
Muscular Dystrophy
मस्कुलर डिस्ट्रॉफी की पूरी जानकारी और management
Muscular Dystrophy
Complete information and management for Muscular Dystrophy
Muscular Dystrophy क्या है? What is Muscular Dystrophy?
Muscular Dystrophy (MD) genetic disorders का एक group है जो progressive muscle weakness और degeneration cause करता है। यह genetic mutations के कारण होता है जो muscle proteins (especially dystrophin) के production को affect करते हैं।
MD में muscles धीरे-धीरे weak होती जाती हैं और waste (atrophy) हो जाती हैं। यह condition progressive है - मतलब समय के साथ symptoms worse होते जाते हैं। Different types की MD हैं, कुछ mild हैं और कुछ severe, कुछ childhood में start होती हैं और कुछ adulthood में।
महत्वपूर्ण जानकारी!
Muscular Dystrophy currently कोई cure नहीं है, लेकिन proper management, therapies, और supportive care से quality of life significantly improve हो सकती है। Early diagnosis और intervention बहुत important हैं।
Muscular Dystrophy (MD) is a group of genetic disorders that cause progressive muscle weakness and degeneration. It is caused by genetic mutations that affect the production of muscle proteins (especially dystrophin).
In MD, muscles gradually become weak and waste away (atrophy). This condition is progressive - meaning symptoms worsen over time. There are different types of MD, some are mild and some are severe, some start in childhood and some in adulthood.
Important Information!
Muscular Dystrophy currently has no cure, but with proper management, therapies, and supportive care, quality of life can be significantly improved. Early diagnosis and intervention are very important.
Muscular Dystrophy के Types Types of Muscular Dystrophy
30+ different types की muscular dystrophies हैं। सबसे common types:
Duchenne MD (DMD)
Most common और severe type
Age of onset: 2-6 years
Affects: Mainly boys (X-linked)
Symptoms: Progressive muscle weakness, starts in legs/pelvis। Walking difficulty by age 12। Wheelchair needed by teens।
Life expectancy: Early 20s-30s (improving with care)
Becker MD (BMD)
Similar to DMD but milder
Age of onset: 10-25 years
Affects: Mainly boys (X-linked)
Symptoms: Slower progression than DMD। Walking ability maintained longer। Heart problems common।
Life expectancy: 40s-50s या longer
Myotonic Dystrophy
Most common adult form
Age of onset: 20-40 years (can be earlier)
Affects: Both males और females
Symptoms: Myotonia (muscle stiffness)। Facial weakness। Heart problems। Cataracts।
Special: Multiple organs affected हो सकते हैं
Congenital MD
Present at birth या early infancy
Age of onset: Birth - 2 years
Affects: Both males और females
Symptoms: Severe muscle weakness from birth। Delayed motor milestones। Joint contractures। Possible brain involvement।
Severity: Varies widely
Limb-Girdle MD
Affects shoulder और hip muscles
Age of onset: Late childhood - early adulthood
Affects: Both males और females
Symptoms: Shoulder और hip weakness। Difficulty raising arms, climbing stairs। Variable progression।
Note: Multiple subtypes हैं
Facioscapulohumeral MD
Face, shoulder blade, upper arm affected
Age of onset: Teens - early 20s
Affects: Both males और females
Symptoms: Facial weakness। Difficulty closing eyes, smiling। Shoulder weakness। Slow progression।
Severity: Generally milder, normal lifespan
There are 30+ different types of muscular dystrophies. Most common types:
Duchenne MD (DMD)
Most common and severe type
Age of onset: 2-6 years
Affects: Mainly boys (X-linked)
Symptoms: Progressive muscle weakness, starts in legs/pelvis. Walking difficulty by age 12. Wheelchair needed by teens.
Life expectancy: Early 20s-30s (improving with care)
Becker MD (BMD)
Similar to DMD but milder
Age of onset: 10-25 years
Affects: Mainly boys (X-linked)
Symptoms: Slower progression than DMD. Walking ability maintained longer. Heart problems common.
Life expectancy: 40s-50s or longer
Myotonic Dystrophy
Most common adult form
Age of onset: 20-40 years (can be earlier)
Affects: Both males and females
Symptoms: Myotonia (muscle stiffness). Facial weakness. Heart problems. Cataracts.
Special: Multiple organs can be affected
Congenital MD
Present at birth or early infancy
Age of onset: Birth - 2 years
Affects: Both males and females
Symptoms: Severe muscle weakness from birth. Delayed motor milestones. Joint contractures. Possible brain involvement.
Severity: Varies widely
Limb-Girdle MD
Affects shoulder and hip muscles
Age of onset: Late childhood - early adulthood
Affects: Both males and females
Symptoms: Shoulder and hip weakness. Difficulty raising arms, climbing stairs. Variable progression.
Note: Multiple subtypes exist
Facioscapulohumeral MD
Face, shoulder blade, upper arm affected
Age of onset: Teens - early 20s
Affects: Both males and females
Symptoms: Facial weakness. Difficulty closing eyes, smiling. Shoulder weakness. Slow progression.
