires prolonged supervision and physiotherapy.
Role of Dr. Gaurav Jain
- Detailed deformity analysis with growth prediction
- Clear distinction between physiological and pathological deformity
- Planning of guided growth, osteotomy and lengthening procedures
- Long-term follow-up with realistic counselling for families
माता–पिता के लिए सुझाव और भविष्य
Parent Tips & Long-term Outlook
घर पर क्या ध्यान रखें?
1. चाल और posture पर नज़र
• फोटो/वीडियो से before–after comparison मददगार हो सकता है।
• child को बार–बार “सीधा चल” कहकर डराने की बजाय positive reinforcement दें।
2. Nutrition और Vitamin D
• संतुलित diet, पर्याप्त protein, calcium और vitamin D deformity की कुछ reversible causes (जैसे nutritional rickets) से बचाती हैं।
• doctor की सलाह से supplements दिया जा सकता है।
3. Activity और Sports
• अधिकांश बच्चों को normal play encourage किया जाता है; high-impact sports पर restriction deformity type और surgery पर निर्भर।
• physiotherapist / surgeon के द्वारा बतायी गई exercises regular कराएँ।
भविष्य की संभावनाएँ
• सही समय पर diagnosis और treatment होने पर अधिकांश बच्चों में normal या near-normal function और appearance संभव है।
• untreated या बहुत late आये severe deformities में early arthritis, pain या cosmetic concern बढ़ सकते हैं – correction quality of life को बेहतर कर सकती है।
• guided growth और modern osteotomy techniques ने कई complex deformities को भी अपेक्षाकृत कम invasive तरीके से correct करना संभव बनाया है।
कब तुरंत specialist को दिखाएँ?
• अचानक deformity बढ़ना, नया limp या pain शुरू होना।
• fracture / infection history के बाद धीरे–धीरे पैर टेढ़ा होना।
• joint के पास swelling, redness या रात में दर्द।
• किसी ने “अब कुछ नहीं हो सकता” कह दिया हो – ऐसे मामलों में भी deformity correction options पर expert से चर्चा करना लाभदायक हो सकता है।
Practical Tips for Parents
1. Observe, Don’t Panic
• Use photos/videos over months to track change rather than daily worry.
• Avoid constant criticism; encourage confidence and regular follow-up.
2. Support Bone Health
• Balanced diet with adequate protein, calcium and vitamin D.
• Supplements if advised by the doctor after evaluation.
3. Activity & Rehabilitation
• Encourage safe physical activity; specific sports restrictions depend on deformity and surgery done.
• Adhere to exercise and physiotherapy plans to maintain correction.
Long-term Outlook
• With accurate planning and timely intervention, most children achieve good alignment and function into adulthood.
• Neglected severe deformities carry higher risk of early arthritis and chronic pain, but staged correction can still improve quality of life.
• Modern guided growth and osteotomy techniques have significantly improved outcomes.
When to Seek Urgent Review?
• Rapid worsening of deformity or new limp/pain.
• Progressive deformity after fracture, infection or surgery.
• Swelling, redness or night pain around joints.
Even if told “nothing can be done”, a fresh pediatric orthopedic opinion can clarify current options.
Limb Deformities – अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले प्रश्न
Limb Deformities – Frequently Asked Questions
क्या हर bow legs / knock knees इलाज की जरूरत होती है? / Do all bow legs or knock knees need treatment?
नहीं। कुछ उम्र पर हल्का bowing या knock knees normal growth का हिस्सा होता है और अपने आप सुधर जाता है। treatment की जरूरत तब होती है जब deformity उम्र और normal range से बाहर हो, progressive हो, असमान हो या pain/function पर असर डाल रही हो।
क्या केवल calcium / vitamin D देने से deformity सीधी हो जाएगी? / Will calcium and vitamin D alone correct deformity?
Nutritional rickets में medical treatment से deformity में कुछ सुधार हो सकता है, लेकिन established बडे angular deformities या growth plate damage में केवल दवा काफी नहीं होती। mechanical axis को सुधारने के लिए guided growth या osteotomy की जरूरत पड़ सकती है।
घर पर “पट्टी बांधकर” या लकड़ी लगाकर पैर सीधा करना सही है? / Is it safe to tie legs at home to straighten them?
नहीं। बिना scientific planning के tight पट्टी या crude splints से skin injury, joint stiffness और कभी–कभी deformity और खराब हो सकती है। deformity correction हमेशा specialist की supervised plan से होना चाहिए, न कि घरेलू जुगाड़ से।
Guided growth surgery कितनी बड़ी होती है? / How big is guided growth surgery?
