
Cerebral Palsy (सेरेब्रल पाल्सी)
Cerebral Palsy Treatment
व्यापक Multidisciplinary Care - Physiotherapy, Botox, Surgery | Indore
Comprehensive Multidisciplinary Care - Physiotherapy, Botox, Surgery | Indore
Cerebral Palsy क्या है?
What is Cerebral Palsy?
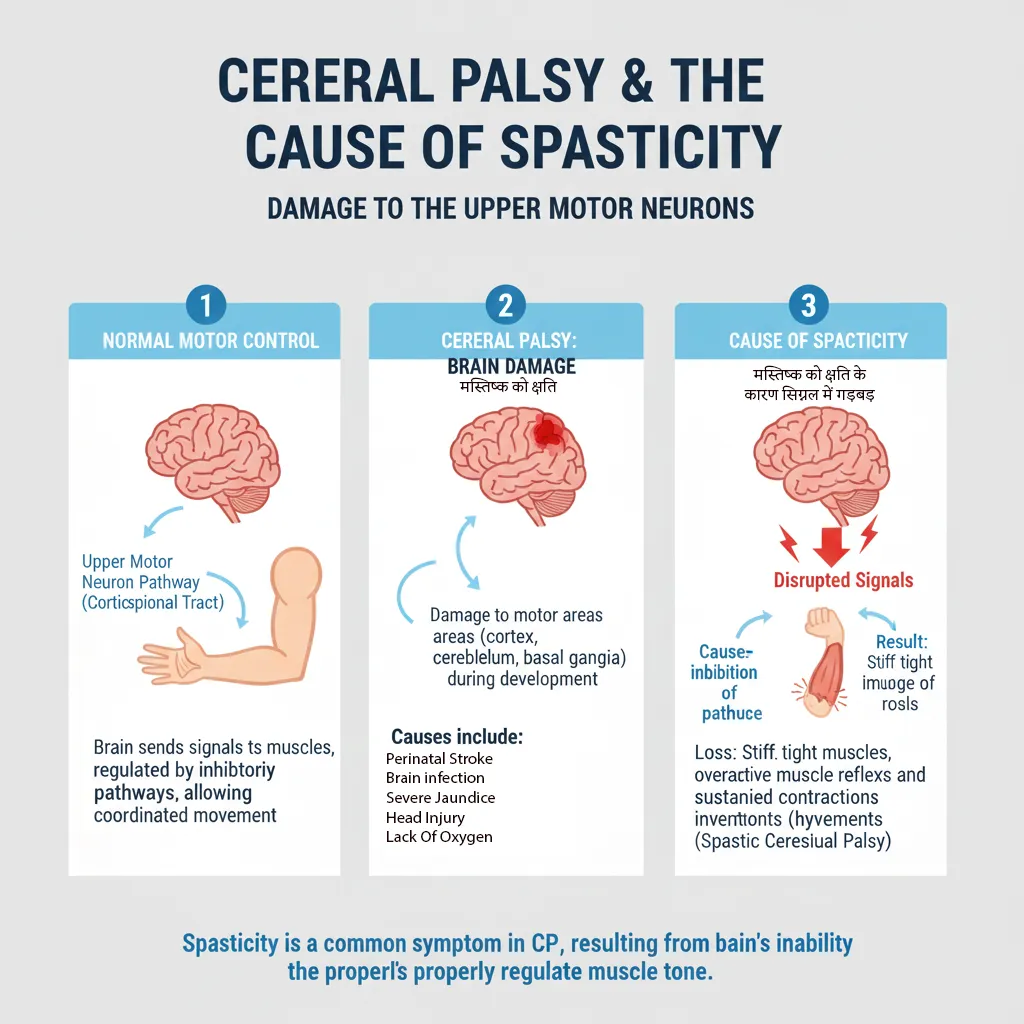
Cerebral Palsy (CP) एक neurological disorder है जो brain damage के कारण होता है - जन्म से पहले, दौरान, या जन्म के तुरंत बाद। यह movement, muscle tone, और posture को प्रभावित करता है। NOT progressive - बढ़ता नहीं, लेकिन lifelong condition है।
🎯 Key Facts!