Severity: Generally milder, normal lifespan
लक्षण Symptoms
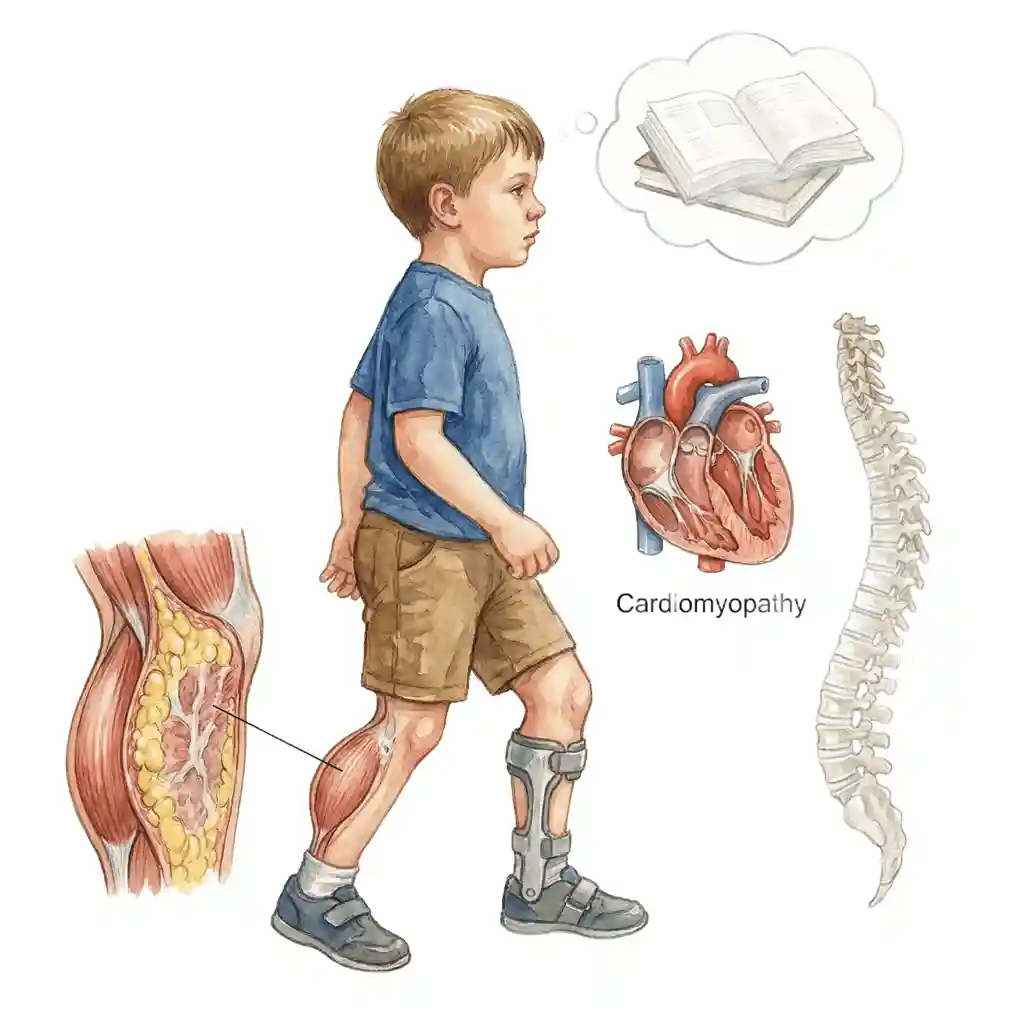
Symptoms vary करते हैं type और severity पर। Common signs:
Symptoms vary on type and severity. Common signs:
Muscles धीरे-धीरे weak होती जाती हैं। आमतौर पर legs और pelvis से start होता है। Upper body muscles later में affected होते हैं।
Muscles gradually become weak. Usually starts from legs and pelvis. Upper body muscles affected later.
Walking में trouble। Frequent falls। Waddling gait (duck walk)। Toe walking common है। Stairs चढ़ने में difficulty।
Trouble walking. Frequent falls. Waddling gait (duck walk). Toe walking is common. Difficulty climbing stairs.
Calf muscles abnormally large दिखते हैं (pseudohypertrophy)। Actually fat और scar tissue replace करते हैं muscle को। Especially DMD में।
Calf muscles appear abnormally large (pseudohypertrophy). Actually fat and scar tissue replace muscle. Especially in DMD.
Joints में tightness और stiffness। Heel cords, hips, knees, elbows tight हो जाते हैं। Movement limited हो जाती है।
Tightness and stiffness in joints. Heel cords, hips, knees, elbows become tight. Movement becomes limited.
Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle weakness)। Irregular heartbeat। Heart failure develop हो सकता है। Regular cardiac monitoring जरूरी है।
Cardiomyopathy (heart muscle weakness). Irregular heartbeat. Heart failure can develop. Regular cardiac monitoring necessary.
Respiratory muscles weak हो जाते हैं। Breathing problems especially रात में। Frequent chest infections। Ventilation support की जरूरत पड़ सकती है।
Respiratory muscles become weak. Breathing problems especially at night. Frequent chest infections. Ventilation support may be needed.
कुछ types में cognitive delays हो सकते हैं। Especially DMD में। Speech और language development affected हो सकता है।
Some types may have cognitive delays. Especially in DMD. Speech and language development may be affected.
Spine curvature develop हो सकती है। Weak back muscles के कारण। Posture affected होता है। Bracing या surgery की जरूरत हो सकती है।
Spine curvature can develop. Due to weak back muscles. Posture is affected. Bracing or surgery may be needed.
कारण - Genetics Causes - Genetics
Muscular Dystrophy purely genetic है। Mutations in genes जो muscle proteins produce करते हैं, especially dystrophin gene। यह proteins muscles को healthy रखने के लिए essential हैं।
X-linked Inheritance
DMD और BMD: X chromosome पर mutation। Boys mainly affected (XY)। Girls carriers हो सकती हैं। Mother से son को pass होता है। 50% chance carrier mother का son affected होगा।
Autosomal Dominant
Myotonic, FSHD: One parent से ही mutated gene मिलने से disease हो सकता है। Both males और females equally affected। 50% chance child को pass होने का।
Autosomal Recessive
कुछ Limb-Girdle types: Both parents से mutated gene चाहिए। Parents carriers होते हैं but affected नहीं। 25% chance child affected होगा।
Spontaneous Mutations
लगभग 1/3 DMD cases में new mutation होता है। Family history नहीं होता। Parents carriers नहीं होते। Child में de novo (new) mutation develop होता है।
Genetic Testing Important है
Genetic testing से accurate diagnosis होता है। Specific type identify हो जाता है। Family planning में help करता है। Carrier testing available है। Prenatal testing possible है। Genetic counseling recommended है।
Muscular Dystrophy is purely genetic. Mutations in genes that produce muscle proteins, especially dystrophin gene. These proteins are essential to keep muscles healthy.