यह आमतौर पर minimally invasive procedure होती है, छोटे incision से growth plate के एक तरफ छोटी plate/ screws लगाई जाती हैं। बच्चा अक्सर जल्दी चलना शुरू कर सकता है और correction समय के साथ धीरे–धीरे होता है। deformity ठीक हो जाने पर implant हटाना भी day-care या short-stay procedure हो सकता है।
क्या osteotomy बहुत risk वाली बड़ी surgery है? / Is corrective osteotomy very risky?
हर surgery की तरह osteotomy के भी risk हैं (bleeding, infection, non-union आदि), लेकिन proper planning, modern implants और good post-op care से ये risk काफी कम किये जा सकते हैं। कई बार severe deformity में osteotomy ही वह विकल्प है जो future में arthritis और disability से बचा सकता है।
Limb lengthening कितना painful और लंबा process है? / Is limb lengthening very painful and prolonged?
Limb lengthening एक लंबा process है (months तक), जिसमें patience, physiotherapy और regular follow-up जरूरी हैं। सही pain control, counselling और modern devices के साथ यह procedure काफी बच्चों के लिए safely possible है, लेकिन सभी cases में इसका indication नहीं होता – careful selection आवश्यक है।
अगर अभी treatment न कराएँ तो आगे क्या risk है? / What happens if deformity is left untreated?
Severe या progressive deformity untreated रहने पर future में early osteoarthritis, chronic pain, walking difficulty, cosmetic bullying और कभी–कभी spine–pelvis alignment problem हो सकती हैं। वहीं कई physiological deformities बिना treatment ठीक भी हो जाती हैं – इसलिए specialist से यह जानना सबसे महत्वपूर्ण है कि आपका बच्चे का pattern किस group में आता है।
क्या correction के बाद बच्चा normal sports कर सकता है? / Can my child play sports normally after correction?
अधिकांश well-corrected deformities में child future में normal या near-normal sports कर सकता है, बशर्ते bone अच्छी तरह जुड़ जाए, alignment संतुलित हो और muscle strength वापस आ जाए। high-impact sports में return हमेशा stepwise और surgeon की सलाह के अनुसार होना चाहिए।
क्या deformity वापस आ सकती है? / Can deformity recur after treatment?
कुछ conditions (जैसे Blount disease, metabolic bone disease या बहुत छोटे बच्चे) में recurrence का risk ज़्यादा हो सकता है। guided growth या osteotomy के बाद भी growth pattern और underlying disease पर depend करते हुए follow-up ज़रूरी है, ताकि early recurrence detect होकर दोबारा से manage किया जा सके।
क्या physiotherapy deformity खुद से सीधी कर सकती है? / Can physiotherapy alone correct deformity?
Exercises muscle strength, balance और gait pattern को improve कर सकते हैं, लेकिन true bony angular/rotational deformity को केवल physiotherapy से पूरी तरह सीधा नहीं किया जा सकता। जहां mechanical axis में दिक्कत हो, वहाँ guided growth या osteotomy जैसी bony correction आवश्यक होती है; physiotherapy इनका important supplement है।
किस specialist को दिखाएँ? / Which specialist should we consult for limb deformities?
Limb deformities, bow legs, knock knees, limb length difference या complex reconstruction के लिए Pediatric Orthopedic / Deformity Correction Surgeon सबसे उपयुक्त specialist हैं। इंदौर में डॉ. गौरव जैन बच्चों की deformity analysis, guided growth, osteotomy और limb lengthening जैसी सेवाएँ प्रदान करते हैं।
Parents की सबसे महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका क्या है? / What is the most important role of parents?
समय पर evaluation कराना, advise के अनुसार follow-up और X-rays कराना, instructions (brace, weight-bearing, physiotherapy) को consistently follow करना और बच्चे को emotional support देना – यही सबसे महत्वपूर्ण भूमिका है। internet myths या अनजाने तरीके अपनाने के बजाय treating specialist के साथ open communication रखना best रहता है।
Limb Deformities के लिए विशेषज्ञ मूल्यांकन और correction – डॉ. गौरव जैन, इंदौर
Expert Evaluation & Correction of Limb Deformities – Dr. Gaurav Jain, Indore
Detailed deformity analysis, guided growth, corrective osteotomy और limb lengthening – एक ही जगह comprehensive pediatric deformity correction care। Detailed deformity analysis, guided growth, corrective osteotomy and limb lengthening – comprehensive pediatric deformity correction care under one roof.
कॉल करें Call Now