सबसे common motor disability in children! 2-3 in 1,000 births। Brain injury causes। Multiple types। Range: mild से severe। Each child different! Treatment improves quality of life। Early intervention = better outcomes!
📊 Key Statistics:
जन्मों में
सबसे common
चलने लगते
बोलने में दिक्कत
🧠 What Happens in Brain?
Brain damage या abnormal development - especially motor control areas।
Causes: Premature birth, low oxygen (hypoxia), infections, brain malformations, genetic factors।
Result: Improper signals to muscles → abnormal movement, tone, coordination।
🔑 Important: NOT progressive! Brain injury doesn't get worse। But effects may change as child grows।
⚠️ Common Misconceptions:
- Myth: CP बढ़ता है। Fact: NOT progressive - brain damage stable!
- Myth: सभी CP children mentally disabled। Fact: Many normal intelligence!
- Myth: Cure possible। Fact: Lifelong condition - but manageable!
- Myth: सभी wheelchair में। Fact: Many walk independently या with aids!
Cerebral Palsy (CP) is a neurological disorder caused by brain damage - before, during, or shortly after birth. It affects movement, muscle tone, and posture. NOT progressive - the brain damage doesn't worsen, but it's a lifelong condition.
🎯 Key Facts!
Most common motor disability in children! 2-3 in 1,000 births. Brain injury causes. Multiple types. Range: mild to severe. Each child different! Treatment improves quality of life. Early intervention = better outcomes!
📊 Key Statistics:
in Births
Most Common
Independently
Speech Difficulty
🧠 What Happens in the Brain?
Brain damage or abnormal development - especially in motor control areas.
Causes: Premature birth, low oxygen (hypoxia), infections, brain malformations, genetic factors.
Result: Improper signals to muscles → abnormal movement, tone, coordination.
🔑 Important: NOT progressive! Brain injury doesn't get worse. But effects may change as child grows.
⚠️ Common Misconceptions:
- Myth: CP gets worse over time. Fact: NOT progressive - brain damage is stable!
- Myth: All CP children are mentally disabled. Fact: Many have normal intelligence!
- Myth: Cure is possible. Fact: Lifelong condition - but manageable!
- Myth: All need wheelchairs. Fact: Many walk independently or with aids!
CP के प्रकार (Types)
Types of Cerebral Palsy
🎯 4 Main Types Based on Movement!
Spastic (70%) | Dyskinetic | Ataxic | Mixed
📋 CP Types Detailed:
1. Spastic CP (70%)
MOST COMMON! Increased muscle tone (stiff, tight muscles)। Jerky movements। Difficulty relaxing muscles। Subtypes: Diplegia (legs), Hemiplegia (one side), Quadriplegia (all limbs)। Scissor gait। Contractures develop।
2. Dyskinetic CP
Involuntary movements! Writhing, twisting। Fluctuating muscle tone। Affects hands, arms, legs। Speech difficulties। Subtypes: Athetoid (slow writhing), Choreoathetoid (jerky + writhing)। Difficulty maintaining posture।
3. Ataxic CP
Balance और coordination issues! Unsteady walk। Wide-based gait। Difficulty with precise movements। Shaky movements (tremor)। Problems with depth perception। Least common type! Affects cerebellum।
4. Mixed CP
Combination of types! Most commonly: Spastic + Dyskinetic। Multiple brain areas damaged। Varied symptoms। More complex management। Each child's mix unique। Requires tailored treatment।
✅ Classification by Body Parts Affected:
- Monoplegia: एक limb (rare)
- Hemiplegia: एक side (arm + leg same side)
- Diplegia: मुख्य रूप से legs (arms less affected)
- Triplegia: तीन limbs (rare)
- Quadriplegia: सभी four limbs + trunk (severe)
🎯 4 Main Types Based on Movement!