X-linked Inheritance
DMD and BMD: Mutation on X chromosome. Boys mainly affected (XY). Girls can be carriers. Passes from mother to son. 50% chance carrier mother's son will be affected.
Autosomal Dominant
Myotonic, FSHD: Disease can occur with mutated gene from just one parent. Both males and females equally affected. 50% chance of passing to child.
Autosomal Recessive
Some Limb-Girdle types: Need mutated gene from both parents. Parents are carriers but not affected. 25% chance child will be affected.
Spontaneous Mutations
About 1/3 of DMD cases have new mutation. No family history. Parents are not carriers. De novo (new) mutation develops in child.
Genetic Testing is Important
Genetic testing provides accurate diagnosis. Specific type is identified. Helps in family planning. Carrier testing available. Prenatal testing possible. Genetic counseling recommended.
Diagnosis कैसे होता है? How is it Diagnosed?
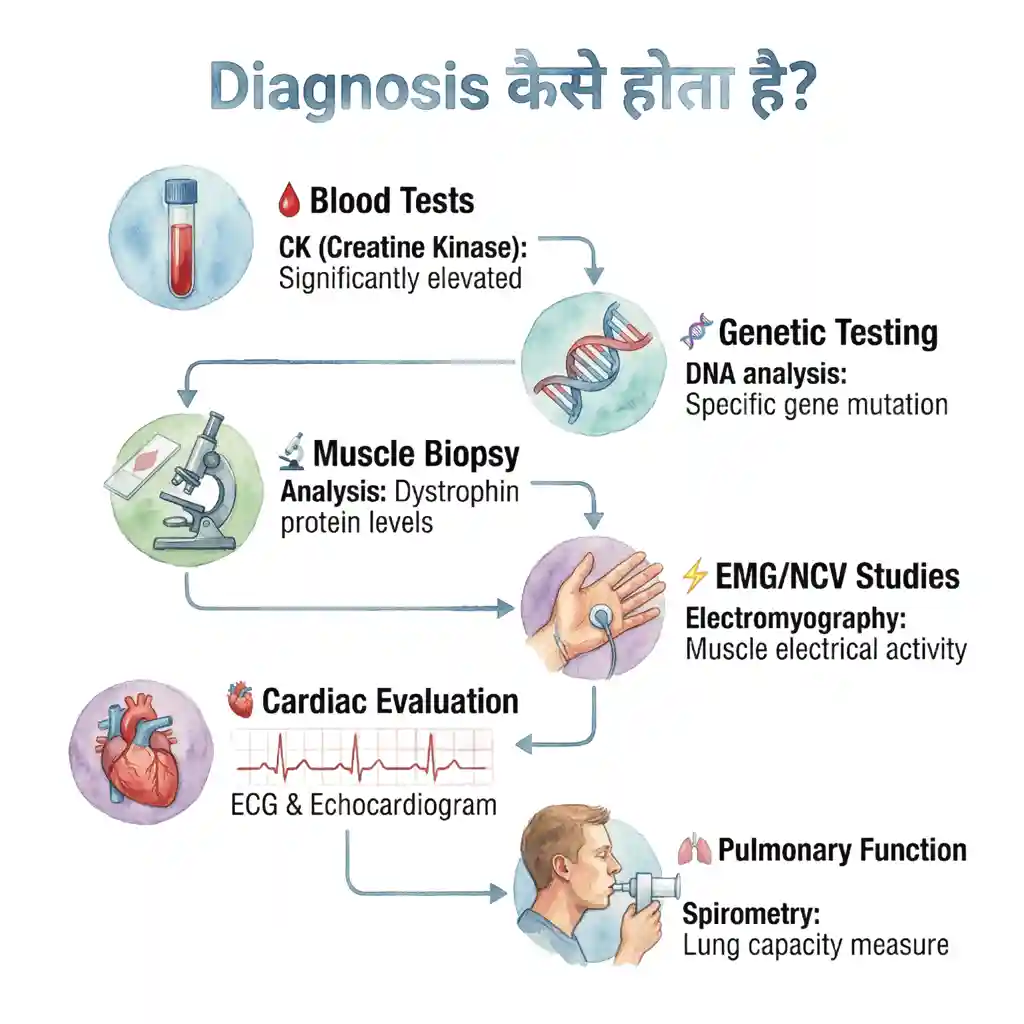
Blood Tests
CK (Creatine Kinase): Significantly elevated होता है MD में। Normal से 10-100 गुना ज्यादा। Muscle damage का indicator।
Other enzymes: ALT, AST भी elevated हो सकते हैं।
Genetic Testing
DNA analysis: Specific gene mutation identify करता है।
Confirms diagnosis: Type of MD determine करता है।
Family testing: Carrier status check कर सकते हैं।
Gold standard: Most accurate diagnostic method
Muscle Biopsy
Procedure: Small muscle tissue sample लेते हैं।
Analysis: Dystrophin protein levels check करते हैं।
Microscopy: Muscle fiber damage visualize करते हैं।
When needed: जब genetic testing inconclusive हो
EMG/NCV Studies
Electromyography: Muscle electrical activity check करता है।
Nerve Conduction: Nerve function assess करता है।
Purpose: Other conditions rule out करने के लिए।
Pattern: Myopathic changes दिखाता है
Cardiac Evaluation
ECG: Heart rhythm check करता है।
Echocardiogram: Heart function assess करता है।
Regular monitoring: Cardiomyopathy detect करने के लिए।
Important: Cardiac involvement common है
Pulmonary Function
Spirometry: Lung capacity measure करता है।
Baseline: Initial assessment important है।
Monitoring: Progressive decline track करते हैं।
Planning: Respiratory support timing decide करने में help
Blood Tests
CK (Creatine Kinase): Significantly elevated in MD. 10-100 times higher than normal. Indicator of muscle damage.
