Neural Tube Defects
NTD की पूरी जानकारी, prevention और management
Neural Tube Defects
Complete information, prevention and management of NTD
Neural Tube Defects क्या हैं? What are Neural Tube Defects?
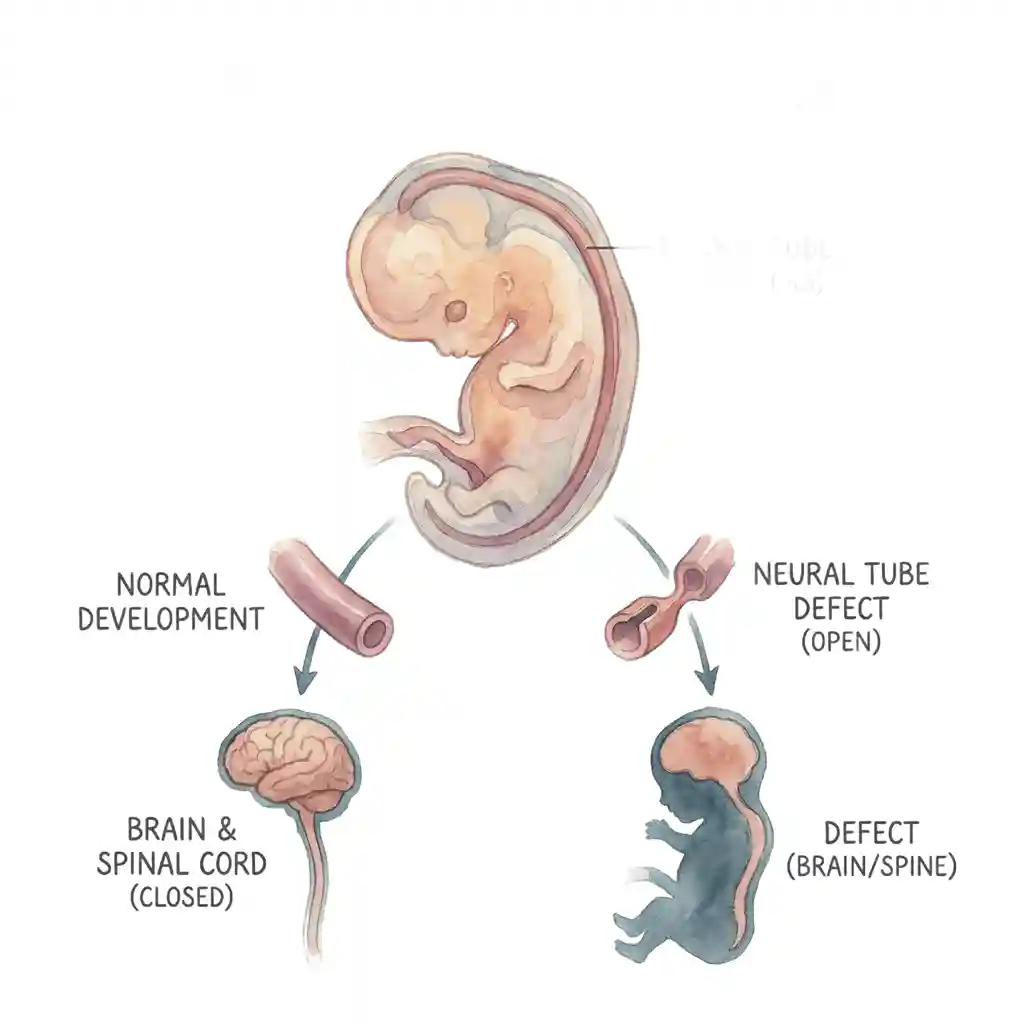
Neural Tube Defects (NTDs) birth defects हैं जो brain, spine, या spinal cord के development में होती हैं। ये defects pregnancy के बहुत early stage में develop होती हैं - आमतौर पर conception के 3-4 weeks के बीच, जब neural tube (जो बाद में brain और spinal cord बनती है) properly close नहीं होती।
Neural tube embryo में developing brain और spinal cord का early form है। Normally यह tube conception के 28 days तक पूरी तरह close हो जाती है। अगर यह tube किसी जगह पर open रह जाती है, तो Neural Tube Defect develop होता है। यह serious birth defects हैं जो lifelong disabilities cause कर सकती हैं।
Good News - Prevention संभव है!
70% तक Neural Tube Defects को Folic Acid supplementation से prevent किया जा सकता है। Pregnancy से पहले और early pregnancy में adequate folic acid लेना बहुत important है। यह एक preventable birth defect है!
Neural Tube Defects (NTDs) are birth defects that occur in the development of the brain, spine, or spinal cord. These defects develop at a very early stage of pregnancy - usually between 3-4 weeks after conception, when the neural tube (which later becomes the brain and spinal cord) doesn't close properly.
The neural tube is the early form of the developing brain and spinal cord in the embryo. Normally this tube closes completely by 28 days after conception. If this tube remains open at some place, a Neural Tube Defect develops. These are serious birth defects that can cause lifelong disabilities.
Good News - Prevention is Possible!
Up to 70% of Neural Tube Defects can be prevented with Folic Acid supplementation. Taking adequate folic acid before pregnancy and in early pregnancy is very important. This is a preventable birth defect!
Neural Tube Defects के Types Types of Neural Tube Defects
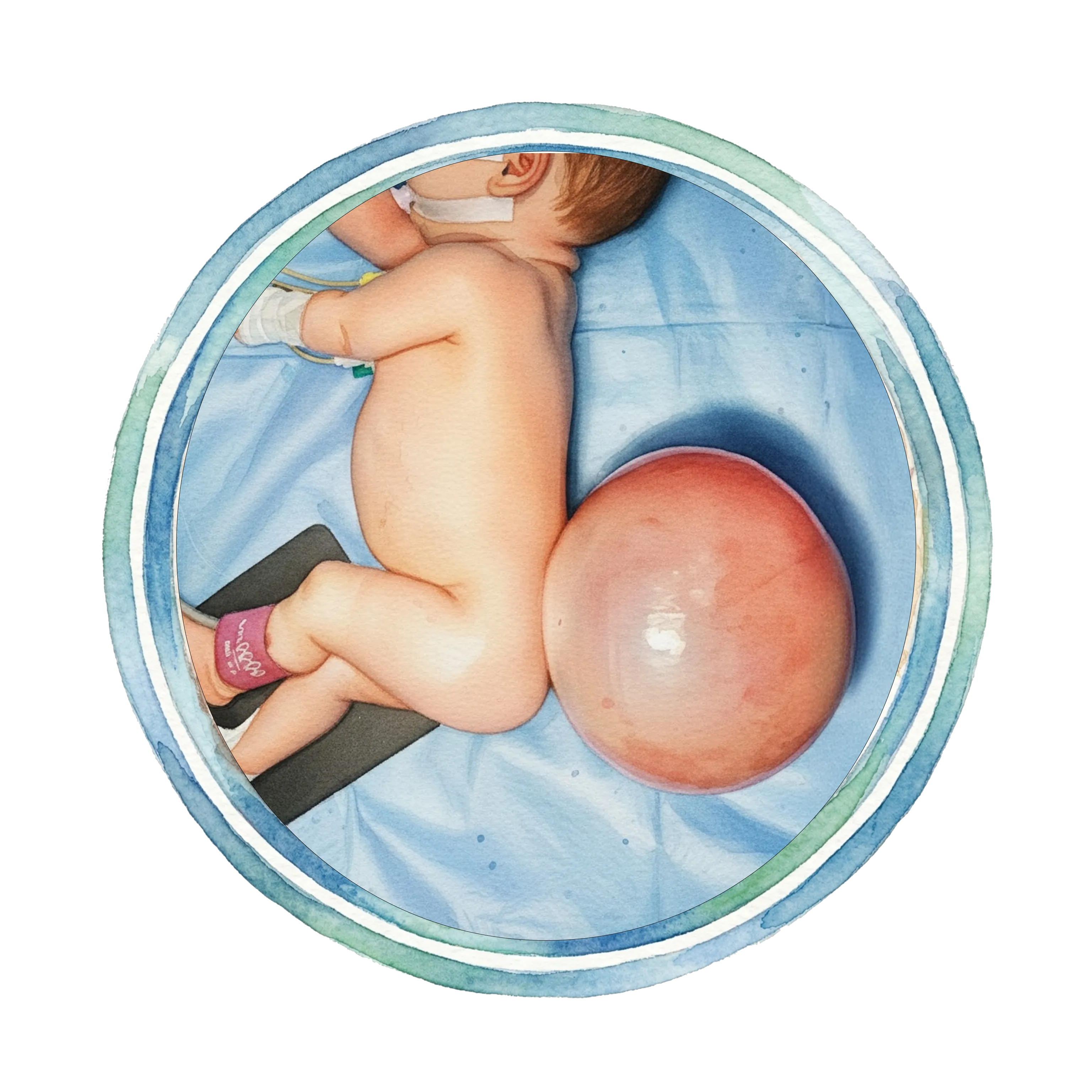
Spina Bifida
Most common NTD (सबसे आम)
क्या है: Spinal column completely close नहीं होती। Spinal cord और meninges (protective coverings) exposed रह सकते हैं।
Severity: Mild से severe तक vary करता है।
Types:
• Occulta: Mildest form, अक्सर symptoms नहीं
• Meningocele: Moderate, sac protrudes
• Myelomeningocele: Most severe, spinal cord exposed
Anencephaly
Most severe NTD
क्या है: Brain का major portion develop नहीं होता। Skull की bones भी absent या incomplete होती हैं।
Outcome: Fatal condition - babies usually stillborn होते हैं या birth के कुछ hours/days में death हो जाती है।
Survival: Long-term survival possible नहीं है।
Prevention: Folic acid से significant reduction
Encephalocele
Rare type (कम common)
क्या है: Skull में opening होती है जिससे brain tissue बाहर protrude करता है। Usually sac-like protrusion back of head पर।
Severity: Varies - mild से severe brain damage तक।
Treatment: Surgery required है।
Prognosis: Depends on size, location, और brain tissue involvement पर
Spina Bifida
Most common NTD
What is it: Spinal column doesn't close completely. Spinal cord and meninges (protective coverings) may be exposed.