Spastic (70%) | Dyskinetic | Ataxic | Mixed
📋 CP Types Detailed:
1. Spastic CP (70%)
MOST COMMON! Increased muscle tone (stiff, tight muscles). Jerky movements. Difficulty relaxing muscles. Subtypes: Diplegia (legs), Hemiplegia (one side), Quadriplegia (all limbs). Scissor gait. Contractures develop.
2. Dyskinetic CP
Involuntary movements! Writhing, twisting. Fluctuating muscle tone. Affects hands, arms, legs. Speech difficulties. Subtypes: Athetoid (slow writhing), Choreoathetoid (jerky + writhing). Difficulty maintaining posture.
3. Ataxic CP
Balance and coordination issues! Unsteady walk. Wide-based gait. Difficulty with precise movements. Shaky movements (tremor). Problems with depth perception. Least common type! Affects cerebellum.
4. Mixed CP
Combination of types! Most commonly: Spastic + Dyskinetic. Multiple brain areas damaged. Varied symptoms. More complex management. Each child's mix unique. Requires tailored treatment.
✅ Classification by Body Parts Affected:
- Monoplegia: One limb (rare)
- Hemiplegia: One side (arm + leg same side)
- Diplegia: Mainly legs (arms less affected)
- Triplegia: Three limbs (rare)
- Quadriplegia: All four limbs + trunk (severe)
लक्षण और निदान
Symptoms & Diagnosis
Symptoms vary - mild से severe। Early signs: delayed milestones, abnormal muscle tone, poor coordination।
👀 Early Warning Signs:
Delayed Milestones
बच्चा late! Rolling, sitting, crawling, walking delayed। Not reaching, not grasping। Head control poor। Red flag: 6 months में head control नहीं!
Abnormal Muscle Tone
Too stiff या too floppy! Spasticity (tight) या hypotonia (floppy)। Hands clenched। Legs scissor। Arched back। Asymmetry।
Abnormal Reflexes
Persistent primitive reflexes! Moro, grasp reflexes beyond normal age। Exaggerated reflexes। Clonus (rhythmic shaking)।
Movement Problems
Favors one side! Doesn't use both hands। Drags one leg। Involuntary movements। Tremors। Poor coordination।
🔍 Diagnosis Process:
Medical Assessment:
1. Clinical Exam: Developmental history, neurological exam, tone assessment।
2. Brain Imaging: MRI (shows brain damage/abnormality), CT scan।
3. Additional Tests: EEG (if seizures), genetic testing, metabolic tests।
4. Developmental Assessment: GMFCS (Gross Motor Function Classification System) - 5 levels।
⏰ Diagnosis Timeline: Often 12-24 months। Mild cases may be later। Early diagnosis = early intervention!
⚠️ Associated Conditions (Often Present):
- Epilepsy (seizures): 30-40% of CP children
- Intellectual disability: 30-50% (varies by type, severity)
- Vision problems: Strabismus (crossed eyes), cortical vision impairment
- Hearing loss: Especially in dyskinetic CP
- Speech difficulties: Dysarthria, communication issues
- Feeding/swallowing problems: Dysphagia, choking risk
- Orthopedic issues: Hip dislocation, scoliosis, contractures
Symptoms vary - mild to severe. Early signs: delayed milestones, abnormal muscle tone, poor coordination.
👀 Early Warning Signs:
Delayed Milestones
Child is late! Rolling, sitting, crawling, walking delayed. Not reaching, not grasping. Head control poor. Red flag: No head control by 6 months!
Abnormal Muscle Tone
Too stiff or too floppy! Spasticity (tight) or hypotonia (floppy). Hands clenched. Legs scissor. Arched back. Asymmetry.