Other enzymes: ALT, AST may also be elevated.
Genetic Testing
DNA analysis: Identifies specific gene mutation.
Confirms diagnosis: Determines type of MD.
Family testing: Can check carrier status.
Gold standard: Most accurate diagnostic method
Muscle Biopsy
Procedure: Take small muscle tissue sample.
Analysis: Check dystrophin protein levels.
Microscopy: Visualize muscle fiber damage.
When needed: When genetic testing inconclusive
EMG/NCV Studies
Electromyography: Checks muscle electrical activity.
Nerve Conduction: Assesses nerve function.
Purpose: To rule out other conditions.
Pattern: Shows myopathic changes
Cardiac Evaluation
ECG: Checks heart rhythm.
Echocardiogram: Assesses heart function.
Regular monitoring: To detect cardiomyopathy.
Important: Cardiac involvement is common
Pulmonary Function
Spirometry: Measures lung capacity.
Baseline: Initial assessment is important.
Monitoring: Track progressive decline.
Planning: Helps decide timing for respiratory support
Treatment और Management Treatment and Management
Important!
Currently MD का कोई cure नहीं है। Treatment focus है symptoms को manage करने पर, complications को prevent करने पर, और quality of life improve करने पर।
Medications
Corticosteroids (Prednisone/Deflazacort): DMD में muscle strength maintain करते हैं। Progression slow करते हैं। Side effects monitor करनी पड़ती हैं।
Heart medications: ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers for cardiomyopathy।
Newer therapies: Exon-skipping drugs (Eteplirsen) specific mutations के लिए
Physical Therapy
Regular exercises: Muscle strength maintain करने के लिए।
Stretching: Contractures prevent करने के लिए।
Range of motion: Joint mobility preserve करने के लिए।
Individualized program: Ability level के according।
Consistency: Daily exercises important हैं
Assistive Devices
Braces/Orthotics: Walking support, contractures prevent।
Wheelchair: Mobility maintain करने के लिए।
Standing frames: Bone health के लिए।
Adapted equipment: Independence promote करता है।
Home modifications: Accessibility improve करते हैं
Respiratory Care
Breathing exercises: Lung capacity maintain करने के लिए।
Cough assist devices: Secretions clear करने के लिए।
BiPAP/CPAP: Night-time ventilation support।
Vaccinations: Flu, pneumonia से protection।
Monitoring: Regular pulmonary function tests
Cardiac Management
Regular monitoring: ECG, Echo annually या more frequent।
Early treatment: Cardiomyopathy के first signs पर।
Medications: Heart function support के लिए।
Lifestyle: Low-sodium diet, fluid management।
Emergency plan: Cardiac complications के लिए
Orthopedic Care
Scoliosis management: Bracing या surgery if needed।
Contracture releases: Surgery to improve mobility।
Bone health: Vitamin D, calcium supplements।
Weight-bearing: Bone density maintain करने के लिए।
Regular monitoring: X-rays to track progression
Nutrition Support
Balanced diet: Adequate calories और protein।
Weight management: Obesity avoid करना important।
Swallowing issues: Texture modifications if needed।
Supplements: Vitamins और minerals।
Feeding tubes: Severe cases में if required
Psychological Support
Counseling: Child और family के लिए।
Coping strategies: Emotional challenges manage करने के लिए।
Support groups: Peer connection important है।
Educational support: Learning difficulties address करना।
Quality of life: Mental health maintain करना
Multidisciplinary Approach Essential है
MD management में multiple specialists की team जरूरी है: Neurologist, Cardiologist, Pulmonologist, Orthopedic surgeon, Physical therapist, Occupational therapist, Nutritionist, Genetic counselor। Coordinated care से best outcomes मिलते हैं।
Important!
Currently there is no cure for MD. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms, preventing complications, and improving quality of life.
Medications
Corticosteroids (Prednisone/Deflazacort): Maintain muscle strength in DMD. Slow progression. Need to monitor side effects.
Heart medications: ACE inhibitors, beta-blockers for cardiomyopathy.
Newer therapies: Exon-skipping drugs (Eteplirsen) for specific mutations
Physical Therapy
Regular exercises: To maintain muscle strength.
Stretching: To prevent contractures.
Range of motion: To preserve joint mobility.
Individualized program: According to ability level.
Consistency: Daily exercises are important
Assistive Devices
Braces/Orthotics: Walking support, prevent contractures.
Wheelchair: To maintain mobility.
Standing frames: For bone health.
Adapted equipment: Promotes independence.
Home modifications: Improve accessibility
Respiratory Care
Breathing exercises: To maintain lung capacity.
Cough assist devices: To clear secretions.
BiPAP/CPAP: Night-time ventilation support.
Vaccinations: Protection from flu, pneumonia.
Monitoring: Regular pulmonary function tests
Cardiac Management
Regular monitoring: ECG, Echo annually or more frequent.
Early treatment: At first signs of cardiomyopathy.
Medications: To support heart function.
Lifestyle: Low-sodium diet, fluid management.
Emergency plan: For cardiac complications
Orthopedic Care
Scoliosis management: Bracing or surgery if needed.
Contracture releases: Surgery to improve mobility.
Bone health: Vitamin D, calcium supplements.
Weight-bearing: To maintain bone density.
Regular monitoring: X-rays to track progression
Nutrition Support
Balanced diet: Adequate calories and protein.