Severity: Varies from mild to severe.
Types:
• Occulta: Mildest form, often no symptoms
• Meningocele: Moderate, sac protrudes
• Myelomeningocele: Most severe, spinal cord exposed
Anencephaly
Most severe NTD
What is it: Major portion of brain doesn't develop. Skull bones are also absent or incomplete.
Outcome: Fatal condition - babies usually stillborn or death occurs within hours/days of birth.
Survival: Long-term survival not possible.
Prevention: Significant reduction with folic acid
Encephalocele
Rare type (less common)
What is it: Opening in skull through which brain tissue protrudes. Usually sac-like protrusion at back of head.
Severity: Varies - from mild to severe brain damage.
Treatment: Surgery is required.
Prognosis: Depends on size, location, and brain tissue involvement
Spina Bifida - विस्तार से Spina Bifida - In Detail
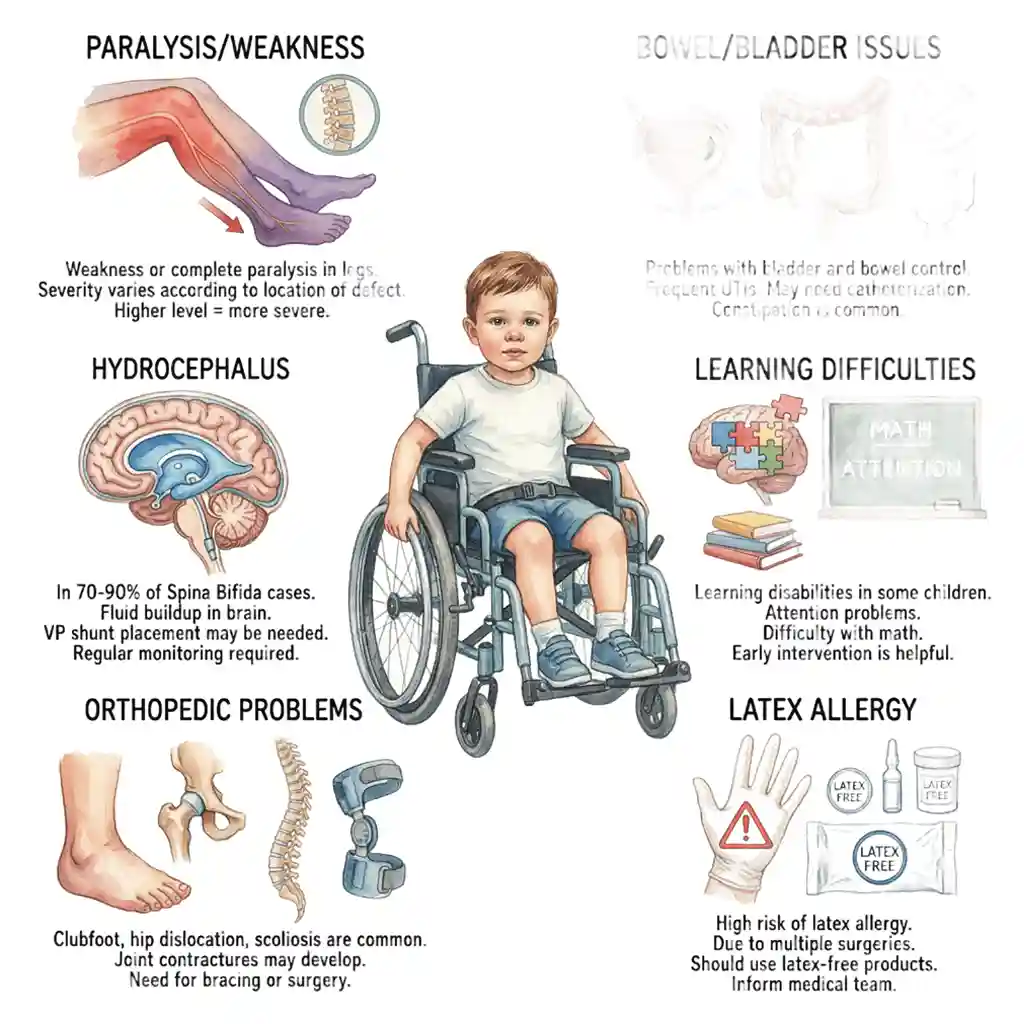
Legs में weakness या complete paralysis। Defect की location के according severity vary करती है। Higher level = more severe।
Weakness or complete paralysis in legs. Severity varies according to location of defect. Higher level = more severe.
Bladder और bowel control में problems। Frequent UTIs। Catheterization की जरूरत हो सकती है। Constipation common है।
Problems with bladder and bowel control. Frequent UTIs. May need catheterization. Constipation is common.
70-90% Spina Bifida cases में। Brain में fluid buildup। VP shunt placement जरूरी हो सकता है। Regular monitoring चाहिए।
In 70-90% of Spina Bifida cases. Fluid buildup in brain. VP shunt placement may be needed. Regular monitoring required.
कुछ children में learning disabilities। Attention problems। Math में difficulty। Early intervention helpful है।
Learning disabilities in some children. Attention problems. Difficulty with math. Early intervention is helpful.
Clubfoot, hip dislocation, scoliosis common हैं। Joint contractures develop हो सकते हैं। Bracing या surgery की जरूरत।
Clubfoot, hip dislocation, scoliosis are common. Joint contractures may develop. Need for bracing or surgery.
High risk of latex allergy। Multiple surgeries के कारण। Latex-free products use करनी चाहिए। Medical team को inform करें।
High risk of latex allergy. Due to multiple surgeries. Should use latex-free products. Inform medical team.
कारण और Risk Factors Causes and Risk Factors
NTDs का exact cause अक्सर पता नहीं होता। Multiple factors combination में role play करते हैं:
Folic Acid Deficiency
सबसे important preventable risk factor
Adequate folic acid (Vitamin B9) की कमी। Pregnancy में 400-800 mcg daily जरूरी है। Periconceptional period (before और early pregnancy) में especially critical। Fortified foods या supplements।
Genetics
Family history होने पर risk बढ़ जाता है। Previous child with NTD होने पर recurrence risk 3-4%। Specific gene variations (MTHFR) associated हैं। Genetic counseling recommended है।
Medications
Anti-seizure drugs: Valproic acid, carbamazepine risk बढ़ाते हैं।
Other meds: Some diabetes medications। Discuss with doctor before pregnancy। Alternative options consider करें।
Maternal Conditions
Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes risk बढ़ाती है।
Obesity: BMI >30 associated है।
Hyperthermia: High fever early pregnancy में। Hot tub, sauna avoid करें।
Maternal Age
Very young mothers (<20 years)। Risk slightly higher है। Teenage pregnancies में nutritional deficiencies common हैं। Proper prenatal care जरूरी है।
Geographic/Ethnic Factors
Hispanic women में slightly higher risk। Ireland, Wales में historically higher rates। Nutritional habits और genetic factors। Folic acid fortification ने rates significantly reduce किए हैं।
The exact cause of NTDs is often unknown. Multiple factors play a role in combination:
Folic Acid Deficiency
Most important preventable risk factor
Lack of adequate folic acid (Vitamin B9). 400-800 mcg daily needed in pregnancy. Especially critical in periconceptional period (before and early pregnancy). Fortified foods or supplements.
Genetics
Risk increases with family history. 3-4% recurrence risk if previous child with NTD. Specific gene variations (MTHFR) are associated. Genetic counseling is recommended.
Medications
Anti-seizure drugs: Valproic acid, carbamazepine increase risk.
Other meds: Some diabetes medications. Discuss with doctor before pregnancy. Consider alternative options.
Maternal Conditions
Diabetes: Poorly controlled diabetes increases risk.
Obesity: BMI >30 is associated.
Hyperthermia: High fever in early pregnancy. Avoid hot tub, sauna.
Maternal Age
Very young mothers (<20 years). Risk is slightly higher. Nutritional deficiencies are common in teenage pregnancies. Proper prenatal care is necessary.
Geographic/Ethnic Factors
Slightly higher risk in Hispanic women. Historically higher rates in Ireland, Wales. Nutritional habits and genetic factors. Folic acid fortification has significantly reduced rates.
Diagnosis कैसे होता है? How is it Diagnosed?