Abnormal Reflexes
Persistent primitive reflexes! Moro, grasp reflexes beyond normal age. Exaggerated reflexes. Clonus (rhythmic shaking).
Movement Problems
Favors one side! Doesn't use both hands. Drags one leg. Involuntary movements. Tremors. Poor coordination.
🔍 Diagnosis Process:
Medical Assessment:
1. Clinical Exam: Developmental history, neurological exam, tone assessment.
2. Brain Imaging: MRI (shows brain damage/abnormality), CT scan.
3. Additional Tests: EEG (if seizures), genetic testing, metabolic tests.
4. Developmental Assessment: GMFCS (Gross Motor Function Classification System) - 5 levels.
⏰ Diagnosis Timeline: Often 12-24 months. Mild cases may be later. Early diagnosis = early intervention!
⚠️ Associated Conditions (Often Present):
- Epilepsy (seizures): 30-40% of CP children
- Intellectual disability: 30-50% (varies by type, severity)
- Vision problems: Strabismus (crossed eyes), cortical vision impairment
- Hearing loss: Especially in dyskinetic CP
- Speech difficulties: Dysarthria, communication issues
- Feeding/swallowing problems: Dysphagia, choking risk
- Orthopedic issues: Hip dislocation, scoliosis, contractures
उपचार और प्रबंधन
Treatment & Management
🏥 Multidisciplinary Team Approach!
Physiotherapy + OT + Speech + Orthopedics + Neurology + More!
NO CURE for CP - but comprehensive management improves quality of life, function, independence! Treatment individualized based on type, severity, needs।
🎯 Main Treatment Approaches:
1. Physiotherapy (PT)
FOUNDATION of CP treatment! Strengthening exercises। Range of motion। Gait training। Stretching। Positioning। Equipment training (walkers, AFOs)। Daily/weekly sessions। Prevents contractures। Improves mobility।
2. Occupational Therapy (OT)
Daily living skills! Hand function। Self-care (eating, dressing)। Fine motor skills। Adaptive equipment। School activities। Independence training। Sensory integration। Play therapy।
3. Speech Therapy
Communication और swallowing! Speech production। Language development। Alternative communication (AAC devices)। Feeding therapy। Oral motor exercises। Augmentative communication।
4. Botox Injections