Weight management: Important to avoid obesity.
Swallowing issues: Texture modifications if needed.
Supplements: Vitamins and minerals.
Feeding tubes: If required in severe cases
Psychological Support
Counseling: For child and family.
Coping strategies: To manage emotional challenges.
Support groups: Peer connection is important.
Educational support: Address learning difficulties.
Quality of life: Maintain mental health
Multidisciplinary Approach is Essential
MD management requires a team of multiple specialists: Neurologist, Cardiologist, Pulmonologist, Orthopedic surgeon, Physical therapist, Occupational therapist, Nutritionist, Genetic counselor. Coordinated care gives best outcomes.
Daily Life Management Daily Life Management
Activity Balance
Active रहना important है but overexertion से बचें। Gentle activities जैसे swimming beneficial हैं। Rest periods include करें। Energy conservation techniques सीखें।
Home Adaptations
Ramps install करें। Bathroom grab bars लगाएं। Wider doorways। Accessible switches और controls। Comfortable seating। Adapted kitchen equipment।
School Support
IEP (Individualized Education Plan) develop करें। Classroom accommodations। Accessible facilities। Support services। Peer education about MD। Social inclusion promote करें।
Social Participation
Social activities encourage करें। Adaptive sports programs। Community involvement। Friendships maintain करें। Hobbies develop करें। Self-esteem build करें।
Future Planning
Vocational training explore करें। Career counseling। Financial planning। Legal documents (power of attorney)। Long-term care planning। Transition to adult services।
Family Support
Respite care arrange करें। Sibling support। Family counseling। Support networks join करें। Self-care practice करें। Stress management।
Technology Use
Communication devices। Computer adaptations। Voice-controlled systems। Mobility apps। Remote learning tools। Social media for connection।
Regular Monitoring
Scheduled appointments maintain करें। Growth और development track करें। Medication compliance। Therapy sessions। Annual comprehensive evaluations। Emergency preparedness।
Activity Balance
Staying active is important but avoid overexertion. Gentle activities like swimming are beneficial. Include rest periods. Learn energy conservation techniques.
Home Adaptations
Install ramps. Add bathroom grab bars. Wider doorways. Accessible switches and controls. Comfortable seating. Adapted kitchen equipment.
School Support
Develop IEP (Individualized Education Plan). Classroom accommodations. Accessible facilities. Support services. Peer education about MD. Promote social inclusion.
Social Participation
Encourage social activities. Adaptive sports programs. Community involvement. Maintain friendships. Develop hobbies. Build self-esteem.
Future Planning
Explore vocational training. Career counseling. Financial planning. Legal documents (power of attorney). Long-term care planning. Transition to adult services.
Family Support
Arrange respite care. Sibling support. Family counseling. Join support networks. Practice self-care. Stress management.
Technology Use
Communication devices. Computer adaptations. Voice-controlled systems. Mobility apps. Remote learning tools. Social media for connection.
Regular Monitoring
Maintain scheduled appointments. Track growth and development. Medication compliance. Therapy sessions. Annual comprehensive evaluations. Emergency preparedness.
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले सवाल (FAQ) Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
MD का detection कई steps में होता है। Early signs: Parents usually notice करते हैं - delayed walking, frequent falls, difficulty climbing stairs, enlarged calf muscles। Pediatrician observation during routine check-ups। Initial screening: Blood test CK (Creatine Kinase) levels check करता है - MD में यह बहुत elevated होता है (normal से 10-100 गुना)। Confirmatory tests: Genetic testing से specific gene mutation identify होता है। Muscle biopsy dystrophin protein levels show करता है। Newborn screening: कुछ countries में DMD के लिए newborn screening start हो रही है। Family history: अगर family में MD है तो early testing recommended है। Timeline: DMD typically 3-5 years age में diagnose होता है। Other types later में। Importance of early diagnosis: Early intervention से better outcomes मिलते हैं। Clinical trials में participate कर सकते हैं। Proactive management planning।
MD detection happens in several steps. Early signs: Parents usually notice - delayed walking, frequent falls, difficulty climbing stairs, enlarged calf muscles. Pediatrician observation during routine check-ups. Initial screening: Blood test checks CK (Creatine Kinase) levels - very elevated in MD (10-100 times normal). Confirmatory tests: Genetic testing identifies specific gene mutation. Muscle biopsy shows dystrophin protein levels. Newborn screening: Some countries are starting newborn screening for DMD. Family history: If MD in family, early testing is recommended. Timeline: DMD typically diagnosed at 3-5 years age. Other types later. Importance of early diagnosis: Better outcomes with early intervention. Can participate in clinical trials. Proactive management planning.
यह depend करता है genetic situation पर। If mother is carrier: हर pregnancy में:
• 50% chance male child DMD से affected होगा
• 50% chance male child healthy होगा
• 50% chance female child carrier होगी
• 50% chance female child neither carrier nor affected होगी
Carrier testing important है: Mother का genetic testing से पता चलता है carrier status। De novo mutation: लगभग 1/3 cases में mother carrier नहीं होती - child में new mutation होता है। इस case में recurrence risk बहुत low है। Prenatal testing options: CVS (10-12 weeks): Chorionic villus sampling से early diagnosis। Amniocentesis (15-18 weeks): Amniotic fluid test करते हैं। PGD: Preimplantation genetic diagnosis - IVF के साथ। Genetic counseling essential है: Proper risk assessment। All options की detailed discussion। Family planning decisions।
This depends on genetic situation. If mother is carrier: In each pregnancy:
• 50% chance male child will be affected by DMD
• 50% chance male child will be healthy
• 50% chance female child will be carrier
• 50% chance female child will be neither carrier nor affected
Carrier testing is important: Mother's genetic testing reveals carrier status. De novo mutation: In about 1/3 cases mother is not carrier - new mutation in child. In this case recurrence risk is very low. Prenatal testing options: CVS (10-12 weeks): Early diagnosis through chorionic villus sampling. Amniocentesis (15-18 weeks): Test amniotic fluid. PGD: Preimplantation genetic diagnosis - with IVF. Genetic counseling is essential: Proper risk assessment. Detailed discussion of all options. Family planning decisions.