Prenatal Diagnosis (Birth से पहले)
AFP Blood Test
Maternal Serum AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein):
When: 15-20 weeks pregnancy
How: Mother के blood में AFP levels check
Result: High levels indicate possible NTD
Accuracy: Screening test - false positives हो सकते हैं
Next step: Further testing needed
Ultrasound
Detailed anatomy scan:
When: 18-22 weeks pregnancy
Detection: Can visualize spina bifida, anencephaly, encephalocele
Accuracy: 95%+ for anencephaly, 80-90% for spina bifida
3D/4D ultrasound: Better visualization
Limitations: Some cases miss हो सकते हैं
Amniocentesis
Confirmatory test:
When: 15-20 weeks if screening positive
Procedure: Amniotic fluid sample लेते हैं
Test: AFP और AChE (acetylcholinesterase) levels
Accuracy: Very high (>99%)
Risk: Small risk of miscarriage (0.1-0.3%)
Fetal MRI
Advanced imaging:
When: जब ultrasound inconclusive हो
Use: Better brain और spine visualization
Planning: Surgical planning में help
Safe: Radiation नहीं है
Detail: Associated abnormalities detect करता है
Postnatal Diagnosis (Birth के बाद)
Physical examination: Visible defect की presence। Back पर opening या sac देखना।
Imaging tests:
• X-rays: Spine की bony defect visualize
• CT scan: Detailed bone structure
• MRI: Spinal cord, brain involvement assess
• Ultrasound: Infants में brain और spine
Neurological exam: Motor और sensory function assess
Prenatal Diagnosis (Before Birth)
AFP Blood Test
Maternal Serum AFP (Alpha-fetoprotein):
When: 15-20 weeks pregnancy
How: Check AFP levels in mother's blood
Result: High levels indicate possible NTD
Accuracy: Screening test - false positives can occur
Next step: Further testing needed
Ultrasound
Detailed anatomy scan:
When: 18-22 weeks pregnancy
Detection: Can visualize spina bifida, anencephaly, encephalocele
Accuracy: 95%+ for anencephaly, 80-90% for spina bifida
3D/4D ultrasound: Better visualization
Limitations: Some cases may be missed
Amniocentesis
Confirmatory test:
When: 15-20 weeks if screening positive
Procedure: Take amniotic fluid sample
Test: AFP and AChE (acetylcholinesterase) levels
Accuracy: Very high (>99%)
Risk: Small risk of miscarriage (0.1-0.3%)
Fetal MRI
Advanced imaging:
When: When ultrasound is inconclusive
Use: Better visualization of brain and spine
Planning: Helps in surgical planning
Safe: No radiation
Detail: Detects associated abnormalities
Postnatal Diagnosis (After Birth)
Physical examination: Presence of visible defect. Looking at opening or sac on back.
Imaging tests:
• X-rays: Visualize bony defect in spine
• CT scan: Detailed bone structure
• MRI: Assess spinal cord, brain involvement
• Ultrasound: Brain and spine in infants
Neurological exam: Assess motor and sensory function
Treatment Options Treatment Options
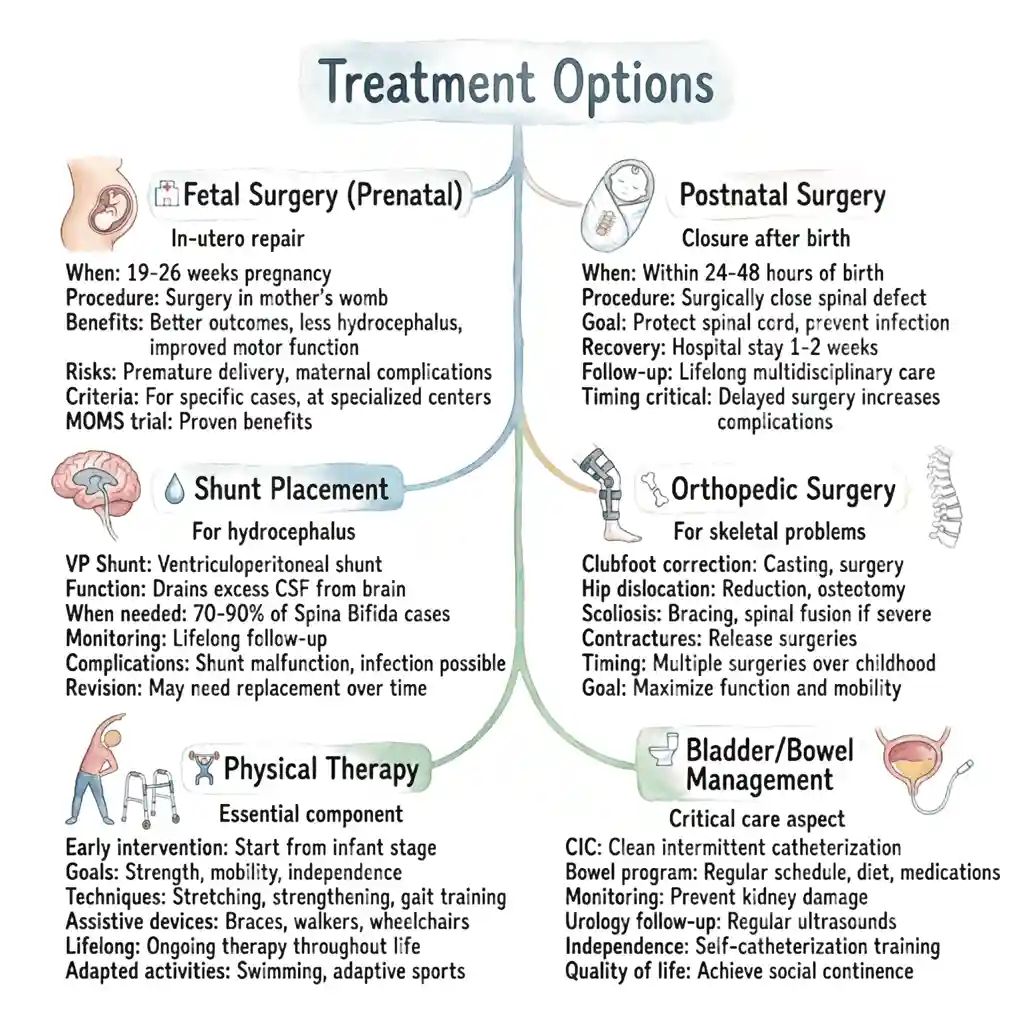
Fetal Surgery (Prenatal)
In-utero repair:
When: 19-26 weeks pregnancy
Procedure: Mother के womb में surgery
Benefits: Better outcomes, less hydrocephalus, improved motor function
Risks: Premature delivery, maternal complications
Criteria: Specific cases के लिए, specialized centers में
MOMS trial: Proven benefits
Postnatal Surgery
Closure after birth:
When: Within 24-48 hours of birth
Procedure: Spinal defect को surgically close करते हैं
Goal: Protect spinal cord, prevent infection
Recovery: Hospital stay 1-2 weeks
Follow-up: Lifelong multidisciplinary care
Timing critical: Delayed surgery complications बढ़ाती है
Shunt Placement
For hydrocephalus:
VP Shunt: Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
Function: Excess CSF को brain से drain करता है
When needed: 70-90% Spina Bifida cases
Monitoring: Lifelong follow-up
Complications: Shunt malfunction, infection possible
Revision: May need replacement over time
Orthopedic Surgery
For skeletal problems:
Clubfoot correction: Casting, surgery
Hip dislocation: Reduction, osteotomy
Scoliosis: Bracing, spinal fusion if severe
Contractures: Release surgeries
Timing: Multiple surgeries over childhood
Goal: Maximize function और mobility
Physical Therapy
Essential component:
Early intervention: Infant से start करें
Goals: Strength, mobility, independence
Techniques: Stretching, strengthening, gait training
Assistive devices: Braces, walkers, wheelchairs
Lifelong: Ongoing therapy throughout life
Adapted activities: Swimming, adaptive sports
Bladder/Bowel Management
Critical care aspect:
CIC: Clean intermittent catheterization
Bowel program: Regular schedule, diet, medications
Monitoring: Prevent kidney damage
Urology follow-up: Regular ultrasounds
Independence: Self-catheterization training
Quality of life: Social continence achieve करना
Fetal Surgery (Prenatal)
In-utero repair:
When: 19-26 weeks pregnancy
Procedure: Surgery in mother's womb
Benefits: Better outcomes, less hydrocephalus, improved motor function
Risks: Premature delivery, maternal complications
Criteria: For specific cases, at specialized centers
MOMS trial: Proven benefits
Postnatal Surgery
Closure after birth:
When: Within 24-48 hours of birth
Procedure: Surgically close spinal defect
Goal: Protect spinal cord, prevent infection
Recovery: Hospital stay 1-2 weeks
Follow-up: Lifelong multidisciplinary care
Timing critical: Delayed surgery increases complications
Shunt Placement
For hydrocephalus:
VP Shunt: Ventriculoperitoneal shunt
Function: Drains excess CSF from brain
When needed: 70-90% of Spina Bifida cases
Monitoring: Lifelong follow-up
Complications: Shunt malfunction, infection possible
Revision: May need replacement over time
Orthopedic Surgery
For skeletal problems:
Clubfoot correction: Casting, surgery
Hip dislocation: Reduction, osteotomy
Scoliosis: Bracing, spinal fusion if severe
Contractures: Release surgeries
Timing: Multiple surgeries over childhood
Goal: Maximize function and mobility
Physical Therapy
Essential component:
Early intervention: Start from infant stage
Goals: Strength, mobility, independence
Techniques: Stretching, strengthening, gait training
Assistive devices: Braces, walkers, wheelchairs
Lifelong: Ongoing therapy throughout life
Adapted activities: Swimming, adaptive sports
Bladder/Bowel Management
Critical care aspect:
CIC: Clean intermittent catheterization
Bowel program: Regular schedule, diet, medications
Monitoring: Prevent kidney damage
Urology follow-up: Regular ultrasounds
Independence: Self-catheterization training
Quality of life: Achieve social continence
Orthopedic Surgery - हड्डी की सर्जरी Orthopedic Surgery
Spina Bifida वाले बच्चों में orthopedic problems बहुत common हैं। लगभग 80-90% patients को किसी न किसी stage पर orthopedic surgery की जरूरत पड़ती है। ये surgeries बच्चे की mobility improve करती हैं, deformities को correct करती हैं, और overall quality of life enhance करती हैं।
Common Orthopedic Problems
Clubfoot (CTEV)
Prevalence: 30-50% Spina Bifida patients में
Types: Rigid, severe clubfoot। Often bilateral (दोनों feet)
Challenge: Muscles के imbalance के कारण। Normal clubfoot से ज्यादा resistant to treatment
Early detection: Birth के time visible
Hip Dislocation/Subluxation
Prevalence: 25-50% patients में
Cause: Muscle weakness और imbalance। Hip abductors weak होते हैं
Types: Unilateral या bilateral। Subluxation से complete dislocation तक
Impact: Walking ability affect करता है
Scoliosis (Spine Curvature)
Prevalence: 50-90% patients में develop होता है
Types: Congenital (birth से), Paralytic (muscle weakness से)
Progression: Age के साथ worsen होता है