For spasticity management! Botulinum toxin। Reduces muscle tightness। Temporary effect (3-6 months)। Allows better PT। Multiple injection sites। Effective for focal spasticity! Repeat injections needed।
5. Medications
Oral muscle relaxants: Baclofen, Diazepam। For seizures: Anti-epileptic drugs। For pain: Pain management। Intrathecal Baclofen pump: Severe spasticity (implanted)।
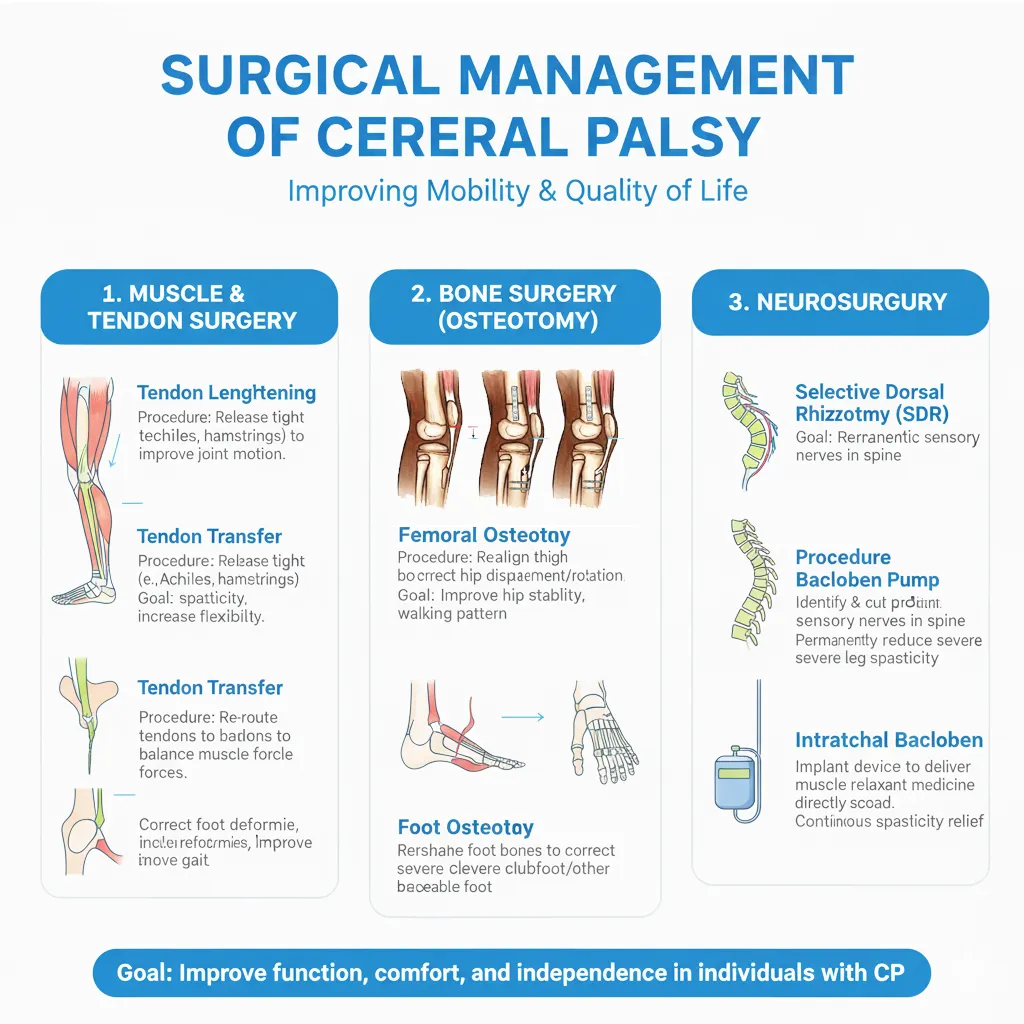
6. Orthopedic Surgery
When non-surgical fails! Tendon lengthening। Muscle/nerve procedures। Hip surgery (prevent dislocation)। Scoliosis correction। SDR (Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy) - nerve cutting। Age 3-7 years optimal।
✅ Additional Therapies & Support:
- Special Education: IEP, resource room, inclusion programs
- Assistive Devices: AFOs, walkers, wheelchairs, communication devices
- Orthotics: Braces, splints to maintain position
- Hydrotherapy: Pool therapy - low impact exercise
- Hippotherapy: Horse riding therapy
- Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT): For hemiplegia
- Psychological Support: For child and family
📅 Treatment Timeline & Approach:
Infancy (0-2 years): Early intervention। Developmental stimulation। Parent training। Positioning।
Childhood (2-12 years): Intensive PT/OT। Botox। Orthotics। Surgery (if needed)। School support।
Adolescence (12-18 years): Maintaining function। Transition planning। Independence skills। Vocational training।
Adulthood: Ongoing management। Preventing secondary complications। Adaptive strategies।
🚨 Dr. Gaurav Jain's Role in CP Management:
As Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon:
- Assessment of orthopedic deformities
- Botox injections for spasticity
- Tendon lengthening surgeries
- Hip surveillance and surgery
- Scoliosis management
- Gait analysis and correction
- AFO/orthotic prescription
- Coordination with multidisciplinary team
🔑 Part of comprehensive CP team! Works with neurologists, therapists, pediatricians।
🏥 Multidisciplinary Team Approach!
Physiotherapy + OT + Speech + Orthopedics + Neurology + More!
NO CURE for CP - but comprehensive management improves quality of life, function, independence! Treatment individualized based on type, severity, needs.