Currently, MD का कोई complete cure नहीं है। Current reality: MD एक genetic condition है। Gene therapy research चल रही है but अभी routine treatment available नहीं है। Hope for future: Gene therapy: Clinical trials चल रहे हैं। Dystrophin gene को replace करने की कोशिश। कुछ promising results आ रहे हैं। Exon skipping: Eteplirsen जैसी drugs specific mutations के लिए approved हैं। Disease progression को slow करती हैं। CRISPR: Gene editing technology research में है। Current management very effective है: Corticosteroids muscle strength maintain करते हैं years तक। Respiratory और cardiac care से life expectancy significantly बढ़ी है। DMD patients अब 30s-40s तक जी रहे हैं (पहले teens में death होती थी)। Quality of life improvements: Assistive technology। Better wheelchairs और devices। Communication aids। Educational opportunities। Research ongoing है: Multiple clinical trials। New therapies development में। Hope है कि future में cure available होगा।
Currently, there is no complete cure for MD. Current reality: MD is a genetic condition. Gene therapy research is ongoing but not yet available as routine treatment. Hope for future: Gene therapy: Clinical trials are ongoing. Attempting to replace dystrophin gene. Some promising results coming. Exon skipping: Drugs like Eteplirsen approved for specific mutations. Slow disease progression. CRISPR: Gene editing technology in research. Current management is very effective: Corticosteroids maintain muscle strength for years. Respiratory and cardiac care has significantly increased life expectancy. DMD patients now living into 30s-40s (previously death in teens). Quality of life improvements: Assistive technology. Better wheelchairs and devices. Communication aids. Educational opportunities. Research is ongoing: Multiple clinical trials. New therapies in development. Hope that cure will be available in future.
DMD के लिए steroids strongly recommended हैं। Benefits - proven और significant: Muscle strength 2-3 years extra maintain होती है। Walking ability longer preserve रहती है। Scoliosis का risk कम होता है। Heart function better रहता है। Lung function preserve होता है। Overall quality of life improve होती है। Two main options: Prednisone: Oldest और most studied। Daily dose 0.75 mg/kg। Deflazacort: Slightly fewer side effects। Daily dose 0.9 mg/kg। Side effects - manageable: Weight gain - diet control जरूरी है। Behavioral changes - mood swings। Bone density issues - vitamin D और calcium supplements। Growth delay - monitor carefully। Cataracts - regular eye checks। Monitoring essential: Regular weight checks। Blood pressure monitoring। Bone density scans। Blood glucose tests। Growth tracking। When to start: Typically 4-8 years age। Plateau phase में या जब decline start हो। Can stop?: Generally long-term treatment है। Benefits outweigh risks significantly। Sudden stopping dangerous है - gradual taper करनी पड़ती है।
For DMD, steroids are strongly recommended. Benefits - proven and significant: Muscle strength maintained 2-3 years extra. Walking ability preserved longer. Reduced risk of scoliosis. Better heart function. Preserved lung function. Improved overall quality of life. Two main options: Prednisone: Oldest and most studied. Daily dose 0.75 mg/kg. Deflazacort: Slightly fewer side effects. Daily dose 0.9 mg/kg. Side effects - manageable: Weight gain - need diet control. Behavioral changes - mood swings. Bone density issues - vitamin D and calcium supplements. Growth delay - monitor carefully. Cataracts - regular eye checks. Monitoring is essential: Regular weight checks. Blood pressure monitoring. Bone density scans. Blood glucose tests. Growth tracking. When to start: Typically 4-8 years age. In plateau phase or when decline starts. Can stop?: Generally long-term treatment. Benefits significantly outweigh risks. Sudden stopping is dangerous - need gradual taper.
हां, but proper guidelines के साथ। Safe exercises - recommended: Swimming: Excellent choice - water support देता है। Low-impact। Full body workout। Fun activity। Gentle stretching: Daily flexibility exercises। Prevent contractures। Range of motion maintain। Light aerobic: Walking (जब possible हो)। Stationary bike। Adapted exercises। Avoid - harmful: Heavy weightlifting। High-intensity workouts। Eccentric exercises (muscle lengthening under load)। Excessive fatigue causing activities। Important principles: Submaximal exercise: Never exercise to exhaustion। 60-70% effort maximum। Frequent rest: Breaks लेते रहें। Overwork से बचें। Listen to body: Pain होने पर stop करें। Excessive soreness avoid करें। Consistency over intensity: Regular gentle exercise better है। Physical therapy guidance: Individualized program बनाएं। Professional supervision। Age-appropriate activities। Ability level के according। Benefits of appropriate exercise: Maintain mobility। Prevent complications। Improve mood। Social interaction। Better quality of life। Warning signs to stop: Muscle pain। Excessive fatigue। Dark urine (rhabdomyolysis का sign)। Prolonged weakness।
Yes, but with proper guidelines. Safe exercises - recommended: Swimming: Excellent choice - water provides support. Low-impact. Full body workout. Fun activity. Gentle stretching: Daily flexibility exercises. Prevent contractures. Maintain range of motion. Light aerobic: Walking (when possible). Stationary bike. Adapted exercises. Avoid - harmful: Heavy weightlifting. High-intensity workouts. Eccentric exercises (muscle lengthening under load). Activities causing excessive fatigue. Important principles: Submaximal exercise: Never exercise to exhaustion. 60-70% effort maximum. Frequent rest: Keep taking breaks. Avoid overwork. Listen to body: Stop if pain occurs. Avoid excessive soreness. Consistency over intensity: Regular gentle exercise is better. Physical therapy guidance: Create individualized program. Professional supervision. Age-appropriate activities. According to ability level. Benefits of appropriate exercise: Maintain mobility. Prevent complications. Improve mood. Social interaction. Better quality of life. Warning signs to stop: Muscle pain. Excessive fatigue. Dark urine (sign of rhabdomyolysis). Prolonged weakness.