Severity: Mild से severe (>90 degrees) तक
Complications: Sitting balance, respiratory function affect
Knee Deformities
Types: Knee flexion contractures। Genu valgum (knock knees)। Genu recurvatum (hyperextension)
Cause: Muscle imbalance। Prolonged sitting
Impact: Difficulty standing, walking
Joint Contractures
Locations: Hips, knees, ankles, elbows
Cause: Lack of movement। Muscle spasticity। Prolonged positioning
Prevention: Daily stretching exercises important
Progressive: Time के साथ worsen होते हैं
Limb Length Discrepancy
Prevalence: Unilateral paralysis में common
Cause: Unequal muscle activity। One leg shorter grow करती है
Impact: Gait abnormality। Spine curvature
Management: Shoe lifts या surgery
Orthopedic Surgical Procedures
Clubfoot Correction
Initial Treatment - Ponseti Method:
Serial casting: Weekly casts for 6-8 weeks। Foot को gradually correct करते हैं।
Tenotomy: Achilles tendon cut (minor procedure)।
Bracing: Foot abduction brace 23 hours/day for 3 months, then nights तक।
Surgical Correction - when casting insufficient:
Age: Usually 6-12 months
Procedures: Soft tissue releases। Tendon transfers। Joint capsule releases।
Goal: Plantigrade foot (flat on ground)। Braceable foot।
Recovery: Casting 2-3 months post-surgery
Challenge: Higher recurrence rate than idiopathic clubfoot। Lifelong bracing often needed।
Hip Surgery
Decision - controversial:
Walking patients: Hip reduction recommended। Better walking ability।
Non-ambulatory: Surgery may not be beneficial। Focus on sitting balance।
Procedures:
Closed Reduction: Non-surgical repositioning (infants)।
Open Reduction: Surgical hip repositioning।
Pelvic Osteotomy: Hip socket को reshape। Better coverage।
Femoral Osteotomy: Thigh bone को reposition।
Muscle Transfers: Weak muscles को strengthen।
Timing: 1-3 years age ideal
Post-op: Spica cast 6-12 weeks। Physical therapy।
Outcomes: Improve walking in ambulators। Better sitting symmetry।
Scoliosis Surgery
Indications - surgery when:
Curve >50 degrees और progressive
Affecting sitting balance - wheelchair users में critical
Respiratory compromise
Pain या skin breakdown
Non-surgical First:
Bracing: Curves 25-45 degrees के लिए। TLSO brace। Growth के time पर।
Wheelchair modifications: Proper support।
Surgical Options:
Posterior Spinal Fusion: Most common। Rods और screws। Curve को stabilize।
Growing Rods: Young children के लिए। Allow continued growth। Periodic lengthening।
VEPTR: Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib। Severe early-onset scoliosis।
Age: Usually 10-14 years (after growth spurt)
Hospital stay: 5-10 days
Recovery: 3-6 months for fusion
Goals: Balanced spine। Better sitting। Prevent progression। Improve respiratory function।
Risks: Infection। Neurological complications। Pseudoarthrosis (non-union)।
Knee Contracture Release
Problem: Fixed knee flexion। Can't straighten leg।
Non-surgical First:
Serial casting: Progressive stretching।
Physical therapy: Aggressive stretching program।
Night splints: Maintain range।
Surgical Procedures:
Hamstring Lengthening: Tight muscles को lengthen।
Posterior Capsulotomy: Joint capsule release।
Supracondylar Extension Osteotomy: Severe cases में। Bone को cut और straighten।
Age: Variable - when contracture significant
Post-op: Serial casting। Bracing। Intensive PT।
Goals: Straight leg for standing। Better brace fit। Improve transfers।
Tendon Transfers
Purpose: Muscle imbalance को correct करना। Stronger muscle की power को weak muscle area में transfer।
Common Transfers:
Posterior Tibialis Transfer: Foot drop correct करने के लिए। Ankle dorsiflexion improve।
Hip Muscle Transfers: Hip stability improve करने के लिए।
Knee Stabilization: Weak quadriceps compensate।
Requirements:
• Donor muscle adequately strong हो
• Patient cooperative for rehab
• Realistic expectations
Outcomes: Variable - depends on muscle strength। Best results in partial paralysis। Requires intensive therapy post-op।
Limb Lengthening
Indication: Significant leg length difference (>2-3 cm)। Affects gait और spine।
Options:
Epiphysiodesis: Growth plate को stop करना। Longer leg की growth arrest। Simpler procedure। Only during growth period।
Limb Lengthening: External fixator (Ilizarov)। Bone को gradually stretch। 1mm per day। Several months में 5-8 cm gain possible। Complex procedure।
Shoe Lift: Non-surgical alternative। <2 cm difference के लिए।
Timing: Epiphysiodesis - remaining growth predict करके। Lengthening - skeletal maturity के पास।
Challenges: Pin site care। Risk of complications। Long treatment duration।
Fracture Management
High Fracture Risk: Osteoporosis common। Lack of weight-bearing। Decreased bone density।
Common Fractures:
Lower extremity: Femur, tibia most common। Often minimal trauma।
Pathological: Weak bones break easily।
Often painless: Lack of sensation। Swelling या deformity से pata चलता है।
Treatment Challenges:
Delayed diagnosis: No pain sensation।
Healing: Slower than normal।
Recurrence: High risk of future fractures।
Treatment: Usually conservative। Casting। Surgery if needed। Weight-bearing encourage (if possible) for bone health।
Prevention Important: Gentle handling। Avoid forceful range of motion। Adequate vitamin D, calcium। Weight-bearing activities जहाँ possible।
Spine Kyphosis Correction
Kyphosis: Forward curvature of spine। Severe gibbus deformity develop हो सकती है।
Problems:
Sitting difficulty: Can't sit upright।
Skin breakdown: Prominent vertebrae पर pressure।
Progressive: Age के साथ worse।
Surgical Correction:
Kyphectomy: Deformed vertebrae remove। Spine straighten।
Spinal Fusion: Stabilize with instrumentation।
Complex surgery: High risk। Significant blood loss। Neurological risks।
Timing: Early childhood often (before severe)।
Benefits: Upright sitting। Better quality of life। Prevent skin problems।
Surgical Planning और Decision Making
किसी भी surgery से पहले important considerations:
1. Ambulatory Status (Walking Ability):
- Community Ambulators: Walk independently या minimal support के साथ। Aggressive surgical treatment worthwhile। Goals: maintain/improve walking।
- Household Ambulators: Walk घर में but wheelchair outside। Moderate surgical approach। Focus on standing transfers।
- Non-Ambulatory: Wheelchair dependent। Surgery goals different - sitting balance, prevent pain, skin care।
2. Neurological Level:
- Thoracic level: No leg function। Surgery mainly for sitting।
- High Lumbar (L1-L2): Hip flexion only। Limited walking potential। Wheelchair primary।
- Mid Lumbar (L3-L4): Some quadriceps। Walking possible with braces। Moderate surgical intervention।
- Low Lumbar (L5): Good walking potential। Aggressive treatment justified।
- Sacral: Near-normal walking। Treat like regular orthopedic problems।
3. Family Situation और Resources:
- Post-operative care ability। Casting, bracing compliance। Physical therapy access। Transportation for follow-ups। Emotional support system।
4. Patient Age और Growth:
- Infants: Early clubfoot treatment। Hip surveillance।
- Toddlers: Optimize standing/walking।
- School Age: Maintain function। Address progressive deformities।
- Adolescents: Scoliosis surgery timing। Final corrections before skeletal maturity।
5. Realistic Goals:
- Surgery can improve function but may not achieve "normal"। Multiple surgeries often needed। Maintenance care lifelong। Some complications unavoidable। Quality of life focus important।
Post-Operative Care और Rehabilitation
Special Considerations - बहुत महत्वपूर्ण!