🎯 Main Treatment Approaches:
1. Physiotherapy (PT)
FOUNDATION of CP treatment! Strengthening exercises. Range of motion. Gait training. Stretching. Positioning. Equipment training (walkers, AFOs). Daily/weekly sessions. Prevents contractures. Improves mobility.
2. Occupational Therapy (OT)
Daily living skills! Hand function. Self-care (eating, dressing). Fine motor skills. Adaptive equipment. School activities. Independence training. Sensory integration. Play therapy.
3. Speech Therapy
Communication and swallowing! Speech production. Language development. Alternative communication (AAC devices). Feeding therapy. Oral motor exercises. Augmentative communication.
4. Botox Injections
For spasticity management! Botulinum toxin. Reduces muscle tightness. Temporary effect (3-6 months). Allows better PT. Multiple injection sites. Effective for focal spasticity! Repeat injections needed.
5. Medications
Oral muscle relaxants: Baclofen, Diazepam. For seizures: Anti-epileptic drugs. For pain: Pain management. Intrathecal Baclofen pump: Severe spasticity (implanted).
6. Orthopedic Surgery
When non-surgical fails! Tendon lengthening. Muscle/nerve procedures. Hip surgery (prevent dislocation). Scoliosis correction. SDR (Selective Dorsal Rhizotomy) - nerve cutting. Age 3-7 years optimal.
✅ Additional Therapies & Support:
- Special Education: IEP, resource room, inclusion programs
- Assistive Devices: AFOs, walkers, wheelchairs, communication devices
- Orthotics: Braces, splints to maintain position
- Hydrotherapy: Pool therapy - low impact exercise
- Hippotherapy: Horse riding therapy
- Constraint-Induced Movement Therapy (CIMT): For hemiplegia
- Psychological Support: For child and family
📅 Treatment Timeline & Approach:
Infancy (0-2 years): Early intervention. Developmental stimulation. Parent training. Positioning.
Childhood (2-12 years): Intensive PT/OT. Botox. Orthotics. Surgery (if needed). School support.
Adolescence (12-18 years): Maintaining function. Transition planning. Independence skills. Vocational training.
Adulthood: Ongoing management. Preventing secondary complications. Adaptive strategies.

🚨 Dr. Gaurav Jain's Role in CP Management:
As Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon:
- Assessment of orthopedic deformities
- Botox injections for spasticity
- Tendon lengthening surgeries
- Hip surveillance and surgery
- Scoliosis management
- Gait analysis and correction
- AFO/orthotic prescription
- Coordination with multidisciplinary team
🔑 Part of comprehensive CP team! Works with neurologists, therapists, pediatricians.
अक्सर पूछे जाने वाले सवाल (FAQ)
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Cerebral Palsy क्या है? / What is CP?
Brain damage से होने वाला neurological disorder। Movement, muscle tone, posture affected। जन्म से पहले/दौरान/बाद में brain injury। NOT progressive - stable condition। Lifelong। 2-3:1000 births। Multiple types। Early intervention helps!
Cure possible? / क्या ठीक हो सकता?
NO CURE available! Brain damage permanent। BUT - comprehensive management greatly improves quality of life, function, independence! PT, OT, speech therapy, Botox, surgery help। Early intervention = better outcomes। Many lead fulfilling lives!
CP के types? / Types of CP?
4 main types: (1) Spastic (70%) - stiff muscles (2) Dyskinetic - involuntary movements (3) Ataxic - balance problems (4) Mixed - combination। Also classified by body parts: Hemiplegia, Diplegia, Quadriplegia। Each child unique!
Treatment options? / इलाज क्या हैं?
Multidisciplinary approach! (1) Physiotherapy - foundation (2) Occupational therapy (3) Speech therapy (4) Botox for spasticity (5) Medications - muscle relaxants, seizure meds (6) Orthopedic surgery - tendon lengthening, SDR (7) Assistive devices - AFOs, wheelchairs। Individualized plan!