हां। DMD/BMD (X-linked) में: Girls usually carriers होती हैं - symptoms नहीं होते। BUT: Rare cases में carrier females को mild symptoms हो सकते हैं। "Manifesting carriers": लगभग 8-20% female carriers में mild muscle weakness। Heart problems develop हो सकते हैं। Regular cardiac monitoring जरूरी है। Why happens: X-inactivation pattern के कारण। कुछ cases में affected X chromosome ज्यादा active रहता है। Very rare - severe in girls: Turner syndrome (single X)। X-chromosome translocations। Father DMD + Mother carrier (extremely rare)। Other MD types - equally affect both: Myotonic dystrophy: Girls और boys equally। Actually females में sometimes more severe। Congenital form में। Limb-Girdle MD: Many types affect both equally। Autosomal recessive या dominant। FSHD: Both sexes affected। Males में sometimes more severe। Congenital MD: Both boys और girls। Important for female carriers: Regular cardiac screening। Consider symptoms seriously। Genetic counseling before pregnancy। Carrier testing for daughters।
Yes. In DMD/BMD (X-linked): Girls are usually carriers - no symptoms. BUT: In rare cases carrier females may have mild symptoms. "Manifesting carriers": About 8-20% of female carriers have mild muscle weakness. Heart problems can develop. Regular cardiac monitoring necessary. Why it happens: Due to X-inactivation pattern. In some cases affected X chromosome remains more active. Very rare - severe in girls: Turner syndrome (single X). X-chromosome translocations. Father DMD + Mother carrier (extremely rare). Other MD types - equally affect both: Myotonic dystrophy: Girls and boys equally. Actually sometimes more severe in females. In congenital form. Limb-Girdle MD: Many types affect both equally. Autosomal recessive or dominant. FSHD: Both sexes affected. Sometimes more severe in males. Congenital MD: Both boys and girls. Important for female carriers: Regular cardiac screening. Take symptoms seriously. Genetic counseling before pregnancy. Carrier testing for daughters.
Comprehensive IEP (Individualized Education Plan) जरूरी है। Physical accommodations: Accessibility: Ramps, elevators। Accessible bathroom। Ground floor classroom (if possible)। Furniture: Adaptive desk और chair। Proper positioning। Good back support। Mobility: Wheelchair access throughout। Wide doorways। Extra time between classes। Elevator key/access। Academic accommodations: Writing support: Laptop या tablet for assignments। Speech-to-text software। Scribe for tests। Extended time for writing। Testing: Separate room if needed। Rest breaks। Oral responses allowed। Modified format। Books/Materials: Lightweight materials। Digital textbooks। Locker accessibility या extra set of books at home। Physical education: Adapted PE program। Alternative activities। Focus on gentle movement। No competitive pressure। Health support: School nurse informed। Emergency plan in place। Medication administration। Rest periods as needed। Bathroom breaks without asking। Social/Emotional: Peer education about MD। Anti-bullying measures। Counselor support। Social skills groups। Inclusion in activities। Cognitive support (if needed): Some MD types have learning difficulties। Special education services। Speech/language therapy। Occupational therapy।
Comprehensive IEP (Individualized Education Plan) is necessary. Physical accommodations: Accessibility: Ramps, elevators. Accessible bathroom. Ground floor classroom (if possible). Furniture: Adaptive desk and chair. Proper positioning. Good back support. Mobility: Wheelchair access throughout. Wide doorways. Extra time between classes. Elevator key/access. Academic accommodations: Writing support: Laptop or tablet for assignments. Speech-to-text software. Scribe for tests. Extended time for writing. Testing: Separate room if needed. Rest breaks. Oral responses allowed. Modified format. Books/Materials: Lightweight materials. Digital textbooks. Locker accessibility or extra set of books at home. Physical education: Adapted PE program. Alternative activities. Focus on gentle movement. No competitive pressure. Health support: School nurse informed. Emergency plan in place. Medication administration. Rest periods as needed. Bathroom breaks without asking. Social/Emotional: Peer education about MD. Anti-bullying measures. Counselor support. Social skills groups. Inclusion in activities. Cognitive support (if needed): Some MD types have learning difficulties. Special education services. Speech/language therapy. Occupational therapy.
Vary करता है MD के type पर। DMD (Duchenne): Past: Teens में death common थी। Now (with modern care): Late 20s - early 40s। Many living into 30s। Some crossing 40। Key improvements: Corticosteroids। Respiratory support (BiPAP/ventilator)। Cardiac medications। Better orthopedic care। BMD (Becker): Much milder progression। 40s, 50s या longer। Some normal lifespan with good cardiac care। Variable presentation। Myotonic Dystrophy: Type 1: Reduced lifespan - 50s-60s। Cardiac और respiratory complications। Type 2: Usually normal या near-normal lifespan। Congenital form: Most severe - survival variable। Other types: FSHD: Usually normal lifespan। Disability है but life-threatening नहीं। Limb-Girdle: Varies by subtype। Many types में normal lifespan। Factors affecting survival: Cardiac care - major factor। Respiratory management। Infection prevention। Nutrition। Quality of medical care। Cause of death typically: Respiratory failure। Cardiac complications। Pneumonia। Important: Life expectancy improving continuously। Better treatments developing। Quality of life also improving। Support और management crucial है।
Varies on type of MD. DMD (Duchenne): Past: Death in teens was common. Now (with modern care): Late 20s - early 40s. Many living into 30s. Some crossing 40. Key improvements: Corticosteroids. Respiratory support (BiPAP/ventilator). Cardiac medications. Better orthopedic care. BMD (Becker): Much milder progression. 40s, 50s or longer. Some normal lifespan with good cardiac care. Variable presentation. Myotonic Dystrophy: Type 1: Reduced lifespan - 50s-60s. Cardiac and respiratory complications. Type 2: Usually normal or near-normal lifespan. Congenital form: Most severe - variable survival. Other types: FSHD: Usually normal lifespan. Disability but not life-threatening. Limb-Girdle: Varies by subtype. Normal lifespan in many types. Factors affecting survival: Cardiac care - major factor. Respiratory management. Infection prevention. Nutrition. Quality of medical care. Cause of death typically: Respiratory failure. Cardiac complications. Pneumonia. Important: Life expectancy continuously improving. Better treatments developing. Quality of life also improving. Support and management are crucial.