Lack of sensation: Pain नहीं होता wounds में। Parents को vigilant रहना पड़ता है। Skin checks daily। Cast problems detect करना कठिन।
Pressure sores risk: Casting के दौरान। Splints, braces में। Insensate skin vulnerable। Frequent monitoring essential।
Latex allergy: 60-70% risk। Latex-free environment critical। All equipment, gloves। Medical team को inform करें।
Hydrocephalus/Shunt: Positioning restrictions। Shunt malfunction watch। Infection risk।
Bladder/Bowel: Continue catheterization schedule। Constipation management। UTI prevention।
Immediate Post-Op (0-2 weeks)
Hospital stay। Pain management (special challenges - may not feel typical pain)। Wound care। Early mobilization जहाँ appropriate। Neurovascular checks। Cast care। Skin monitoring।
Recovery Phase (2-12 weeks)
Home care with precautions। Serial casting कई surgeries में। Cast changes scheduled। Skin inspection at each change। Gradual weight-bearing। Early physical therapy। Monitor for complications।
Rehabilitation (3-6 months)
Intensive physical therapy। Strengthen surgical area। Improve range of motion। Gait training। Brace fitting और training। Return to activities gradually। School accommodations।
Long-term (6+ months)
Continued bracing often lifelong। Regular follow-ups (3-6 months)। Monitor for recurrence। Brace adjustments as child grows। Maintain gains through exercises। Watch for new problems।
Outcomes और Expectations
Realistic Expectations Important हैं
Success Rates - Overall Good:
• Clubfoot correction: 70-80% achieve plantigrade foot। Higher recurrence than idiopathic।
• Hip surgery: Variable based on level। Better in ambulatory patients।
• Scoliosis: 80-90% good correction। Sitting balance improved।
• Knee contractures: Good correction possible। Recurrence common without bracing।
Challenges:
• Multiple surgeries often needed over childhood
• Recurrence rates higher than normal children
• Lifelong bracing frequently required
• Some deformities progressive despite surgery
• Complications more common (poor sensation, healing)
Positive Outcomes:
• Many children walk with braces
• Improved sitting balance and positioning
• Better quality of life
• Reduced pain and skin problems
• Greater independence in daily activities
• Successful school participation
Key to Success:
Multidisciplinary team approach। Early और consistent intervention। Family commitment crucial। Regular follow-up। Realistic goal-setting। Focus on functional outcomes।
Orthopedic problems are very common in children with Spina Bifida. Approximately 80-90% of patients need orthopedic surgery at some stage. These surgeries improve child's mobility, correct deformities, and enhance overall quality of life.
Common Orthopedic Problems
Clubfoot (CTEV)
Prevalence: In 30-50% of Spina Bifida patients
Types: Rigid, severe clubfoot. Often bilateral (both feet)
Challenge: Due to muscle imbalance. More resistant to treatment than normal clubfoot
Early detection: Visible at birth
Hip Dislocation/Subluxation
Prevalence: In 25-50% of patients
Cause: Muscle weakness and imbalance. Hip abductors are weak
Types: Unilateral or bilateral. From subluxation to complete dislocation
Impact: Affects walking ability
Scoliosis (Spine Curvature)
Prevalence: Develops in 50-90% of patients
Types: Congenital (from birth), Paralytic (from muscle weakness)
Progression: Worsens with age
Severity: From mild to severe (>90 degrees)
Complications: Affects sitting balance, respiratory function
Knee Deformities
Types: Knee flexion contractures. Genu valgum (knock knees). Genu recurvatum (hyperextension)
Cause: Muscle imbalance. Prolonged sitting
Impact: Difficulty standing, walking
Joint Contractures
Locations: Hips, knees, ankles, elbows
Cause: Lack of movement. Muscle spasticity. Prolonged positioning
Prevention: Daily stretching exercises important
Progressive: Worsen over time
Limb Length Discrepancy
Prevalence: Common in unilateral paralysis
Cause: Unequal muscle activity. One leg grows shorter
Impact: Gait abnormality. Spine curvature
Management: Shoe lifts or surgery
Orthopedic Surgical Procedures
Clubfoot Correction
Initial Treatment - Ponseti Method:
Serial casting: Weekly casts for 6-8 weeks. Gradually correct foot.
Tenotomy: Cut Achilles tendon (minor procedure).
Bracing: Foot abduction brace 23 hours/day for 3 months, then nights only.
Surgical Correction - when casting insufficient:
Age: Usually 6-12 months
Procedures: Soft tissue releases. Tendon transfers. Joint capsule releases.
Goal: Plantigrade foot (flat on ground). Braceable foot.
Recovery: Casting 2-3 months post-surgery
Challenge: Higher recurrence rate than idiopathic clubfoot. Lifelong bracing often needed.
Hip Surgery
Decision - controversial:
Walking patients: Hip reduction recommended. Better walking ability.
Non-ambulatory: Surgery may not be beneficial. Focus on sitting balance.
Procedures:
Closed Reduction: Non-surgical repositioning (infants).
Open Reduction: Surgical hip repositioning.
Pelvic Osteotomy: Reshape hip socket. Better coverage.
Femoral Osteotomy: Reposition thigh bone.
Muscle Transfers: Strengthen weak muscles.
Timing: 1-3 years age ideal
Post-op: Spica cast 6-12 weeks. Physical therapy.
Outcomes: Improve walking in ambulators. Better sitting symmetry.
Scoliosis Surgery
Indications - surgery when:
Curve >50 degrees and progressive
Affecting sitting balance - critical in wheelchair users
Respiratory compromise
Pain or skin breakdown
Non-surgical First:
Bracing: For curves 25-45 degrees. TLSO brace. During growth period.
Wheelchair modifications: Proper support.
Surgical Options:
Posterior Spinal Fusion: Most common. Rods and screws. Stabilize curve.
Growing Rods: For young children. Allow continued growth. Periodic lengthening.
VEPTR: Vertical Expandable Prosthetic Titanium Rib. Severe early-onset scoliosis.
Age: Usually 10-14 years (after growth spurt)
Hospital stay: 5-10 days
Recovery: 3-6 months for fusion
Goals: Balanced spine. Better sitting. Prevent progression. Improve respiratory function.
Risks: Infection. Neurological complications. Pseudoarthrosis (non-union).
Knee Contracture Release
Problem: Fixed knee flexion. Can't straighten leg.
Non-surgical First:
Serial casting: Progressive stretching.
Physical therapy: Aggressive stretching program.
Night splints: Maintain range.
Surgical Procedures:
Hamstring Lengthening: Lengthen tight muscles.
Posterior Capsulotomy: Joint capsule release.
Supracondylar Extension Osteotomy: In severe cases. Cut and straighten bone.
Age: Variable - when contracture significant
Post-op: Serial casting. Bracing. Intensive PT.
Goals: Straight leg for standing. Better brace fit. Improve transfers.
Tendon Transfers
Purpose: Correct muscle imbalance. Transfer power of stronger muscle to weak muscle area.
Common Transfers:
Posterior Tibialis Transfer: To correct foot drop. Improve ankle dorsiflexion.
Hip Muscle Transfers: To improve hip stability.
Knee Stabilization: Compensate weak quadriceps.
Requirements:
• Donor muscle adequately strong
• Patient cooperative for rehab
• Realistic expectations
Outcomes: Variable - depends on muscle strength. Best results in partial paralysis. Requires intensive therapy post-op.
Limb Lengthening
Indication: Significant leg length difference (>2-3 cm). Affects gait and spine.
Options:
Epiphysiodesis: Stop growth plate. Arrest growth of longer leg. Simpler procedure. Only during growth period.
Limb Lengthening: External fixator (Ilizarov). Gradually stretch bone. 1mm per day. 5-8 cm gain possible in several months. Complex procedure.
Shoe Lift: Non-surgical alternative. For <2 cm difference.
Timing: Epiphysiodesis - predict remaining growth. Lengthening - near skeletal maturity.
Challenges: Pin site care. Risk of complications. Long treatment duration.
Fracture Management
High Fracture Risk: Osteoporosis common. Lack of weight-bearing. Decreased bone density.
Common Fractures:
Lower extremity: Femur, tibia most common. Often minimal trauma.
Pathological: Weak bones break easily.
Often painless: Lack of sensation. Detected by swelling or deformity.
Treatment Challenges:
Delayed diagnosis: No pain sensation.
Healing: Slower than normal.
Recurrence: High risk of future fractures.
Treatment: Usually conservative. Casting. Surgery if needed. Encourage weight-bearing (if possible) for bone health.
Prevention Important: Gentle handling. Avoid forceful range of motion. Adequate vitamin D, calcium. Weight-bearing activities where possible.
Spine Kyphosis Correction
Kyphosis: Forward curvature of spine. Severe gibbus deformity can develop.
Problems:
Sitting difficulty: Can't sit upright.
Skin breakdown: Pressure on prominent vertebrae.
Progressive: Gets worse with age.
Surgical Correction:
Kyphectomy: Remove deformed vertebrae. Straighten spine.
Spinal Fusion: Stabilize with instrumentation.
Complex surgery: High risk. Significant blood loss. Neurological risks.
Timing: Often early childhood (before severe).
Benefits: Upright sitting. Better quality of life. Prevent skin problems.
Surgical Planning and Decision Making
Important considerations before any surgery:
1. Ambulatory Status (Walking Ability):
- Community Ambulators: Walk independently or with minimal support. Aggressive surgical treatment worthwhile. Goals: maintain/improve walking.
- Household Ambulators: Walk at home but wheelchair outside. Moderate surgical approach. Focus on standing transfers.
- Non-Ambulatory: Wheelchair dependent. Different surgery goals - sitting balance, prevent pain, skin care.
2. Neurological Level:
- Thoracic level: No leg function. Surgery mainly for sitting.
- High Lumbar (L1-L2): Hip flexion only. Limited walking potential. Wheelchair primary.
- Mid Lumbar (L3-L4): Some quadriceps. Walking possible with braces. Moderate surgical intervention.
- Low Lumbar (L5): Good walking potential. Aggressive treatment justified.
- Sacral: Near-normal walking. Treat like regular orthopedic problems.
3. Family Situation and Resources:
- Post-operative care ability. Casting, bracing compliance. Physical therapy access. Transportation for follow-ups. Emotional support system.
4. Patient Age and Growth:
- Infants: Early clubfoot treatment. Hip surveillance.
- Toddlers: Optimize standing/walking.
- School Age: Maintain function. Address progressive deformities.
- Adolescents: Scoliosis surgery timing. Final corrections before skeletal maturity.
5. Realistic Goals:
- Surgery can improve function but may not achieve "normal". Multiple surgeries often needed. Maintenance care lifelong. Some complications unavoidable. Quality of life focus important.
Post-Operative Care and Rehabilitation
Special Considerations - Very Important!
Lack of sensation: No pain in wounds. Parents must be vigilant. Daily skin checks. Cast problems hard to detect.