Botox कैसे काम करता? / How does Botox work?
Botulinum toxin injected into spastic muscles। Blocks nerve signals to muscle। Reduces tightness/spasticity। Temporary - lasts 3-6 months। Allows better PT, stretching। Multiple injection sites। Repeat injections needed। Safe when done by expert। Dr. Gaurav Jain provides Botox therapy!
Surgery कब? / When is surgery needed?
When non-surgical treatment insufficient। (1) Severe contractures (2) Hip dislocation/subluxation (3) Scoliosis (4) Gait problems। Types: Tendon lengthening, muscle releases, bone cuts, SDR (nerve cutting)। Optimal age: 3-7 years for many procedures। Followed by intensive PT!
Causes? / कारण क्या?
Brain damage/abnormal development। Causes: (1) Premature birth - #1 cause (2) Low oxygen (hypoxia/asphyxia) (3) Infections - meningitis, encephalitis (4) Maternal infections (5) Brain malformations (6) Jaundice (severe kernicterus) (7) Stroke in fetus/newborn। Often no single identifiable cause!
Walk करेंगे? / Will child walk?
Depends on severity and type! About 40% walk independently। 30% walk with aids (walkers, crutches)। 30% need wheelchairs। Early sign: sitting independently by age 2 = good prognosis for walking। Intensive PT helps। GMFCS level predicts mobility। Many achieve some form of mobility!
Education? / पढ़ाई कर सकते?
YES! Many CP children attend school। Intelligence varies - 50-70% normal intelligence। Special education services available। IEP (Individualized Education Program)। Resource rooms। Inclusion programs। Assistive technology helps। Communication devices for non-verbal। Many complete education, higher studies, employment!
Life expectancy? / जीवनकाल?
Varies by severity। Mild CP: normal या near-normal lifespan। Severe CP (quadriplegia, profound disability): reduced lifespan। Factors affecting: feeding ability, respiratory health, seizure control, mobility। With good care: many live into adulthood। Quality medical care extends life। Focus on quality of life!
Physiotherapy कितना important? / PT importance?
EXTREMELY IMPORTANT - foundation of CP treatment! Prevents contractures। Maintains ROM (range of motion)। Strengthens muscles। Improves gait। Promotes motor development। Daily exercises essential। Professional sessions + home program। Consistency key। Lifelong commitment। Without PT: rapid deterioration, contractures, disability!
Seizures होते? / Do seizures occur?
30-40% of CP children have epilepsy/seizures। More common in: spastic quadriplegia, severe CP। Controlled with anti-epileptic drugs। Regular monitoring needed। EEG testing। Seizure control important for development। Good news: many remain seizure-free या controlled!
Feeding problems? / खाने में दिक्कत?
Common in moderate-severe CP! Dysphagia (swallowing difficulty)। Choking risk। Poor oral motor control। Aspiration (food in lungs)। Treatment: Speech therapy, feeding therapy, modified textures, positioning। Severe cases: G-tube (feeding tube)। Weight monitoring important। Nutritionist consultation।
Mental disability? / मानसिक अक्षमता?
NOT always! 50-70% have normal intelligence। 30-50% have intellectual disability - varies by CP type and severity। Spastic diplegia: often normal intelligence। Dyskinetic CP: often normal। Severe quadriplegia: higher chance of cognitive impairment। Important: physical disability ≠ mental disability! Many are intellectually normal!
CP progressive? / क्या बढ़ता है?
NO! CP is NOT progressive। Brain injury stable - doesn't worsen। BUT - effects may change as child grows। Contractures can develop if not managed। Orthopedic issues emerge। Scoliosis। Hip problems। THIS IS WHY ongoing PT, monitoring essential। Brain damage itself doesn't progress!
Which specialists? / कौन से doctors?