"Normal" का definition different है, लेकिन meaningful और fulfilling life definitely possible है। What's possible: Education: Regular school attendance (with accommodations)। Higher education। Many MD patients college graduate हैं। Career opportunities available हैं। Social life: Friendships maintain कर सकते हैं। Relationships। Some marry और families बनाते हैं (genetic counseling के साथ)। Social activities participate कर सकते हैं। Hobbies/Interests: Technology use - gaming, social media। Art, music, writing। Adaptive sports। Advocacy और awareness work। Independence: Technology से बहुत कुछ possible है। Voice-controlled devices। Powered wheelchairs। Adapted vehicles कुछ cases में। Achievements: Many MD patients inspirational lives जीते हैं। Authors, speakers, advocates। Contributing members of society। Challenges - real: Progressive physical limitations। Dependence on caregivers। Medical appointments frequent हैं। Fatigue management। Financial burden। Support systems essential: Family involvement। Professional caregivers। Peer support groups। Community resources। Mental health support। Focus on abilities: What CAN do, not what CAN'T। Adaptive strategies। Technology leverage करें। Positive mindset maintain करें। Quality of life improving: Better assistive technology। More inclusion in society। Greater awareness और acceptance। Better medical care।
Definition of "normal" is different, but meaningful and fulfilling life is definitely possible. What's possible: Education: Regular school attendance (with accommodations). Higher education. Many MD patients are college graduates. Career opportunities available. Social life: Can maintain friendships. Relationships. Some marry and build families (with genetic counseling). Can participate in social activities. Hobbies/Interests: Technology use - gaming, social media. Art, music, writing. Adaptive sports. Advocacy and awareness work. Independence: Much possible with technology. Voice-controlled devices. Powered wheelchairs. Adapted vehicles in some cases. Achievements: Many MD patients live inspirational lives. Authors, speakers, advocates. Contributing members of society. Challenges - real: Progressive physical limitations. Dependence on caregivers. Frequent medical appointments. Fatigue management. Financial burden. Support systems essential: Family involvement. Professional caregivers. Peer support groups. Community resources. Mental health support. Focus on abilities: What CAN do, not what CAN'T. Adaptive strategies. Leverage technology. Maintain positive mindset. Quality of life improving: Better assistive technology. More inclusion in society. Greater awareness and acceptance. Better medical care.
यह important decision है। Benefits of participating: Access to new treatments जो otherwise available नहीं हैं। Close medical monitoring। Contributing to research - future generations को help। Hope के लिए। Free treatment और care (trial में)। Expert medical team। Considerations/Risks: Unknown side effects possible हैं। Placebo group में आ सकते हैं (no active treatment)। Time commitment - frequent visits। Strict eligibility criteria। May not work - experimental है। Travel requirements। Types of trials: Gene therapy: Most promising but early stage। Limited availability। Specific mutations के लिए। Drug trials: Exon-skipping therapies। Anti-inflammatory agents। Muscle-building compounds। Device/Therapy trials: New ventilation methods। Exercise protocols। How to decide: Discuss thoroughly with doctor। Understand risks और benefits। Read informed consent carefully। Ask questions। Consider child's/patient's wellbeing। Family impact assess करें। Where to find: ClinicalTrials.gov। MD advocacy organizations। Muscular Dystrophy Association। Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy। Research centers। Important: Not abandoning current care। Can withdraw anytime। Second opinions helpful हैं। Support groups से feedback लें।
This is an important decision. Benefits of participating: Access to new treatments not otherwise available. Close medical monitoring. Contributing to research - helping future generations. For hope. Free treatment and care (in trial). Expert medical team. Considerations/Risks: Unknown side effects possible. May be in placebo group (no active treatment). Time commitment - frequent visits. Strict eligibility criteria. May not work - it's experimental. Travel requirements. Types of trials: Gene therapy: Most promising but early stage. Limited availability. For specific mutations. Drug trials: Exon-skipping therapies. Anti-inflammatory agents. Muscle-building compounds. Device/Therapy trials: New ventilation methods. Exercise protocols. How to decide: Discuss thoroughly with doctor. Understand risks and benefits. Read informed consent carefully. Ask questions. Consider child's/patient's wellbeing. Assess family impact. Where to find: ClinicalTrials.gov. MD advocacy organizations. Muscular Dystrophy Association. Parent Project Muscular Dystrophy. Research centers. Important: Not abandoning current care. Can withdraw anytime. Second opinions are helpful. Get feedback from support groups.
अपॉइंटमेंट बुक करें
Book Your Appointment
Muscular Dystrophy के expert diagnosis और comprehensive management के लिए
Dr. Gaurav Jain से आज ही संपर्क करें।
For expert diagnosis and comprehensive management of Muscular Dystrophy
Contact Dr. Gaurav Jain today.