Pressure sores risk: During casting. In splints, braces. Insensate skin vulnerable. Frequent monitoring essential.
Latex allergy: 60-70% risk. Latex-free environment critical. All equipment, gloves. Inform medical team.
Hydrocephalus/Shunt: Positioning restrictions. Watch for shunt malfunction. Infection risk.
Bladder/Bowel: Continue catheterization schedule. Constipation management. UTI prevention.
Immediate Post-Op (0-2 weeks)
Hospital stay. Pain management (special challenges - may not feel typical pain). Wound care. Early mobilization where appropriate. Neurovascular checks. Cast care. Skin monitoring.
Recovery Phase (2-12 weeks)
Home care with precautions. Serial casting in many surgeries. Scheduled cast changes. Skin inspection at each change. Gradual weight-bearing. Early physical therapy. Monitor for complications.
Rehabilitation (3-6 months)
Intensive physical therapy. Strengthen surgical area. Improve range of motion. Gait training. Brace fitting and training. Gradual return to activities. School accommodations.
Long-term (6+ months)
Continued bracing often lifelong. Regular follow-ups (3-6 months). Monitor for recurrence. Brace adjustments as child grows. Maintain gains through exercises. Watch for new problems.
Outcomes and Expectations
Realistic Expectations are Important
Success Rates - Overall Good:
• Clubfoot correction: 70-80% achieve plantigrade foot. Higher recurrence than idiopathic.
• Hip surgery: Variable based on level. Better in ambulatory patients.
• Scoliosis: 80-90% good correction. Sitting balance improved.
• Knee contractures: Good correction possible. Recurrence common without bracing.
Challenges:
• Multiple surgeries often needed over childhood
• Recurrence rates higher than normal children
• Lifelong bracing frequently required
• Some deformities progressive despite surgery
• Complications more common (poor sensation, healing)
Positive Outcomes:
• Many children walk with braces
• Improved sitting balance and positioning
• Better quality of life
• Reduced pain and skin problems
• Greater independence in daily activities
• Successful school participation
Key to Success:
Multidisciplinary team approach. Early and consistent intervention. Family commitment crucial. Regular follow-up. Realistic goal-setting. Focus on functional outcomes.
Prevention - कैसे बचें? Prevention - How to Prevent?
Folic Acid - सबसे महत्वपूर्ण!
400 mcg (0.4 mg) daily - सभी reproductive age की women को
जब start करें: Pregnancy plan करने से पहले (at least 1 month before conception)
कब तक: Pregnancy के first 12 weeks तक continue
High-risk women: 4000 mcg (4 mg) daily - previous NTD child होने पर, anti-seizure medications लेने पर
Sources: Prenatal vitamins, folic acid supplements, fortified foods
Folate-Rich Foods
Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale)। Legumes (dal, beans, lentils)। Fortified cereals और bread। Citrus fruits। Avocado। Supplements के साथ diet भी important है।
Medication Review
Pregnancy plan करने पर doctor से all medications discuss करें। Anti-seizure drugs adjust करने की जरूरत हो सकती है। Valproic acid alternatives consider करें। Never stop medications without doctor advice।
Preconception Care
Diabetes को well-controlled रखें। Obesity को manage करें। Healthy lifestyle maintain करें। Regular check-ups। Planning pregnancy important है - unplanned pregnancies में risk ज्यादा।
Avoid Hyperthermia
Early pregnancy में high fever treat करें promptly। Hot tubs, saunas avoid करें। Fever होने पर doctor से consult करें। Temperature control important है।
Genetic Counseling
Previous child with NTD। Family history of NTD। High-risk categories। Testing options discuss करें। Recurrence prevention strategies। Informed decision making।
Early Prenatal Care
Pregnancy confirm होने पर immediately doctor से मिलें। Regular prenatal visits। Proper screening। Early detection important है। Specialized care if needed।
Folic Acid - Most Important!
400 mcg (0.4 mg) daily - for all reproductive age women
When to start: Before planning pregnancy (at least 1 month before conception)
How long: Continue through first 12 weeks of pregnancy
High-risk women: 4000 mcg (4 mg) daily - if previous NTD child, taking anti-seizure medications
Sources: Prenatal vitamins, folic acid supplements, fortified foods
Folate-Rich Foods
Dark leafy greens (spinach, kale). Legumes (dal, beans, lentils). Fortified cereals and bread. Citrus fruits. Avocado. Diet is important along with supplements.
Medication Review
Discuss all medications with doctor when planning pregnancy. Anti-seizure drugs may need adjustment. Consider alternatives to valproic acid. Never stop medications without doctor advice.
Preconception Care
Keep diabetes well-controlled. Manage obesity. Maintain healthy lifestyle. Regular check-ups. Planning pregnancy is important - risk is higher in unplanned pregnancies.
Avoid Hyperthermia
Treat high fever promptly in early pregnancy. Avoid hot tubs, saunas. Consult doctor if fever occurs. Temperature control is important.
Genetic Counseling
Previous child with NTD. Family history of NTD. High-risk categories. Discuss testing options. Recurrence prevention strategies. Informed decision making.
Early Prenatal Care
Meet doctor immediately when pregnancy is confirmed. Regular prenatal visits. Proper screening. Early detection is important. Specialized care if needed.
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले सवाल (FAQ) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
नहीं, लेकिन significant reduction होता है। Prevention rate: Adequate folic acid से लगभग 70% NTDs prevent हो सकते हैं। यह dramatic reduction है but 100% guarantee नहीं है। क्यों नहीं 100%: कुछ NTDs non-folate-responsive हैं। Genetic factors भी role play करते हैं। Other unknown factors contribute कर सकते हैं। लेकिन बहुत effective: Countries जिन्होंने folic acid fortification शुरू की, उनमें NTD rates में 50-70% decrease देखा गया है। USA, Canada में flour fortification के बाद cases significantly कम हुए। Dosage important है: Regular 400 mcg daily minimum है। Higher doses (4 mg) high-risk women के लिए। Consistency जरूरी है - miss न करें। Timing critical: Neural tube 28 days में form होती है। अक्सर women को पता ही नहीं होता कि pregnant हैं। इसलिए preconception से start करना जरूरी है। सभी reproductive age women को लेनी चाहिए: Half pregnancies unplanned होती हैं। इसलिए सभी को daily folic acid लेना चाहिए।
No, but significant reduction occurs. Prevention rate: About 70% of NTDs can be prevented with adequate folic acid. This is dramatic reduction but not 100% guarantee. Why not 100%: Some NTDs are non-folate-responsive. Genetic factors also play a role. Other unknown factors may contribute. But very effective: Countries that started folic acid fortification saw 50-70% decrease in NTD rates. Cases significantly reduced in USA, Canada after flour fortification. Dosage is important: Regular 400 mcg daily is minimum. Higher doses (4 mg) for high-risk women. Consistency is necessary - don't miss. Timing is critical: Neural tube forms in 28 days. Often women don't even know they're pregnant. Therefore starting from preconception is necessary. All reproductive age women should take it: Half of pregnancies are unplanned. Therefore everyone should take daily folic acid.
Recurrence risk बढ़ जाता है लेकिन still manageable है। Recurrence rate: General population में NTD risk: 1-2 per 1000 (0.1-0.2%)। Previous child with NTD: 3-4% (30-40 per 1000)। दूसरा affected child होने पर: 10% तक बढ़ सकता है। Prevention strategies - बहुत effective: High-dose folic acid: 4000 mcg (4 mg) daily। Conception से 3 months पहले start करें। First trimester throughout continue। Timing crucial: 1 month before trying to conceive। Reduction: High-dose folic acid से recurrence risk को 70% तक reduce किया जा सकता है। Enhanced screening: Early और detailed ultrasounds। AFP testing। Amniocentesis if needed। Level 2 ultrasound specialists। Genetic counseling essential: Family planning discussion। Testing options review। Risk assessment। Prenatal diagnosis options। Prenatal diagnosis: Earlier detection possible। Fetal MRI for detailed evaluation। Management planning। Positive outlook: 96-97% chance next child NTD-free होगी (proper folic acid के साथ)। Most families successful second pregnancy have करती हैं।
Recurrence risk increases but is still manageable. Recurrence rate: NTD risk in general population: 1-2 per 1000 (0.1-0.2%). Previous child with NTD: 3-4% (30-40 per 1000). If second affected child: May increase up to 10%. Prevention strategies - very effective: High-dose folic acid: 4000 mcg (4 mg) daily. Start 3 months before conception. Continue throughout first trimester. Timing crucial: 1 month before trying to conceive. Reduction: Recurrence risk can be reduced by up to 70% with high-dose folic acid. Enhanced screening: Early and detailed ultrasounds. AFP testing. Amniocentesis if needed. Level 2 ultrasound specialists. Genetic counseling is essential: Family planning discussion. Review testing options. Risk assessment. Prenatal diagnosis options. Prenatal diagnosis: Earlier detection possible. Fetal MRI for detailed evaluation. Management planning. Positive outlook: 96-97% chance next child will be NTD-free (with proper folic acid). Most families have successful second pregnancy.