Multidisciplinary team! (1) Pediatric Neurologist - diagnosis, seizures (2) Pediatric Orthopedic Surgeon (Dr. Gaurav Jain!) - orthopedic issues, Botox, surgery (3) Developmental Pediatrician (4) Physiatrist (PM&R) (5) Physiotherapist (6) Occupational Therapist (7) Speech Therapist (8) Nutritionist। Team approach = best outcomes!
Treatment cost? / खर्चा कितना?
Varies widely! PT/OT sessions: ₹500-2,000/session। Botox: ₹20,000-50,000/treatment। Surgery: ₹1,00,000-5,00,000+। Medications, assistive devices additional। Lifelong expenses। Government schemes available। NGO support। Insurance coverage। Early intervention programs। Prioritize essential therapies!
Prevention? / रोकथाम?
Reduce risk, not eliminate! (1) Good prenatal care (2) Avoid infections during pregnancy (3) Manage maternal health (4) Prevent premature birth when possible (5) Proper delivery care (6) Treat jaundice promptly। But many cases unavoidable। Focus: early detection + intervention if CP develops!
Home care tips? / घर पर देखभाल?
(1) Daily PT exercises - consistency key! (2) Proper positioning - prevent contractures (3) Nutritious diet - adequate calories (4) Communication - respond to child (5) Play and stimulation (6) Assistive devices use (7) Skin care - prevent pressure sores (8) Social interaction (9) Celebrate progress! (10) Parent self-care - support groups। Love and consistency matter!
Future? / भविष्य कैसा होगा?
Depends on severity! Mild CP: near-normal life - education, employment, relationships, independence। Moderate: adaptive strategies, may need assistance, can work, live semi-independently। Severe: significant support needed - but quality of life possible! Early intervention, consistent therapy, family support = better outcomes। Many CP adults lead fulfilling lives!
📞 Dr. Gaurav Jain से Consult करें - Indore!
📞 Consult Dr. Gaurav Jain - Indore!
Cerebral Palsy Management Expert | Botox Therapy | Orthopedic Surgery Cerebral Palsy Management Expert | Botox Therapy | Orthopedic Surgery
📞 अभी Call करें 📞 Call Nowविशेषज्ञ वीडियो
Expert Videos
डॉ. गौरव जैन द्वारा सेरेब्रल पाल्सी के उपचार और प्रबंधन पर विशेषज्ञ जानकारी
Expert insights on Cerebral Palsy treatment and management by Dr. Gaurav Jain

सेरेब्रल पाल्सी उपचार - भाग 1
Cerebral Palsy Treatment - Part 1
डॉ. गौरव जैन द्वारा सेरेब्रल पाल्सी के उपचार पर विस्तृत जानकारी
Comprehensive guide to Cerebral Palsy treatment by Dr. Gaurav Jain
YouTube पर देखें Watch on YouTube
सेरेब्रल पाल्सी प्रबंधन
Cerebral Palsy Management
बच्चों में सीपी के प्रबंधन के लिए व्यापक दृष्टिकोण
Comprehensive approach to managing CP in children
YouTube पर देखें Watch on YouTube
उपचार विकल्प समझें
Understanding Treatment Options
सेरेब्रल पाल्सी के लिए उपलब्ध विभिन्न उपचार विकल्प
Various treatment options available for Cerebral Palsy
YouTube पर देखें Watch on YouTube
बाल आर्थोपेडिक दृष्टिकोण
Pediatric Orthopedic Approach
सेरेब्रल पाल्सी के लिए बाल आर्थोपेडिक उपचार दृष्टिकोण
Pediatric orthopedic treatment approach for Cerebral Palsy
YouTube पर देखें Watch on YouTube
उन्नत प्रबंधन तकनीक
Advanced Management Techniques
सेरेब्रल पाल्सी के लिए आधुनिक और उन्नत प्रबंधन तकनीकें
Modern and advanced management techniques for Cerebral Palsy
YouTube पर देखें Watch on YouTube