हां, कुछ cases miss हो सकते हैं। Detection rates - generally high: Anencephaly: >95% detected। Almost never missed - very obvious। Open Spina Bifida: 80-90% detected। Good ultrasound quality और experienced operator के साथ। Closed Spina Bifida (Occulta): Detection difficult। Often not visible on ultrasound। Factors affecting detection: Operator experience: Skilled sonographer important है। Level 2 ultrasounds more detailed। Timing: 18-22 weeks optimal है। Too early = difficult to see। Maternal factors: Obesity makes imaging difficult। Fetal position। Amniotic fluid amount। Type of defect: Small defects miss हो सकते हैं। Lower spine defects visualize करना कठिन। What increases detection: Specialized fetal medicine centers। 3D/4D ultrasound। Multiple views। Fetal MRI if suspicious। Additional screening: AFP blood test combination। Amniocentesis for high-risk। Not perfect but good: Majority detected हो जाते हैं। Multiple screening methods combination बेहतर है। If concerned: Request detailed anatomy scan। Consider fetal medicine specialist। Second opinion।
Yes, some cases can be missed. Detection rates - generally high: Anencephaly: >95% detected. Almost never missed - very obvious. Open Spina Bifida: 80-90% detected. With good ultrasound quality and experienced operator. Closed Spina Bifida (Occulta): Detection difficult. Often not visible on ultrasound. Factors affecting detection: Operator experience: Skilled sonographer is important. Level 2 ultrasounds are more detailed. Timing: 18-22 weeks is optimal. Too early = difficult to see. Maternal factors: Obesity makes imaging difficult. Fetal position. Amount of amniotic fluid. Type of defect: Small defects can be missed. Lower spine defects are harder to visualize. What increases detection: Specialized fetal medicine centers. 3D/4D ultrasound. Multiple views. Fetal MRI if suspicious. Additional screening: AFP blood test combination. Amniocentesis for high-risk. Not perfect but good: Majority are detected. Combination of multiple screening methods is better. If concerned: Request detailed anatomy scan. Consider fetal medicine specialist. Second opinion.
नहीं, strict criteria होती है। Eligibility criteria - specific cases only: Gestational age: 19-26 weeks pregnancy। Too early या too late नहीं कर सकते। Type of defect: Myelomeningocele (open spina bifida)। Specific spinal level (T1-S1)। Associated conditions: Severe fetal abnormalities नहीं होनी चाहिए। Kyphosis नहीं। Chromosomal abnormalities ruled out। Maternal health: Mother medically fit हो। BMI requirements। No placental issues (placenta previa)। Benefits - proven by MOMS trial: Reduced need for shunt (40% vs 82%)। Better motor function। Improved walking ability। Less hindbrain herniation। Risks - significant: Maternal: Hysterotomy scar। Increased risk of complications in future pregnancies। Risk of pulmonary edema। Fetal: Premature delivery (most babies born before 37 weeks)। Oligohydramnios। Placental abruption। Availability - limited: Only specialized fetal surgery centers। Requires multidisciplinary team। Expensive procedure। Not available everywhere in India। Alternative - postnatal repair: Still excellent option। Standard of care। Safer for mother। Good outcomes with proper care।
No, there are strict criteria. Eligibility criteria - specific cases only: Gestational age: 19-26 weeks pregnancy. Can't do too early or too late. Type of defect: Myelomeningocele (open spina bifida). Specific spinal level (T1-S1). Associated conditions: Should not have severe fetal abnormalities. No kyphosis. Chromosomal abnormalities ruled out. Maternal health: Mother should be medically fit. BMI requirements. No placental issues (placenta previa). Benefits - proven by MOMS trial: Reduced need for shunt (40% vs 82%). Better motor function. Improved walking ability. Less hindbrain herniation. Risks - significant: Maternal: Hysterotomy scar. Increased risk of complications in future pregnancies. Risk of pulmonary edema. Fetal: Premature delivery (most babies born before 37 weeks). Oligohydramnios. Placental abruption. Availability - limited: Only specialized fetal surgery centers. Requires multidisciplinary team. Expensive procedure. Not available everywhere in India. Alternative - postnatal repair: Still excellent option. Standard of care. Safer for mother. Good outcomes with proper care.
यह depend करता है severity पर, लेकिन बहुत कुछ possible है। Severity spectrum - varies widely: Spina Bifida Occulta: Often asymptomatic। Completely normal life। No treatment needed usually। Meningocele: Good prognosis with surgery। Minimal neurological issues। Near-normal function। Myelomeningocele: More challenging but manageable। Wide range of outcomes। What's possible - encouraging: Education: Regular school attendance (with accommodations)। Many graduate college। Successful careers। Mobility: Some walk independently। Some use braces/crutches। Wheelchairs for others। Technology improving constantly। Independence: Self-catheterization। Bowel management। Daily living skills। Many live independently as adults। Social life: Friendships, relationships। Marriage possible। Some have children (with genetic counseling)। Adaptive sports participation। Achievements: Many with Spina Bifida lead inspirational lives। Athletes, professionals, advocates। Contributing members of society। Challenges - real but manageable: Multiple surgeries possible। Bladder/bowel management lifelong। Mobility limitations। Medical appointments frequent। Key success factors: Early और consistent intervention। Multidisciplinary care। Family support crucial। Positive attitude। Access to resources। Technology और assistive devices।
This depends on severity, but much is possible. Severity spectrum - varies widely: Spina Bifida Occulta: Often asymptomatic. Completely normal life. Usually no treatment needed. Meningocele: Good prognosis with surgery. Minimal neurological issues. Near-normal function. Myelomeningocele: More challenging but manageable. Wide range of outcomes. What's possible - encouraging: Education: Regular school attendance (with accommodations). Many graduate college. Successful careers. Mobility: Some walk independently. Some use braces/crutches. Wheelchairs for others. Technology constantly improving. Independence: Self-catheterization. Bowel management. Daily living skills. Many live independently as adults. Social life: Friendships, relationships. Marriage possible. Some have children (with genetic counseling). Adaptive sports participation. Achievements: Many with Spina Bifida lead inspirational lives. Athletes, professionals, advocates. Contributing members of society. Challenges - real but manageable: Multiple surgeries possible. Lifelong bladder/bowel management. Mobility limitations. Frequent medical appointments. Key success factors: Early and consistent intervention. Multidisciplinary care. Family support crucial. Positive attitude. Access to resources. Technology and assistive devices.
Variable है, लेकिन revisions common हैं। Shunt lifespan - unpredictable: कोई fixed duration नहीं है। Some work for years without problems। Others may need revision within months। Average: Every 5-7 years। लेकिन highly variable। Why revision needed: Malfunction/Blockage: Most common reason (40-50% of revisions)। Catheter blocked हो सकता है। Debris, tissue overgrowth। Infection: 5-15% risk especially in first months। Requires shunt removal और replacement। Growth: Child grows, catheter length insufficient हो जाता है। Needs lengthening। Overdrainage/Underdrainage: Pressure settings adjust करने की जरूरत। Frequency - varies by age: First year: Highest revision rate। 40% need revision। Childhood: Multiple revisions possible। Due to growth। Adults: Less frequent but still possible। Warning signs - parents को पता होना चाहिए: Headaches। Vomiting। Irritability। Lethargy। Seizures। Swelling along shunt tract। Fever (infection)। Changes in school performance। Lifetime management: Regular neurosurgery follow-ups। Be aware of symptoms। Quick medical attention if concerned। Not all need multiple revisions: Some children lucky होते हैं। Years तक problem-free। Quality of life: Modern shunts reliable हैं। Programmable valves allow non-surgical adjustments। Most children शунत के साथ normal activities कर सकते हैं।
Variable, but revisions are common. Shunt lifespan - unpredictable: No fixed duration. Some work for years without problems. Others may need revision within months. Average: Every 5-7 years. But highly variable. Why revision needed: Malfunction/Blockage: Most common reason (40-50% of revisions). Catheter may get blocked. Debris, tissue overgrowth. Infection: 5-15% risk especially in first months. Requires shunt removal and replacement. Growth: Child grows, catheter length becomes insufficient. Needs lengthening. Overdrainage/Underdrainage: Need to adjust pressure settings. Frequency - varies by age: First year: Highest revision rate. 40% need revision. Childhood: Multiple revisions possible. Due to growth. Adults: Less frequent but still possible. Warning signs - parents should know: Headaches. Vomiting. Irritability. Lethargy. Seizures. Swelling along shunt tract. Fever (infection). Changes in school performance. Lifetime management: Regular neurosurgery follow-ups. Be aware of symptoms. Quick medical attention if concerned. Not all need multiple revisions: Some children are lucky. Problem-free for years. Quality of life: Modern shunts are reliable. Programmable valves allow non-surgical adjustments. Most children can do normal activities with shunt.
Immediately start करें - still beneficial है। Don't panic: Most babies healthy ही होते हैं। NTD risk without folic acid भी relatively low है (0.1-0.2%)। Start immediately: आज से ही prenatal vitamin लेना शुरू करें। Doctor को बताएं। Standard dose 400-800 mcg। Still helps - even after conception: Neural tube 28 days में close होती है। अगर बहुत early pregnancy है, तो still prevention possible है। Late भी folic acid beneficial है - अन्य development के लिए। Enhanced screening: AFP blood test: 15-20 weeks पर। High-risk के लिए। Detailed ultrasound: 18-22 weeks anatomy scan। Level 2 ultrasound consider करें। Amniocentesis: If screening tests abnormal। Fetal MRI: For detailed evaluation if needed। Other prenatal care important: Regular check-ups। Healthy diet - folate-rich foods। Avoid risk factors। Control diabetes if present। Avoid hyperthermia। Future pregnancies: Start folic acid 3 months before next pregnancy। Learn from this। Plan ahead। Most likely outcome: Baby completely healthy होगा। Risk बहुत low है। Proper screening से early detection possible। Stay positive: Stress baby के लिए अच्छा नहीं। Follow prenatal care। Trust screening process।
Start immediately - still beneficial. Don't panic: Most babies are healthy. NTD risk without folic acid is also relatively low (0.1-0.2%). Start immediately: Start taking prenatal vitamin from today. Tell doctor. Standard dose 400-800 mcg. Still helps - even after conception: Neural tube closes in 28 days. If very early pregnancy, prevention still possible. Even late, folic acid is beneficial - for other development. Enhanced screening: AFP blood test: At 15-20 weeks. For high-risk. Detailed ultrasound: 18-22 weeks anatomy scan. Consider level 2 ultrasound. Amniocentesis: If screening tests abnormal. Fetal MRI: For detailed evaluation if needed. Other prenatal care important: Regular check-ups. Healthy diet - folate-rich foods. Avoid risk factors. Control diabetes if present. Avoid hyperthermia. Future pregnancies: Start folic acid 3 months before next pregnancy. Learn from this. Plan ahead. Most likely outcome: Baby will be completely healthy. Risk is very low. Early detection possible with proper screening. Stay positive: Stress not good for baby. Follow prenatal care. Trust screening process.
Multiple challenges हैं but support available है। Medical care - intensive: Frequent appointments: Multiple specialists - neurosurgeon, urologist, orthopedist, physiatrist। Regular follow-ups। Multiple medical visits per month possible। Surgeries: Multiple surgeries over childhood। Shunt revisions। Orthopedic procedures। Hospital stays। Daily care - demanding: Catheterization: Every 3-4 hours daily। Clean technique maintain करना। Supplies management। Bowel program: Regular schedule। Diet management। Medications। Wound care: Skin breakdown prevention। Pressure sores risk। Mobility assistance: Transfers। Equipment maintenance। Financial burden - significant: Medical expenses high हो सकते हैं। Equipment costs (wheelchair, braces)। Home modifications। Therapy costs। Absorbent products। Transportation। Emotional challenges: Stress, anxiety। Grief process। Worry about child's future। Sibling jealousy possible। Marriage strain। Time demands: 24/7 care initially। Balancing other responsibilities। Work adjustments needed। Social impact: Social isolation। Activities limited। Explaining to others। Dealing with stares। BUT - support available: Resources: Support groups। Spina Bifida associations। Online communities। Services: Early intervention programs। Special education। Respite care। Financial: Insurance coverage। Government programs। Non-profit assistance। Positive aspects - often overlooked: Family bonds strengthen। Resilience develops। Appreciation for small victories। Community support। Children are inspirational। Coping strategies: Connect with other families। Take breaks (respite)। Celebrate milestones। Focus on abilities। Seek counseling if needed।
Multiple challenges but support is available. Medical care - intensive: Frequent appointments: Multiple specialists - neurosurgeon, urologist, orthopedist, physiatrist. Regular follow-ups. Multiple medical visits per month possible. Surgeries: Multiple surgeries over childhood. Shunt revisions. Orthopedic procedures. Hospital stays. Daily care - demanding: Catheterization: Every 3-4 hours daily. Maintain clean technique. Supplies management. Bowel program: Regular schedule. Diet management. Medications. Wound care: Prevent skin breakdown. Risk of pressure sores. Mobility assistance: Transfers. Equipment maintenance. Financial burden - significant: Medical expenses can be high. Equipment costs (wheelchair, braces). Home modifications. Therapy costs. Absorbent products. Transportation. Emotional challenges: Stress, anxiety. Grief process. Worry about child's future. Possible sibling jealousy. Marriage strain. Time demands: 24/7 care initially. Balancing other responsibilities. Work adjustments needed. Social impact: Social isolation. Limited activities. Explaining to others. Dealing with stares. BUT - support available: Resources: Support groups. Spina Bifida associations. Online communities. Services: Early intervention programs. Special education. Respite care. Financial: Insurance coverage. Government programs. Non-profit assistance. Positive aspects - often overlooked: Family bonds strengthen. Resilience develops. Appreciation for small victories. Community support. Children are inspirational. Coping strategies: Connect with other families. Take breaks (respite). Celebrate milestones. Focus on abilities. Seek counseling if needed.
यह बहुत difficult decision है। Options available हैं। First step - confirm diagnosis: Detailed level 2 ultrasound। Fetal MRI for complete assessment। Amniocentesis for confirmation। Genetic testing। Rule out other abnormalities। Options - counseling important: 1. Continue pregnancy: Spina Bifida: Many families choose to continue। Early planning for care। Consider fetal surgery if eligible (19-26 weeks)। Prepare for postnatal care। Connect with support groups। Plan delivery at specialized center। Anencephaly: Some continue for organ donation। Palliative care planning। Emotional preparation। 2. Termination: Legal considerations vary। Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP)। Gestational age limits। Decision factors - very personal: Severity of defect। Associated abnormalities। Family circumstances। Religious/cultural beliefs। Support system। Financial considerations। Emotional readiness। Counseling essential: Genetic counselor: Explain condition thoroughly। Discuss recurrence risks। Maternal-fetal medicine: Medical aspects। Neonatologist: Prognosis discussion। Neurosurgeon: Treatment options। Social worker: Resources, support। No "right" choice: Both decisions valid हैं। Personal choice। No judgment। Support available: Whatever decision, support important है। Grief counseling। Support groups। Perinatal hospice (if continuing with anencephaly)। Time to decide: Don't rush। Get all information। Second opinions okay। Discuss with family। For future: High-dose folic acid। Genetic counseling। Enhanced screening next time।
This is a very difficult decision. Options are available. First step - confirm diagnosis: Detailed level 2 ultrasound. Fetal MRI for complete assessment. Amniocentesis for confirmation. Genetic testing. Rule out other abnormalities. Options - counseling important: 1. Continue pregnancy: Spina Bifida: Many families choose to continue. Early planning for care. Consider fetal surgery if eligible (19-26 weeks). Prepare for postnatal care. Connect with support groups. Plan delivery at specialized center. Anencephaly: Some continue for organ donation. Palliative care planning. Emotional preparation. 2. Termination: Legal considerations vary. Medical termination of pregnancy (MTP). Gestational age limits. Decision factors - very personal: Severity of defect. Associated abnormalities. Family circumstances. Religious/cultural beliefs. Support system. Financial considerations. Emotional readiness. Counseling essential: Genetic counselor: Explain condition thoroughly. Discuss recurrence risks. Maternal-fetal medicine: Medical aspects. Neonatologist: Prognosis discussion. Neurosurgeon: Treatment options. Social worker: Resources, support. No "right" choice: Both decisions are valid. Personal choice. No judgment. Support available: Whatever decision, support is important. Grief counseling. Support groups. Perinatal hospice (if continuing with anencephaly). Time to decide: Don't rush. Get all information. Second opinions okay. Discuss with family. For future: High-dose folic acid. Genetic counseling. Enhanced screening next time.
Transition to adulthood challenging होता है। Medical issues - ongoing: Shunt complications: Risk lifelong रहता है। Headaches, malfunction। Bladder/kidney: Continuing catheterization। UTIs, kidney damage risk। Regular monitoring जरूरी। Bowel management: Lifelong challenge। Social continence maintain करना। Orthopedic: Progressive scoliosis। Arthritis। Pain management। Skin breakdown: Pressure sores। Wheelchair users में common। Transition of care challenges: Finding adult providers: Pediatric doctors को adult doctors में transfer। Adult specialists often less familiar with Spina Bifida। Insurance changes: Losing pediatric coverage। Adult insurance complex। Self-management: Taking responsibility for own care। Appointment scheduling। Medication management। Social/Emotional: Independence: Living independently challenging हो सकता है। Accessible housing। Transportation। Employment: Finding suitable work। Workplace accommodations। Discrimination possible। Relationships: Dating, intimacy। Marriage। Some fear rejection। Sexual health: Function varies। Fertility possible (both males और females)। Genetic counseling before pregnancy। Mental health: Depression, anxiety common। Social isolation। Body image issues। Positive outcomes - many succeed: Many adults with SB lead fulfilling lives। Employment, marriage, children। Advocacy work। Athletic achievements। Higher education। Keys to success: Good medical care transition। Strong support system। Assistive technology। Vocational training। Counseling/therapy। Peer support groups। Positive attitude। Focus on abilities।
Transition to adulthood is challenging. Medical issues - ongoing: Shunt complications: Risk remains lifelong. Headaches, malfunction. Bladder/kidney: Continuing catheterization. UTIs, risk of kidney damage. Regular monitoring necessary. Bowel management: Lifelong challenge. Maintain social continence. Orthopedic: Progressive scoliosis. Arthritis. Pain management. Skin breakdown: Pressure sores. Common in wheelchair users. Transition of care challenges: Finding adult providers: Transfer from pediatric to adult doctors. Adult specialists often less familiar with Spina Bifida. Insurance changes: Losing pediatric coverage. Adult insurance complex. Self-management: Taking responsibility for own care. Appointment scheduling. Medication management. Social/Emotional: Independence: Living independently can be challenging. Accessible housing. Transportation. Employment: Finding suitable work. Workplace accommodations. Discrimination possible. Relationships: Dating, intimacy. Marriage. Some fear rejection. Sexual health: Function varies. Fertility possible (both males and females). Genetic counseling before pregnancy. Mental health: Depression, anxiety common. Social isolation. Body image issues. Positive outcomes - many succeed: Many adults with SB lead fulfilling lives. Employment, marriage, children. Advocacy work. Athletic achievements. Higher education. Keys to success: Good medical care transition. Strong support system. Assistive technology. Vocational training. Counseling/therapy. Peer support groups. Positive attitude. Focus on abilities.
अपॉइंटमेंट बुक करें
Book Your Appointment
Neural Tube Defects के expert diagnosis, prenatal counseling और comprehensive management के लिए
Dr. Gaurav Jain से आज ही संपर्क करें।
For expert diagnosis, prenatal counseling and comprehensive management of Neural Tube Defects
Contact Dr. Gaurav Jain today.